Comparison of the Effectiveness of Parent-Child Relationship-Based Play Therapy and Attachment-Based Play Therapy on Internalizing and Externalizing Behavioral Disorders in Children with Learning Disabilities
Keywords:
Play therapy, parent-child relationship, attachment-based play therapy, behavioral disorders, learning difficultiesAbstract
Objective: The study aimed to compare the effectiveness of attachment-based play therapy and parent-child relationship-based play therapy on internalizing and externalizing behavioral disorders in children with learning disabilities.
Methods: This quasi-experimental study employed a pre-test, post-test, and follow-up design with a control group. A total of 45 children with learning disabilities were selected through purposive sampling and randomly assigned to three groups: attachment-based play therapy, parent-child relationship-based play therapy, and a control group. The study used the Achenbach and Rescorla (2001) Behavioral Disorders Questionnaire to measure internalizing and externalizing behaviors at each stage. Both experimental groups received nine 60-minute therapy sessions. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA and ANCOVA to compare the effectiveness of the interventions.
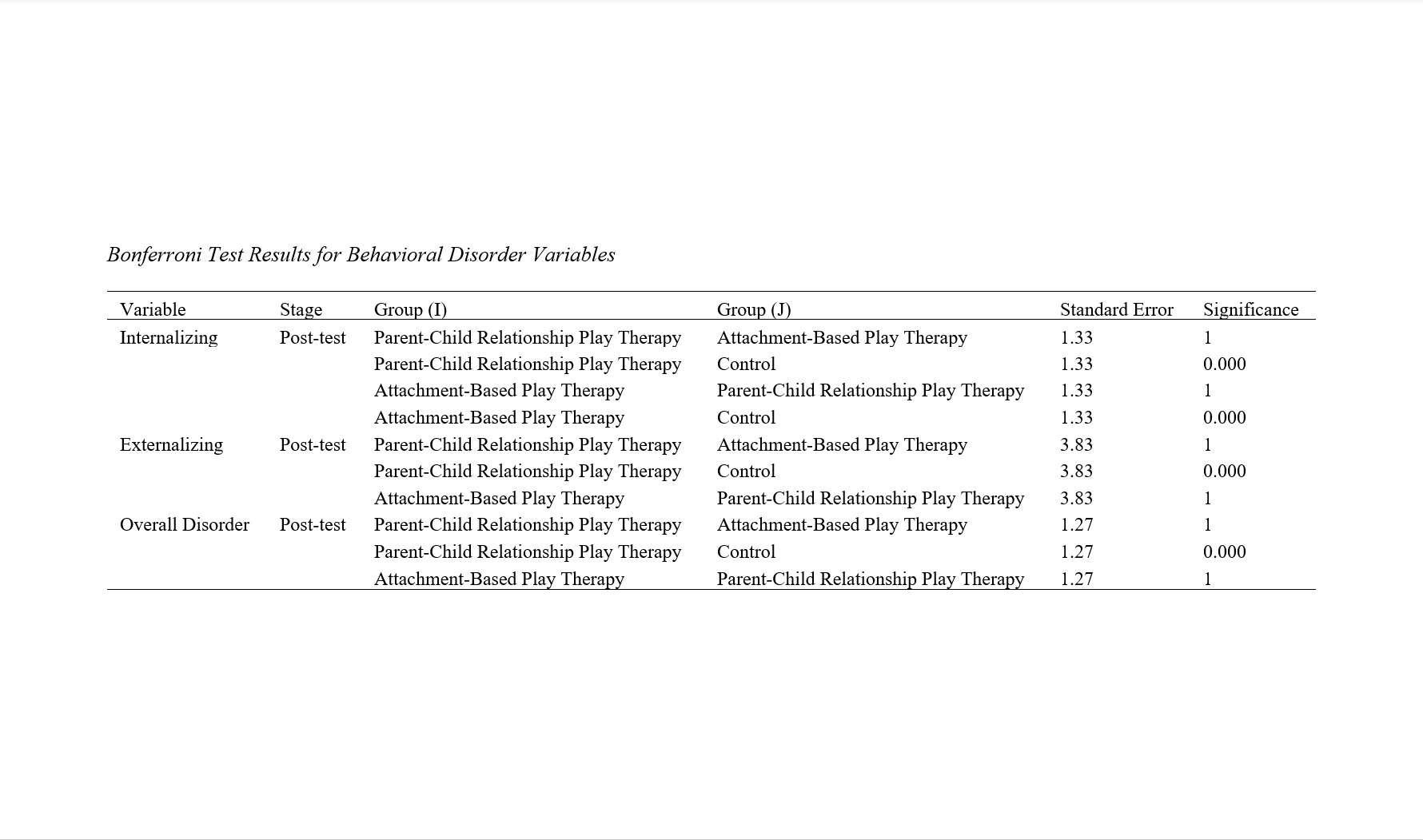
Findings: The findings indicated that both attachment-based play therapy and parent-child relationship-based play therapy significantly reduced internalizing and externalizing behavioral disorders in children with learning disabilities, with large effect sizes (η² = 0.864 and η² = 0.773, respectively). Repeated measures ANOVA and ANCOVA confirmed the interventions' effectiveness (p < 0.001), and Bonferroni post-hoc tests revealed significant differences between the experimental groups and the control group, but no significant differences between the two experimental groups. The positive effects were sustained over time, demonstrating the long-term efficacy of both therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion: Both attachment-based play therapy and parent-child relationship-based play therapy effectively reduce internalizing and externalizing disorders in children with learning disabilities, with lasting effects over time.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Toktam Bijari (Author); Toktam Sadat Jafar Tabatabaei (Corresponding Author); Samaneh Sadat Jafar Tabatabaei, Fatemeh Shahabizadeh (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















