Structural Modeling of Risky Behaviors Based on Attention, Memory, and Inhibition Systems with the Mediating Role of Emotion Regulation in Female Drug Users
Keywords:
Risky behaviors, Attention, Emotion regulation, Drug useAbstract
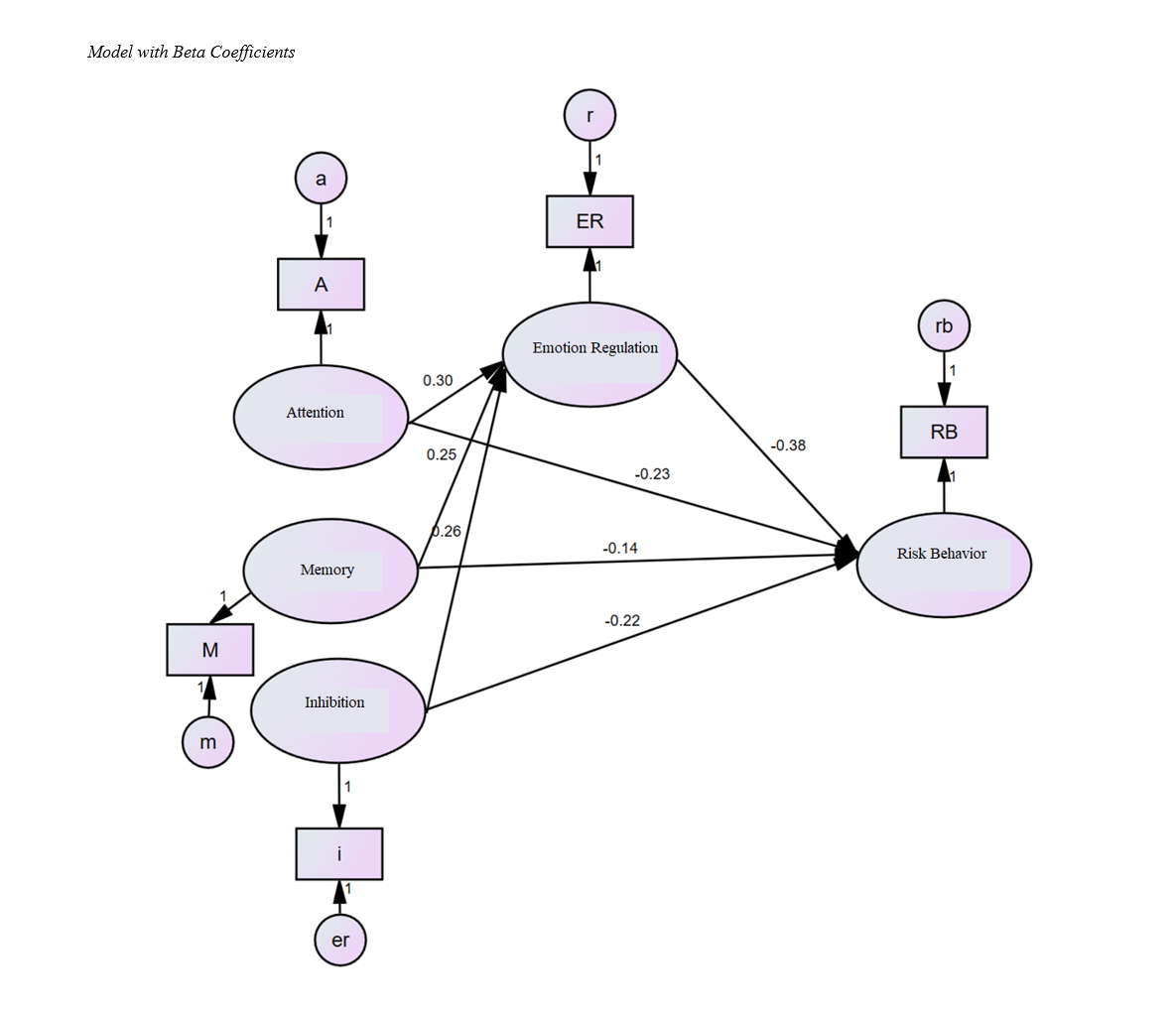
Objective: The purpose of this study was to determine the structural model of risky behaviors based on attention, memory, and inhibition systems with the mediating role of emotion regulation in female drug users.
Methods: This research was descriptive-correlational and employed structural equation modeling. The study population consisted of all drug users (marijuana) in Isfahan who visited addiction treatment centers during 2023. The sample included 200 female drug users (marijuana) selected through convenience sampling based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data were collected using the Attention and Memory Improvement Software, Wechsler's Clinical Memory Test, the Behavioral Inhibition and Activation Scales (Carver & White, 1994), the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (Garnefski & Kraaij, 2006), and the Risk-Taking Behavior Questionnaire (Lejuez, 2002). In this study, descriptive statistics such as mean and standard deviation were used to organize, summarize, and describe the characteristics of the participants and research variables. In the inferential statistics section, structural equation modeling and Pearson correlation methods were employed for data analysis using SPSS.22 and AMOS.22 software.
Findings: Fit indices 0.599=PCFI, 0.611=PNFI, 2.88=CMIN/DF, 0.072=RMSEA, 0.913=IFI, 0.920=CFI, and 0.909=GFI indicated a good fit of the proposed model with the data. Hence, the proposed model is suitably fitted.
Conclusion: Thus, it can be concluded that the structural model of risky behaviors based on the attention system with the mediating role of emotion regulation fits well for drug-using individuals.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















