Examining the Role of Social Networks and Subjective Norms within Rusbult's Investment Model Framework to Predict the Stability of Marital Relationships in Divorce-Seeking Couples
Keywords:
investment model, marital satisfaction, quality of alternative relationships, relationship investment, relationship commitment, social networks, subjective norms, marital stabilityAbstract
Objective: The primary aim of this study was to integrate the role of social networks and subjective norms into the theoretical framework of the investment model of relationships to predict marital stability among divorce-seeking couples in the city of Ilam.
Methods: This research employed a correlational design. The statistical population included all divorce-seeking couples in Ilam during 2019–2020 who visited family courts, counseling centers, and divorce registry offices. A sample of 160 participants was selected using convenience sampling. Data collection utilized the following instruments: the Marital Instability Index (Edwards et al., 1987), the Social Networks in Marital Relationships Scale (researcher-developed, 2019), the Subjective Norms in Marital Relationships Scale (researcher-developed, 2019), and Rusbult’s Investment Model Scale (1980). Data analysis was conducted using path analysis via AMOS version 23.
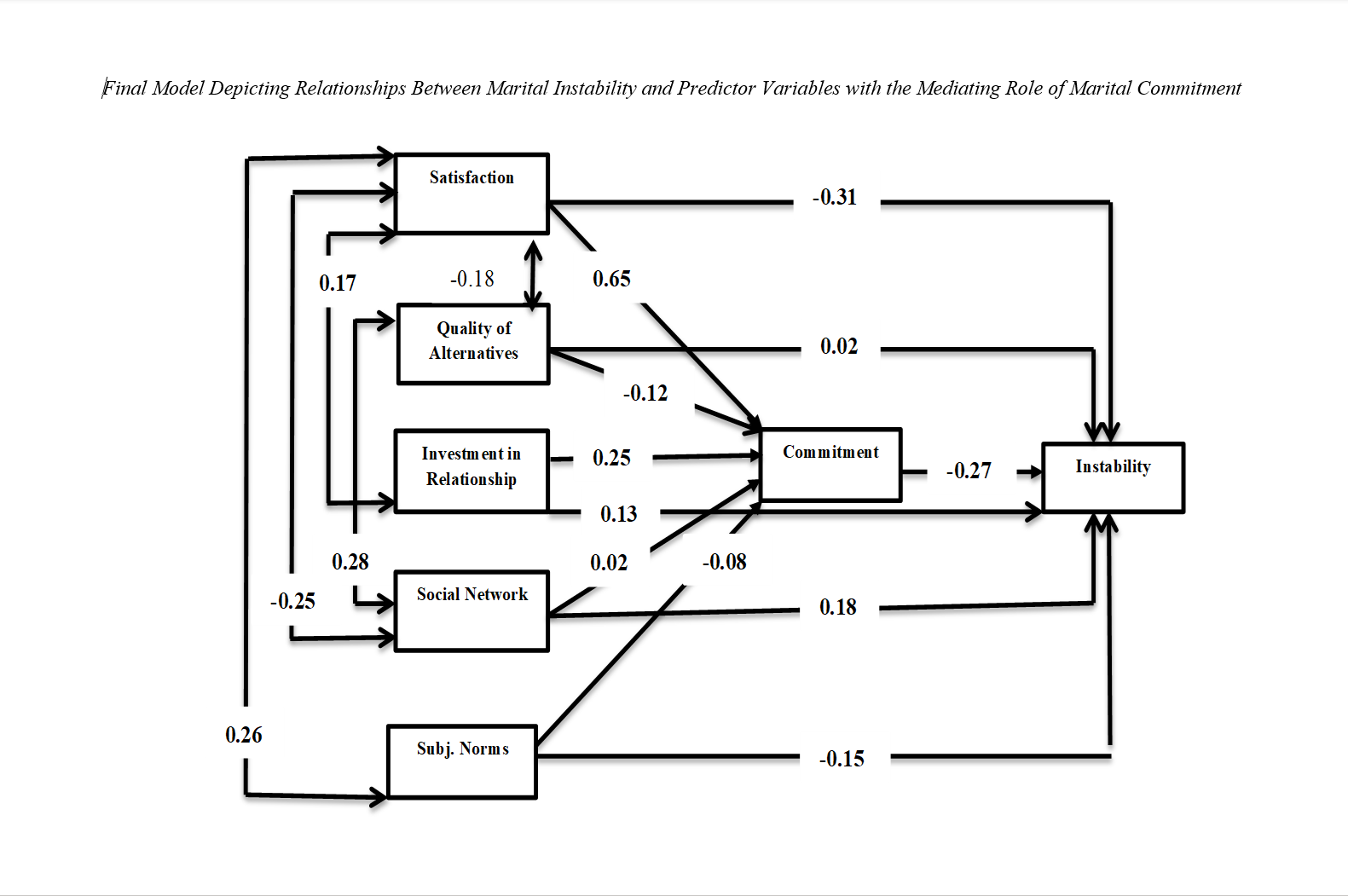
Findings: The findings indicated that the tested model exhibited acceptable fit. Significant positive correlations were found between marital satisfaction and marital commitment, while significant negative correlations were observed between the quality of alternative relationships and marital commitment. Additionally, relationship investment and marital commitment were significantly positively correlated. A significant relationship was identified between marital commitment and marital instability at the level of p<0.05. However, no significant relationship was observed between social networks and marital commitment or between subjective norms in marital relationships and marital commitment. Furthermore, the results demonstrated that marital commitment mediated the relationship between satisfaction with the relationship and marital instability (p≤.05), the quality of alternative relationships and marital instability (p≤.05), relationship investment and marital instability (p≤.01), and subjective norms and marital instability (p≤.05). However, marital commitment did not significantly mediate the relationship between the influence of social networks in marital relationships and marital instability.
Conclusion: Based on the findings and the role of subjective norms and social networks within Rusbult’s investment model, the results of this study can be utilized in counseling centers to enhance and prevent the instability of marital relationships.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















