The Effectiveness of Stress Inoculation Training (SIT) on Co-Parenting Quality and Interpersonal Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms in Mothers
Keywords:
Stress Inoculation Training, Co-Parenting Quality, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, Mothers, Randomized Controlled Trial, Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy, Mental Health InterventionAbstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of Stress Inoculation Training (SIT) on improving co-parenting quality and reducing interpersonal obsessive-compulsive symptoms in mothers with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
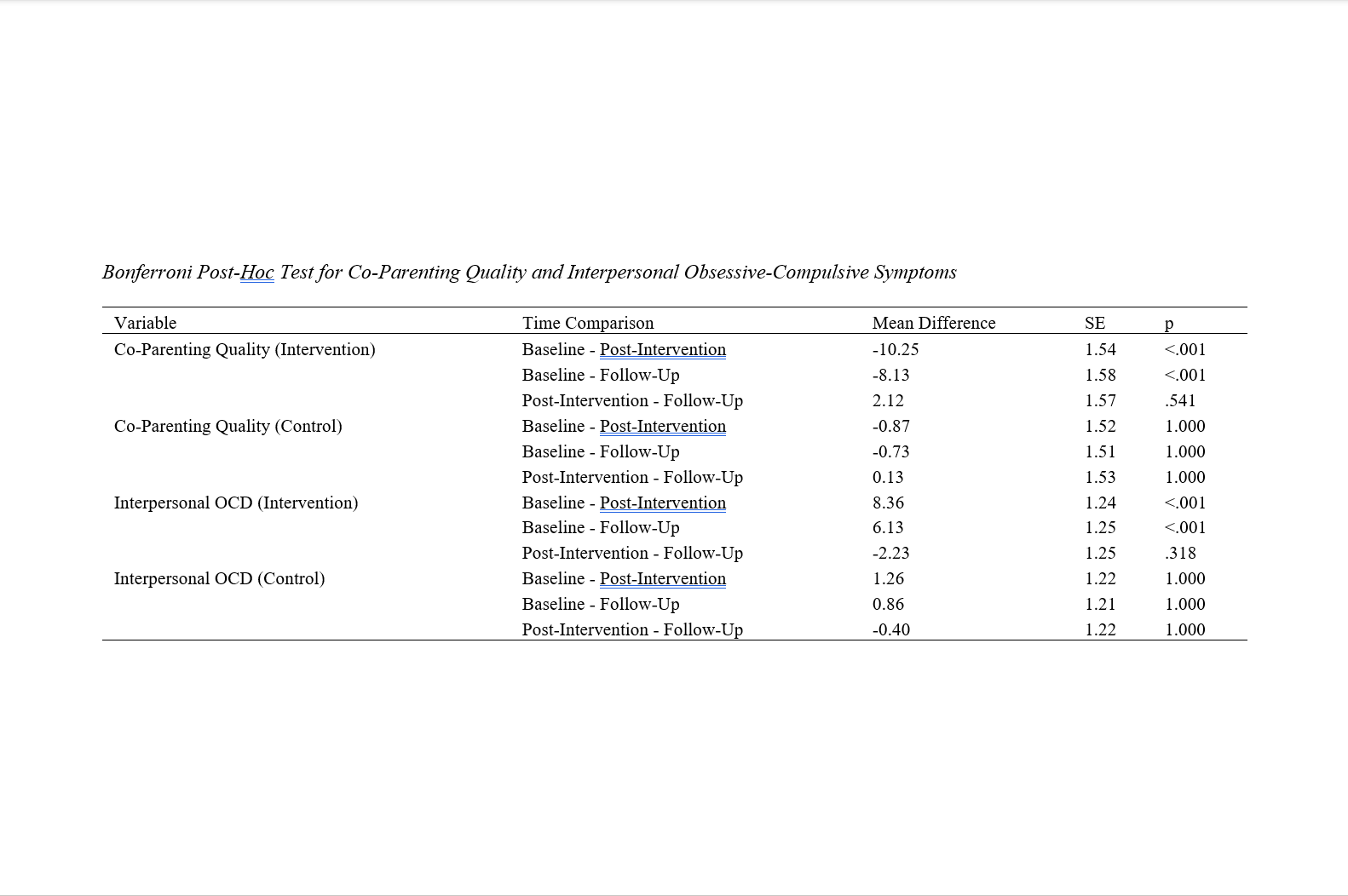
Method: This study employed a randomized controlled trial (RCT) design with 30 mothers diagnosed with OCD, randomly assigned to either the intervention group (n = 15) or the control group (n = 15). The intervention group received eight 60-minute SIT sessions over eight weeks. Co-parenting quality and interpersonal obsessive-compulsive symptoms were assessed at baseline, post-intervention, and four-month follow-up using validated questionnaires. Data were analyzed using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) with repeated measurements and Bonferroni post-hoc tests, conducted via SPSS-27.
Findings: The intervention group showed significant improvements in co-parenting quality from baseline (M = 48.67, SD = 8.92) to post-intervention (M = 58.92, SD = 7.41), with effects maintained at the four-month follow-up (M = 56.80, SD = 7.93). Interpersonal obsessive-compulsive symptoms significantly decreased from baseline (M = 30.53, SD = 6.47) to post-intervention (M = 22.17, SD = 5.32), with sustained reductions at follow-up (M = 24.40, SD = 5.89). The ANOVA results indicated significant effects of time (p < .001) and group (p < .001), as well as significant time-by-group interactions (p < .001) for both variables.
Conclusion: SIT significantly enhances co-parenting quality and reduces interpersonal obsessive-compulsive symptoms in mothers with OCD. These improvements were maintained at the four-month follow-up, indicating the intervention's long-term efficacy. SIT offers a promising therapeutic approach for addressing the unique challenges faced by parents with OCD.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zahra Rasouli (Author); Masoumeh Abdollahi (Corresponding Author); Majid shamsaee, Mehran Haidarinia (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















