The Model for Predicting Self-Harming Behaviors Based on Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies and Emotional Distress Tolerance in Adolescents Visiting Harm Reduction Centers in Tehran: The Mediating Role of Internalized Shame
Keywords:
Emotional distress tolerance, cognitive emotion regulation strategies, self-harming behaviors, internalized shame, adolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to predict self-harming behaviors based on cognitive emotion regulation strategies and emotional distress tolerance, with the mediating role of internalized shame in adolescents visiting harm reduction centers in Tehran.
Methods: The research employed a descriptive correlational design. The statistical population included adolescents aged 14 to 18 who attended drop-in harm reduction centers in District 12 of Tehran (Shush-Harandi neighborhood) during the first four months of 2022. A total of 300 participants were selected using purposive sampling. The research tools included the Self-Injury Questionnaire (Sansone et al., 1998), the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (Garnefski et al., 2001), the Distress Tolerance Scale (Simons & Gaher, 2005), and the Internalized Shame Scale (Cook, 1993). Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling and AMOS24 software.
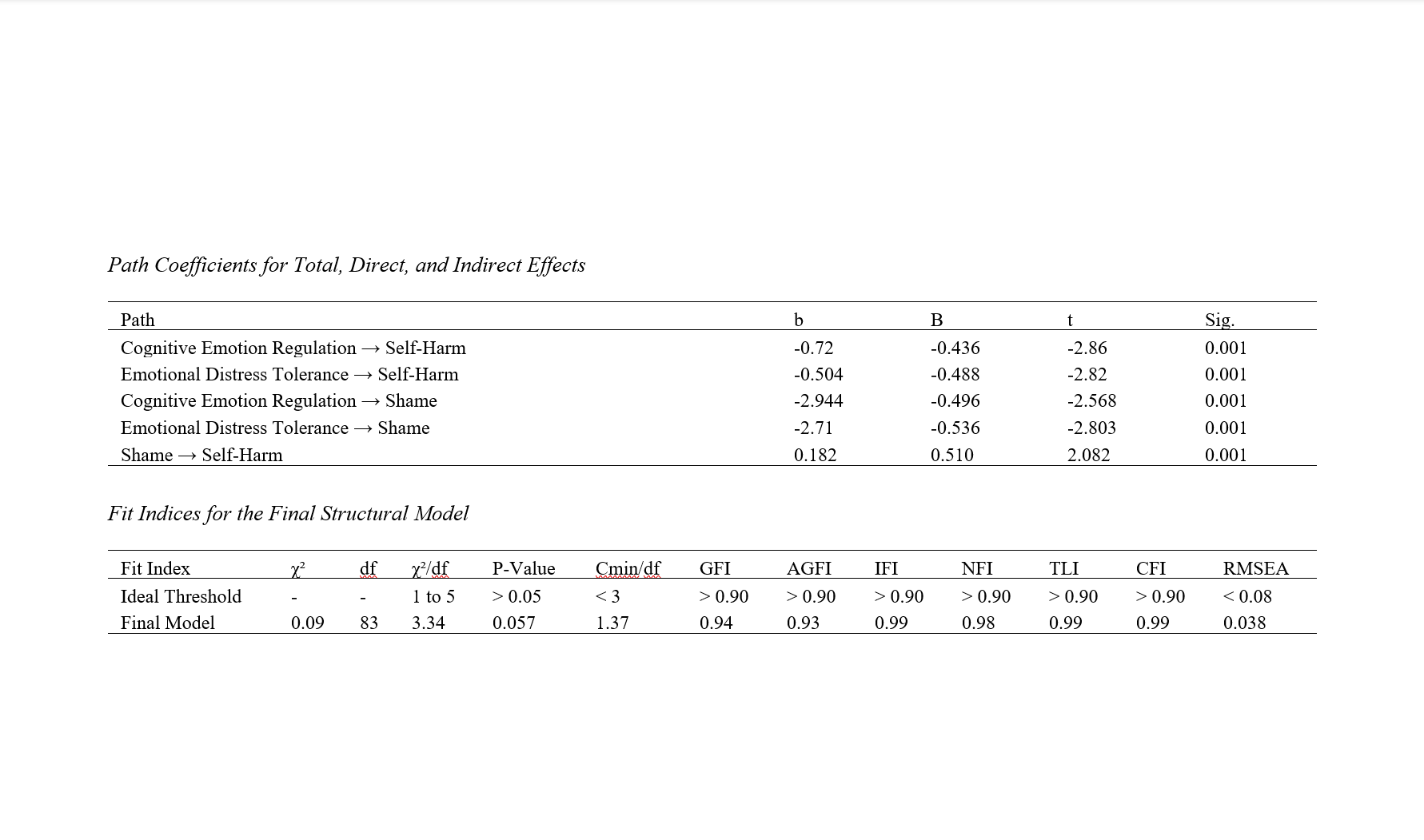
Findings: The results indicated a relationship between cognitive emotion regulation strategies (-0.39), emotional distress tolerance (-0.41), internalized shame (0.36), and self-harming behaviors (P < 0.01). Furthermore, internalized shame mediated the relationship between cognitive emotion regulation strategies (B = 0.52) and emotional distress tolerance (B = 0.45) with self-harming behaviors in adolescents (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Based on these findings, it can be concluded that since internalized shame mediates the relationship between cognitive emotion regulation strategies and emotional distress tolerance with self-harming behaviors, focusing on factors influencing these behaviors can help reduce the risks associated with this developmental period.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















