Comparing the Physical Fitness Conditions of Boys' School Students in the City of Kashan
Keywords:
Students, Body Mass Index, Sports FacilitiesAbstract
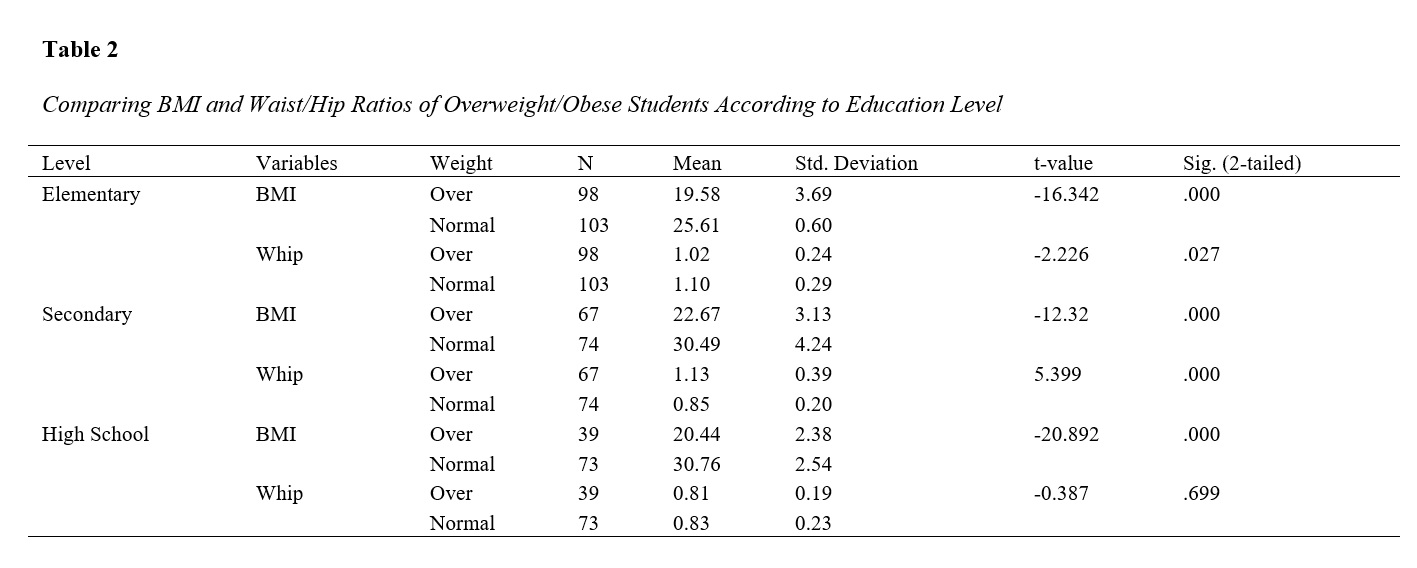
Overweight and obesity are significant health risk factors. Regular physical activity, which leads to physical fitness, requires access to sports facilities. This research aimed to assess the relationship between physical fitness conditions and access to sports facilities among overweight and normal-weight students in elementary, secondary, and high schools. In this cross-sectional study, the BMI and waist-to-hip ratios of overweight/obese and normal-weight boy students from elementary, secondary, and high schools were measured using scales equipped with height bars and flexible tapes in gymnasiums. Demographic data were collected and recorded using researcher-designed questionnaires. Statistical analysis, including descriptive and inferential analysis, was performed using SPSS version 22. A total of 542 students participated in this research. The results showed significant differences in BMI and waist-to-hip ratios among elementary, secondary, and high school students (P<0.0001), except for the waist-to-hip ratio of high school students (P=0.699). Additionally, there was a significant association between being overweight and access to sports facilities at home for secondary and high school students (P=0.000, P=0.014), but not for elementary students (P=0.384). Based on the findings of this research, access to sports facilities at home and school significantly contributes to the health conditions of students at all school levels. Therefore, school authorities and parents should ensure sufficient sports facilities are available for children.
Downloads