The Role of Self-Control and Emotional Processing in Predicting Psychological Well-Being Among Young Adults in Tabriz
Keywords:
Psychological Well-Being, Self-Control, Emotional Processing, Young Adults, Mental HealthAbstract
Objective: This study aims to examine the relationship between self-control, emotional processing, and psychological well-being among young adults in Tabriz.
Methods and Materials: A cross-sectional design was employed, involving a sample of 385 young adults aged 19 to 30 from Tabriz, selected through convenience sampling. Participants completed standardized questionnaires measuring self-control, emotional processing, and psychological well-being. Descriptive statistics, Pearson’s correlation, and multiple regression analysis were conducted using SPSS version 22 to assess the relationships between the variables.
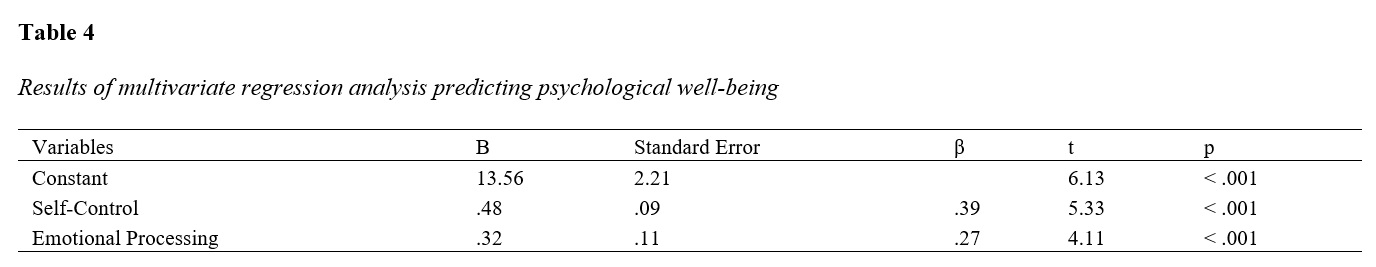
Findings: Pearson’s correlation analysis revealed significant positive correlations between psychological well-being and both self-control (r = .45, p < .001) and emotional processing (r = .38, p < .001). Multiple regression analysis indicated that self-control (B = .48, β = .39, p < .001) and emotional processing (B = .32, β = .27, p < .001) were significant predictors of psychological well-being, explaining 27% of the variance in well-being (R² = .27, F(2, 382) = 72.85, p < .001).
Conclusion: The findings suggest that both self-control and emotional processing are significant predictors of psychological well-being among young adults, with self-control playing a slightly more substantial role. These results underscore the importance of developing interventions aimed at enhancing self-control and emotional processing to promote mental health and well-being in this population.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Saeeda Babapouragadham (Author); Jalil Babapour Khairuddin (Corresponding Author); Marziyeh Alivandi Vafa (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














