Predicting Addiction Proneness Based on Emotional Intelligence, Moral Intelligence, Mental Health, and the Mediation of Life Stressful Events in Working Children
Keywords:
Addiction Potential, Emotional Intelligence , moral intelligence, mental health, stressful events, Child LaborAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to predict addiction proneness based on emotional intelligence, moral intelligence, mental health, and the mediation of life stressful events in working children in Tehran.
Methods and Materials: This correlational study employed structural equation modeling. The statistical population included all working children aged 12 to 18 in Tehran in 2024. A total of 215 participants were selected using a non-random convenience sampling method. Data were collected using a demographic questionnaire, the Addiction Proneness Scale (APS), the Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ), the 25-Symptom Checklist (SCL-25), the Lennick and Kiel Moral Intelligence Questionnaire (MIQ), and the Life Stressful Events Questionnaire by Khodayari Fard and colleagues. The reliability of the tools was assessed through internal consistency, using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. Data were analyzed using SPSS-24 and AMOS-24.
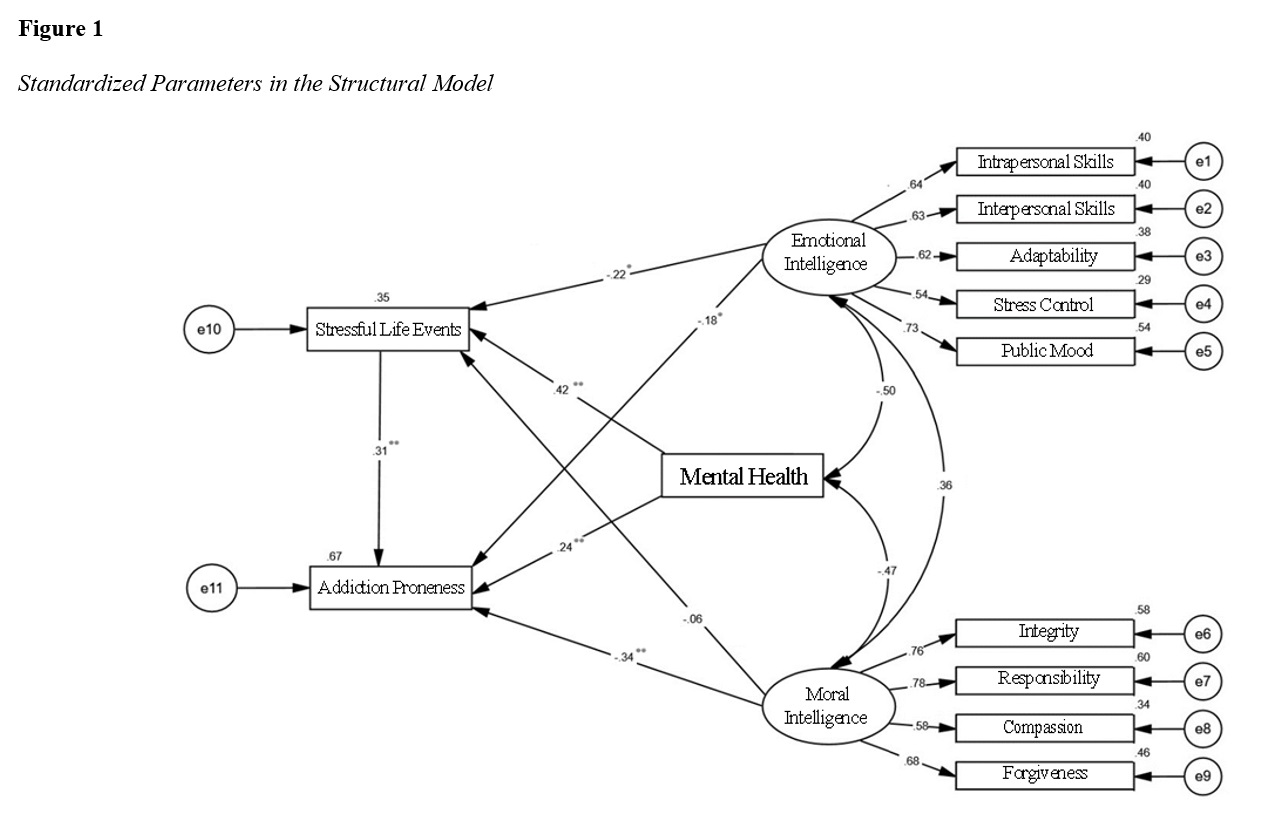
Findings: The findings indicated that mental health (P = 0.001, β = 0.365), emotional intelligence (P = 0.005, β = -0.251), and moral intelligence (P = 0.001, β = -0.359) predict addiction proneness in working children. Life stressful events mediated the correlation between mental health (P = 0.001, β = 0.128) and addiction proneness. Life stressful events also mediated the correlation between emotional intelligence and addiction proneness (P = 0.029, β = -0.067). Notably, the indirect path coefficient between moral intelligence and addiction proneness was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Based on the study findings, there is a significant relationship between addiction proneness and emotional intelligence, moral intelligence, and mental health. Life stressful events mediate the relationship between addiction proneness, emotional intelligence, and mental health.
Downloads
References
Amonini, C., & Donovan, R. J. (2006). The relationship between youth's moral and legal perceptions of alcohol, tobacco and marijuana and use of these substances. Health Education Research, 21(2), 276-286. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/cyh064
Buccheri, T., Musaad, S., Bost, K. K., & Fiese, B. H. (2018). Development and assessment of stressful life events subscales - A preliminary analysis. Journal of affective disorders, 226, 178-187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.09.046
Chukwudeh, O. S., & Oduaran, A. (2021). Liminality and Child Labour: Experiences of School Aged Working Children with Implications for Community Education in Africa. Social Sciences, 10(3), 2-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci10030093
Coles, R. (1998). The Moral Intelligence of Children. Family Court Review, 36(1), 5-108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.174-1617.1998.tb00496.x
Gholizadeh, M., & Manzari, M. (2019). The Effectiveness of Moral Intelligence Training on Students' Attitudes towards Substance, Social Health and Addiction. 6(21), 45-56. https://magiran.com/p2009844
Guerra-Bustamante, J., León-Del-Barco, B., Yuste-Tosina, R., López-Ramos, V. M., & Mendo-Lázaro, S. (2019). Emotional Intelligence and Psychological Well-Being in Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(10), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101720
Hamid, N., Hajizadeh, S., Marashy, S., & Hajy, S. (2017). The causal relationship of diffuse-avoidant style, self-efficacy and moral intelligence with addiction potential by the intermediation of sensation seeking within the male students. Journal of Social Psychology, 5(45), 55-70. https://magiran.com/p2371446
Herman, J. (2015). Trauma and Recovery. Basic Books. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Group_Trauma_Treatment_in_Early_Recovery/o0FWDwAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Holmes, T. H., & Rahe, R. H. (1967). The Social Readjustment Rating Scale. Journal of psychosomatic research, 11(2), 213-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(67)90010-4
Jalalvnd, M., Dariush, M., Sanatpour, S., & Jadidi, K. (2019). Prediction of addiction tendency based on self-efficacy and moral intelligence in students of Borujerd city. The First National Conference on Prevention of Secondhand Drug Use Among Students, Kermanshah.
Jameh Bozorg, A., & Javdan, Z. (2019). Readiness for addiction in students: the role of mental health components and social support in predicting it, the first national conference on the prevention of drug use among students, Kermanshah.
Jebraeili, H., & Habibi, M. (2016). Investigation the moderator role of emotional intelligence in related to effect of addiction vulnerability on substance use. Clinical Psychology Achievements, 2(1), 69-84. https://doi.org/10.22055/jacp.2017.13198
Kanesan, P., & Fauzan, N. (2019). Models of emotional intelligence: A review. e-BANGI, 16, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.55324/iss.v2i5.399
KaramiRad, B., Zarga, Y., & Mehrabizadeh Honarmand, M. (2015). Effectiveness of emotional intelligence training in addiction potential among students. etiadpajohi, 8(32), 37-50. http://etiadpajohi.ir/article-1-761-fa.html
Khoush Solook, M. (2024). Examining the causes of the phenomenon of street children's labor and comparing it with criminal laws. National Conference on Management and Humanities Research in Iran,
King, D. L., Herd, M. C. E., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2017). Tolerance in Internet gaming disorder: A need for increasing gaming time or something else? Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 6(4), 525-533. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.6.2017.072
Krasanakis, S. (2017). Dramatherapy and Drug Addiction Treatment. Dramatherapy, 38(1), 53-58. https://doi.org/10.1080/02630672.2017.1290888
Kuther, T. L. (2000). Moral reasoning, perceived competence, and adolescent engagement in risky activity. Journal of adolescence, 23(5), 599-604. https://doi.org/10.1006/jado.2000.0346
MacCann, C., Jiang, Y., Brown, L. E. R., Double, K. S., Bucich, M., & Minbashian, A. (2020). Emotional intelligence predicts academic performance: A meta-analysis. Psychological bulletin, 146(2), 150-186. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000219
Martins, A., Ramalho, N., & Morin, E. (2010). A comprehensive meta-analysis of the relationship between emotional intelligence and health. Personality and individual differences, 49(6), 554-564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2010.05.029
Meyers, L. S., Gamest, G., & Goarin, A. J. (2006). Applied Multivariate Research, Design and Interpretation. Sage Publications. https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2119780
Mohammadi Ahmadabadi, N., & Golestanejad, R. (2019). The mediating role of stressful life events in the relationship between personality traits and readiness for addiction. Addiction Research, 14(58), 191-216. https://sid.ir/paper/959912/fa
Moltafet, H., Hazbavi, A., & Moghadam, M. H. (2021). Exploring Family Contexts and its Role in Reproducing Street Child Labor in Ahvaz. Social Problems of Iran, 12(1), 381-402. https://doi.org/10.52547/jspi.12.1.381
Navabinejad, S. (2024). Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Well-being and Intervention Strategies across Life Stages. KMAN Counseling & Psychology Nexus, 2(1), 1-3. https://journals.kmanpub.com/index.php/psychnexus/article/view/2217
Nobakht, M., Mazin, g., Mansourinejad, M., & Razzaghi, I. (2016). The relationship between readiness for addiction and mental health in high school students, the first national conference on social harms.
Ottonello, M., Fiabane, E., Pistarini, C., Spigno, P., & Torselli, E. (2019). Difficulties In Emotion Regulation During Rehabilitation For Alcohol Addiction: Correlations With Metacognitive Beliefs About Alcohol Use And Relapse Risk. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 15, 2917-2925. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S214268
Penga, W., Lia, D., Lib, D., Jiaa, J., Wangc, Y., & Sun, W. (2019). School disconnectedness and Adolescent Internet Addiction: Mediation by self-esteem and moderation by emotional intelligence. Computers in human Behavior, 98, 111-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.04.011
Rachlin, H. (1995). Self-control: Beyond commitment. Behavioral and brain sciences, 18(1), 109-121. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X00037602
Roberts, Y. H., English, D., Thompson, R., & White, C. R. (2018). The impact of childhood stressful life events on health and behavior in at-risk youth. Children and Youth Services Review, 85, 117-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.11.029
Savage, J. E., Kaprio, J., & Korhonen, T. (2016). The effects of social anxiety on alcohol and cigarette use across adolescence: Results from a longitudinal twin study in Finland. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 30(4), 462-474. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000183
Schroder, H. S., Yalch, M. M., Dawood, S., Callahan, C. P., Brent Donnellan, M., & Moser, J. S. (2017). Growth mindset of anxiety buffers the link between stressful life events and psychological distress and coping strategies. Personality and individual differences, 110, 23-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.01.016
Skiba, D., Monroe, J., & Wodarski, J. (2004). Adolescent substance use: Reviewing the effectiveness of prevention strategies. Social Work, 49, 343-353. https://doi.org/10.1093/sw/49.3.343
Sohrabi, F., Mamsharifi, P., Rafezi, Z., & A'Azami, Y. (2019). Predicting Addiction Potential based on Mental Health, Social Support and Neuroticism and Agreeableness Personality Traits. ijpn, 6(6), 57-66. https://doi.org/10.21859/ijpn-06067
Taghizadeh, K., Lotfabadi, F., & Siami Alighialou, M. (2024). The Effectiveness of Reality Therapy on Identity Crisis and Mental Well-being of Child Laborers. Iranian Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 2(4), 43-50. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jndd.2.4.6
Tanhaye Reshvanloo, F., & Saadati Shamir, A. (2015). Construct validity and reliability of Symptom Checklist-25 (SCL-25). Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health, 18(1), 48-56. https://doi.org/10.22038/jfmh.2015.6255
UNICEF Iran. (2017). https://www.unicef.org/iran/
Wiss, D. A., Criscitelli, K., Gold, M., & Avena, N. (2017). Preclinical evidence for the addiction potential of highly palatable foods: Current developments related to maternal influence. Appetite, 115, 19-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.12.019
Yaghoubi, H., Shalchi, B., & Sheikhi, S. (2022). The Structural Relationship of Moral Intelligence and Self-Efficacy with Students' Addiction. Journal of Police Medicine, 11(1), e21. http://jpmed.ir/article-1-1067-fa.html
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hosna Karimi (Author); Marjan Jafari Roshan (Corresponding Author); Azin Taghipour (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














