Structural Model for Predicting Psychological Well-being and Emotional Regulation Based on Resilience and Self-Efficacy in MS Patients
Keywords:
Psychological Well-being, Emotional Regulation, Resilience, Self-EfficacyAbstract
Objective: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is one of the most common chronic diseases of the central nervous system, and the disability resulting from the disease impacts self-efficacy and various mental health dimensions of these patients. Therefore, the present study aimed to propose a structural model for predicting psychological well-being and emotional regulation based on resilience and self-efficacy among MS patients in Tehran.
Methods: Given its objective, this research is of the applied type and descriptive in nature concerning data collection methods, specifically employing structural equation modeling. The statistical population of this study included all individuals with MS attending treatment centers in Tehran in 2021, with a minimum sample size estimated at 150. The variables studied were based on the Ryff's Psychological Well-being Scale, the Gross and John's Emotional Regulation Questionnaire, the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and the Schwarzer and Jerusalem's Self-Efficacy Scale. Ultimately, data were analyzed using structural equation modeling in AMOS software.
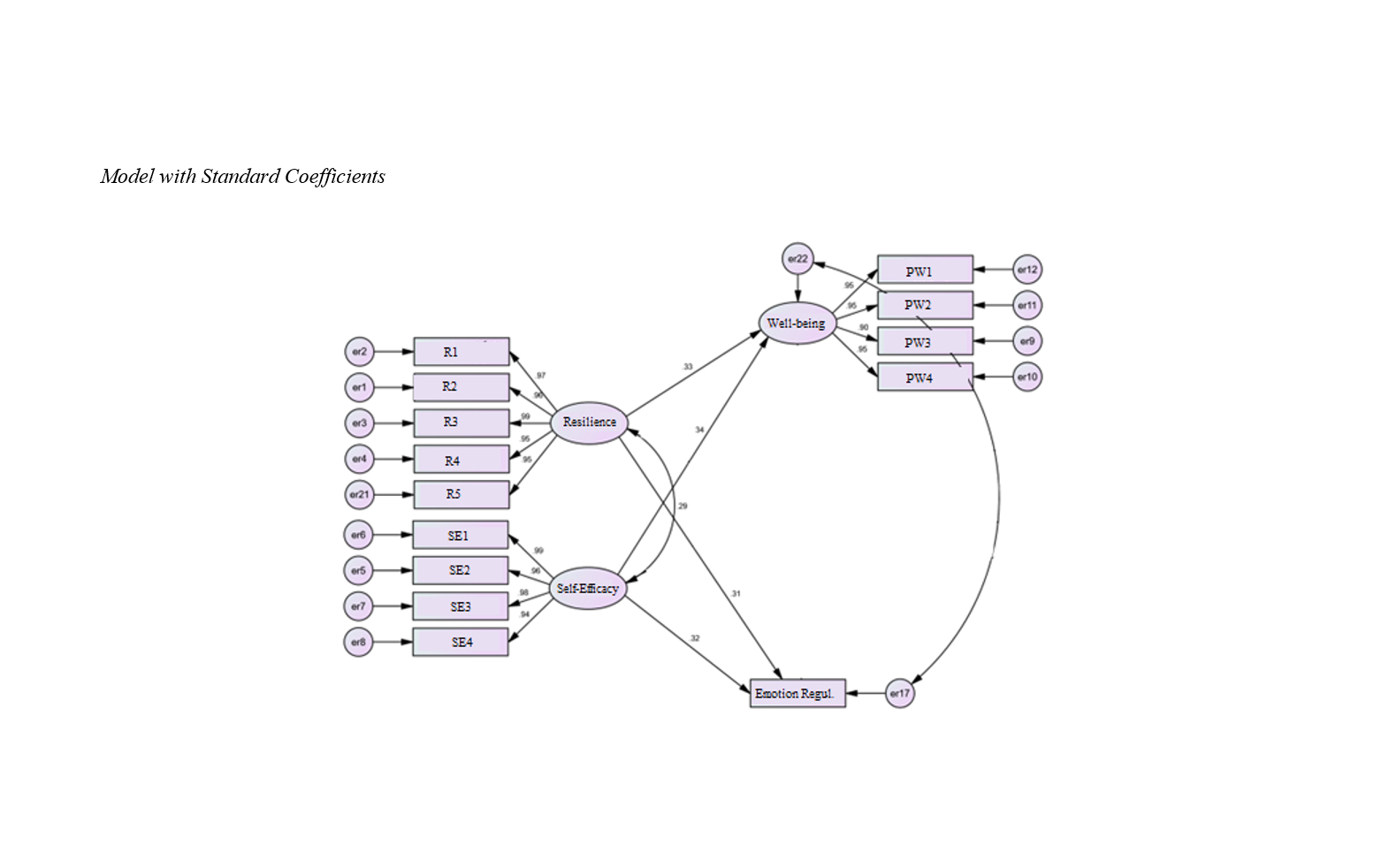
Findings: According to the study's findings, all standardized coefficient values related to the dimensions of the latent variables were higher than 0.4, indicating that this measurement model has adequate reliability regarding the items of latent variables. Critical ratio values are usually introduced as validity parameters associated with the structural model and, in this study, all values were significant and outside the range of (-1.96, 1.96), with Cronbach's alpha and composite reliability values greater than 0.7 and AVE values greater than 0.5.
Conclusion: Thus, the model enjoys appropriate validity and reliability.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















