Parenting Styles as Predictors of Cognitive Emotion Regulation Among High School Students
Keywords:
Parenting styles, cognitive emotion regulation, adolescents, emotional development, cross-sectional studyAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between different dimensions of parenting styles and cognitive emotion regulation among high school students in Tabriz, Iran.
Methods and Materials: A cross-sectional design was employed, with a sample size of 416 high school students determined using the Cochran formula. Participants were selected through multistage cluster random sampling. Data were collected using the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (CERQ) and the Family as a Social Context (FSC) Questionnaire. Pearson correlation was used to examine relationships between cognitive emotion regulation and each parenting dimension. Additionally, linear regression analyses were conducted to determine the predictive power of parenting styles on emotion regulation. SPSS-27 software was used for statistical analyses.
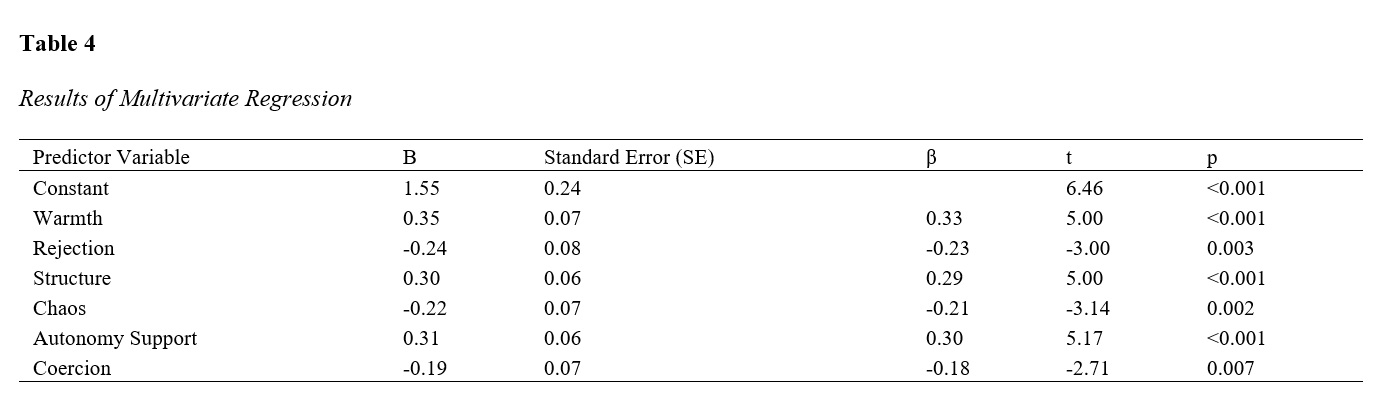
Findings: Descriptive statistics indicated that warmth had the highest mean score among parenting dimensions, while rejection had the lowest. Significant correlations were found between cognitive emotion regulation and all six subscales of parenting styles. Warmth (r = 0.45), structure (r = 0.38), and autonomy support (r = 0.41) were positively correlated with cognitive emotion regulation, whereas rejection (r = -0.32), chaos (r = -0.29), and coercion (r = -0.27) showed negative correlations. Regression analyses confirmed that these dimensions significantly predicted cognitive emotion regulation, explaining 46% of the variance.
Conclusion: The study highlights the crucial role of parenting styles in shaping cognitive emotion regulation among adolescents. Positive dimensions such as warmth, structure, and autonomy support enhance emotion regulation, while negative dimensions like rejection, chaos, and coercion hinder it.
Downloads
References
Agbaria, Q., Mahamid, F., & Veronese, G. (2021). The Association Between Attachment Patterns and Parenting Styles With Emotion Regulation Among Palestinian Preschoolers. Sage Open, 11(1), 215824402198962. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244021989624
Behjame, F., Zandi, H. G., & Khabiri, M. M. (2021). The Role of Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies on Predicting Aggression and Competitive Anger Among Athletic Students. International Journal of Motor Control and Learning, 3(4), 19-26. https://doi.org/10.52547/ijmcl.3.4.19
Besharat, M. A. (2014). Mediating Role of Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies on the Relationship Between Attachment Styles and Alexithymia. Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 10(2), 352-362. https://doi.org/10.5964/ejop.v10i2.671
Boediman, L. M., & Desnawati, S. (2019). The Relationship Between Parenting Style and Children's Emotional Development Among Indonesian Population. Jurnal Ilmiah Psikologi Mind Set, 10(01), 17-24. https://doi.org/10.35814/mindset.v10i01.735
Cueli, M. (2024). The Impact of Children’s and Parents’ Perceptions of Parenting Styles on Attention, Hyperactivity, Anxiety, and Emotional Regulation. Children, 11(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030313
Etemadi, M., Aghebati, A., Ayatmehr, F., & Ahmad, A. (2020). Predicting Borderline Personality Traits in Adolescents Based on Parenting Styles and Emotion Regulation Strategies. Practice in Clinical Psychology, 133-142. https://doi.org/10.32598/jpcp.8.2.656.1
Hao, Y., Chen, S., & Gu, X. (2022). The Impact of Parenting Styles on Undergraduate Students’ Emotion Regulation: The Mediating Role of Academic-Social Student-Faculty Interaction. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.972006
Haslam, D., Poniman, C., Filus, A., Sumargi, A. M., & Boediman, L. M. (2020). Parenting Style, Child Emotion Regulation and Behavioral Problems: The Moderating Role of Cultural Values in Australia and Indonesia. Marriage & Family Review, 56(4), 320-342. https://doi.org/10.1080/01494929.2020.1712573
Karim, A., Sharafat, T., & Mahmud, A. Y. (2014). Cognitive Emotion Regulation in Children as Related to Their Parenting Style, Family Type and Gender. Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bangladesh Science, 39(2), 211-220. https://doi.org/10.3329/jasbs.v39i2.17860
Khanum, S. (2023). The Influence of Parenting Styles on Child Development. JPR, 9(2), 808-816. https://doi.org/10.61506/02.00022
Kheradmand, M., & Ghahhari, S. (2018). The Relationship of Parenting Stress and Parenting Styles With Coping Strategies in Adolescents: The Role of Modulators of Emotion Regulation and Mindfulness. Iranian journal of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, In Press(In Press). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijpbs.12108
Lagacá-Ságuin, D. G., & Gionet, A. (2009). Parental Meta-Emotion and Temperament Predict Coping Skills in Early Adolescence. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 14(4), 367-382. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673843.2009.9748015
Loechner, J., Sfärlea, A., Starman, K., Oort, F., Thomsen, L. A., Schulte‐Körne, G., & Platt, B. (2019). Risk of Depression in the Offspring of Parents With Depression: The Role of Emotion Regulation, Cognitive Style, Parenting and Life Events. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 51(2), 294-309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-019-00930-4
Martins, E. C., Soares, I., Martins, C., & Osório, A. A. C. (2015). Infants’ Style of Emotion Regulation With Their Mothers and Fathers: Concordance Between Parents and the Contribution of Father–Infant Interaction Quality. Social Development, 25(4), 812-827. https://doi.org/10.1111/sode.12171
Muna, S. M., Saidah, Q. I., Ernawati, D., & Panduragan, S. L. (2022). Parenting Style and Emotional Regulation in Children With Intellectual Disability. The Malaysian Journal of Nursing, 14(02), 117-123. https://doi.org/10.31674/mjn.2022.v14i02.019
Pellerone, M., Iacolino, C., Mannino, G., Formica, I., & Zabbara, S. M. (2017). The Influence of Parenting on Maladaptive Cognitive Schema: A Cross-Sectional Research on a Group of Adults. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 10, 47-58. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s117371
Razavi, S. (2024). The Causal Model of Cognitive Emotion Regulation: Maladaptive Early Schemas and Parenting Styles. Jayps, 5(6), 68-77. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.5.6.8
Sara Aman Alah Khani, G. (2024). Modeling Anxiety Sensitivity Based on Early Maladaptive Schemas and Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies With the Mediating Role of Parenting Styles. Jayps, 5(6), 30-40. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.5.6.4
Tang, H., Lyu, J., & Xu, M. (2022). Direct and Indirect Effects of Strength-Based Parenting on Depression in Chinese High School Students: Mediation by Cognitive Reappraisal and Expression Suppression. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 15, 3367-3378. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s390790
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sepideh Razavi (Author); Leila Khajehpour (Corresponding Author); Ghavam Moltafet (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














