Predicting Psychological Well-Being Based on Digital Self-Efficacy and Emotional Intelligence in Students
Keywords:
Psychological well-being, Digital self-efficacy, Emotional intelligence, StudentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the prediction of psychological well-being based on digital self-efficacy and emotional intelligence among students at the Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch.
Methods and Materials: The study type is correlational-descriptive and cross-sectional. The statistical population includes all students of the Islamic Azad University, South Tehran Branch, in the academic year 2023-2024. Sampling was conducted using the convenience method, and 200 individuals were selected based on the Morgan table, considering the possibility of statistical attrition. Data collection tools included standardized questionnaires on psychological well-being, digital self-efficacy, and emotional intelligence. Data were analyzed using Pearson correlation and multiple regression methods.
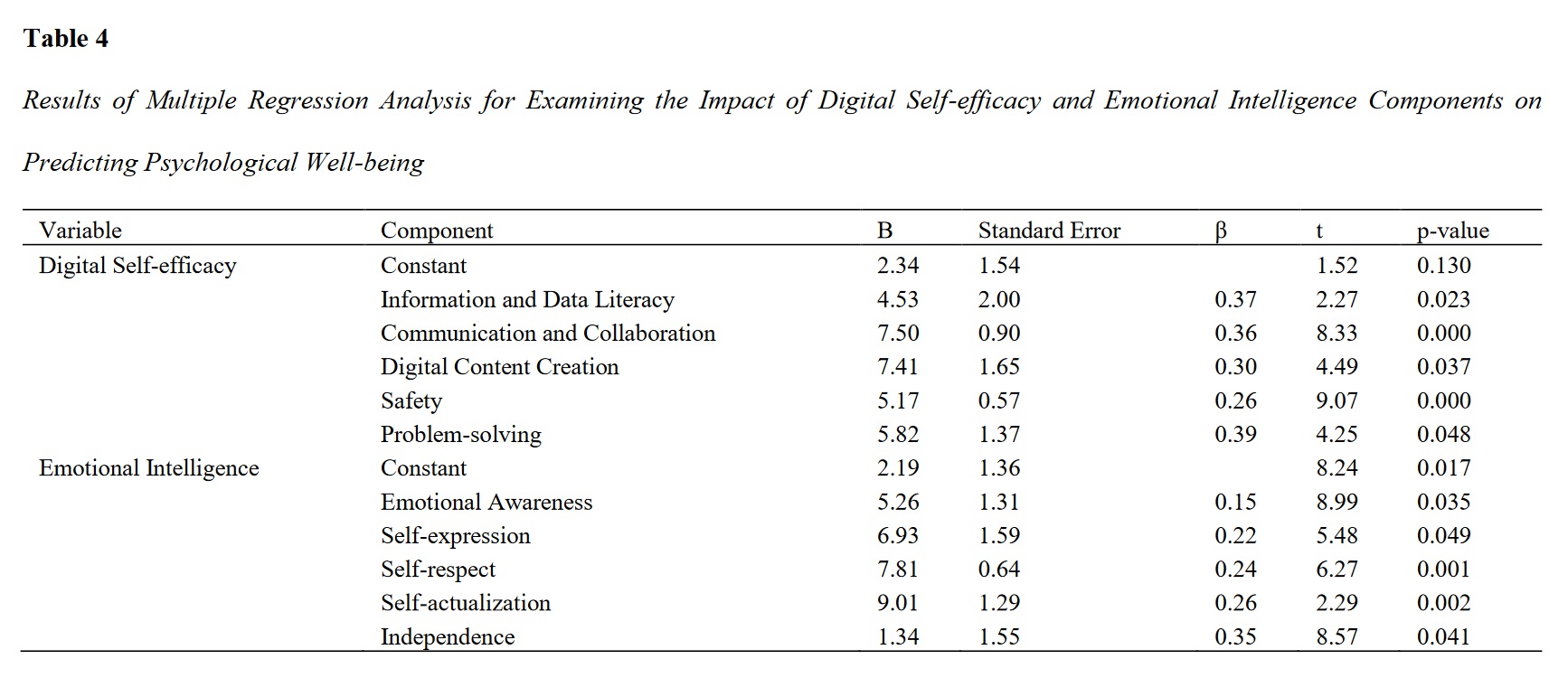
Findings: Results showed that all components of digital self-efficacy and emotional intelligence have a significant relationship with psychological well-being. The highest correlation coefficient was related to the security component in digital self-efficacy (p<0.05, 0.64) and the emotional awareness component in emotional intelligence (p<0.05, 0.69). Multiple regression analysis showed that both independent variables significantly predict psychological well-being. The coefficient of determination (R²) was 0.30 for digital self-efficacy and 0.48 for emotional intelligence, indicating significant variance explained in psychological well-being by these variables.
Conclusion: Based on the results of this study, increasing digital self-efficacy and emotional intelligence skills can help improve students' psychological well-being. Universities and educational institutions can help students enhance their abilities and, consequently, achieve better quality of life and mental health by designing and implementing special educational programs in this area.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nasrin Zavari (Author); Majid Mahmoudi Mozaffar (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







































