Development of a Structural Model of Quality of Life Based on Resilience with the Mediation of Perceived Stress in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Keywords:
Quality of life, resilience, perceived stress, rheumatoid arthritisAbstract
Objective: Musculoskeletal diseases are among the most common and costly illnesses across all age groups and various communities, leading to disability, incapacity, early retirement, and job loss. The present study aimed to develop a structural model of quality of life based on resilience with the mediation of perceived stress in women with rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: The research method was descriptive-survey with a structural equation modeling design. The statistical population included women with rheumatoid arthritis in the city of Isfahan. The women with rheumatoid arthritis referred to medical centers in Isfahan had at least one year of disease history. Data were collected using the Varni-Kazisnki and Keller Quality of Life Questionnaire (1996), the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, Antonovsky’s Sense of Coherence Questionnaire (1993), Cohen, Kamarck, and Mermelstein’s Perceived Stress Questionnaire (1983), and the Gratz and Roemer Emotion Regulation Difficulty Scale (2004). Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling and Amos26 software.
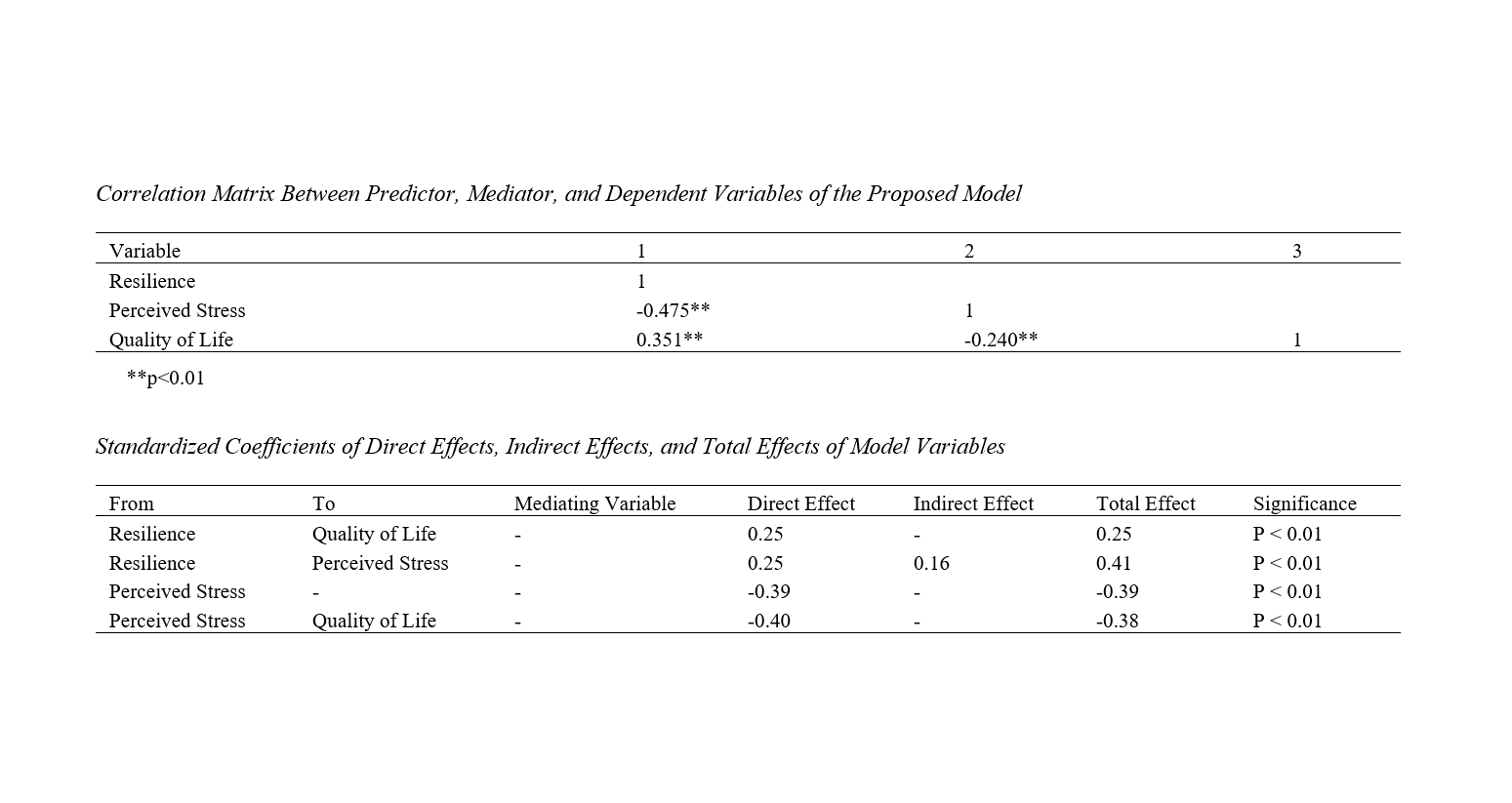
Findings: The results showed that the direct effect of resilience on the quality of life of patients with rheumatoid arthritis was significant (β = 0.25; P < 0.01). The indirect effect of resilience through the mediation of perceived stress on the quality of life of patients with rheumatoid arthritis was significant (β = 0.16; P < 0.01). Additionally, the total effect of resilience through the mediation of perceived stress on quality of life was significant (β = 0.41; P < 0.01).
Conclusion: It can be concluded that the structural model of quality of life based on resilience with the mediation of perceived stress was well-fitted, and perceived stress played a mediating role in the relationship between quality of life and resilience in women with rheumatoid arthritis.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















