Explainable AI Identification of Protective Family Factors Against Adolescent Substance Abuse
Keywords:
Adolescent substance abuse, family protective factors, explainable artificial intelligence, parental monitoring, prevention modelingAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to employ explainable artificial intelligence to identify and quantify the most influential protective family factors associated with reduced risk of adolescent substance abuse among adolescents.
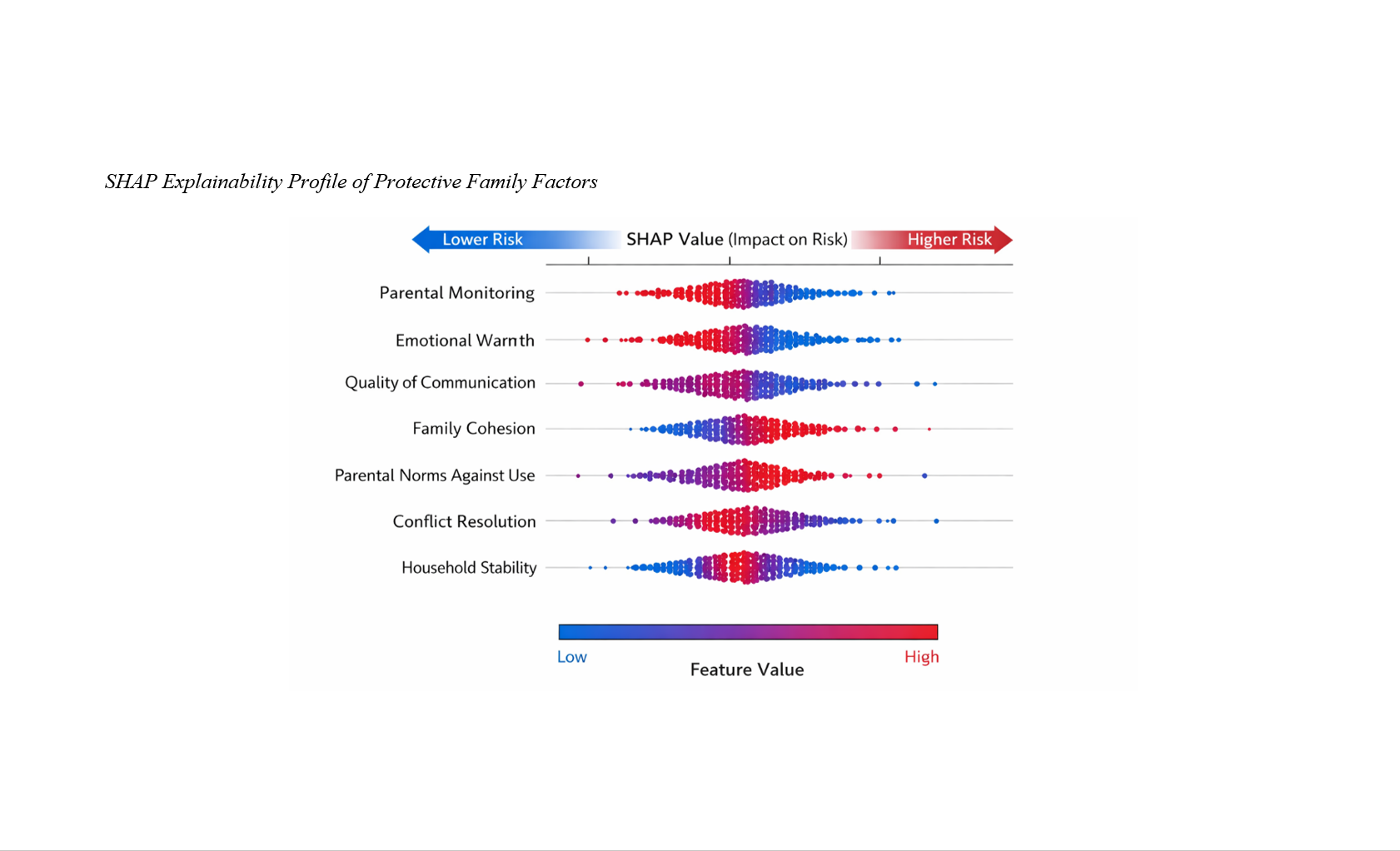
Methods and Materials: This study adopted a cross-sectional predictive-analytic design involving 684 adolescent–caregiver dyads recruited from public schools, community youth centers, and family health clinics across Michigan. Adolescents aged 13–18 years and their primary caregivers completed a comprehensive battery of validated psychosocial assessments measuring substance use behaviors, parental monitoring, emotional warmth, family cohesion, quality of communication, parental norms against substance use, conflict resolution skills, and household stability. Data were analyzed using advanced supervised machine learning algorithms, with gradient boosting selected as the optimal model based on performance indices. Explainable artificial intelligence techniques, including SHAP analysis, were applied to interpret model outputs and identify the relative contribution and interaction of protective family factors.
Findings: The final model demonstrated high predictive accuracy (AUC = 0.93; F1-score = 0.87), indicating strong discriminative ability in identifying adolescents at reduced risk of substance abuse. Parental monitoring emerged as the most influential protective factor, followed by emotional warmth, quality of parent–adolescent communication, family cohesion, and parental norms against substance use. Significant interaction effects were observed, particularly between parental monitoring and emotional warmth, yielding a 34.6% reduction in predicted substance abuse risk. Nonlinear patterns revealed threshold effects whereby moderate improvements in core family processes produced substantial decreases in risk probability.
Conclusion: The findings demonstrate that explainable artificial intelligence provides powerful and interpretable insights into the complex family mechanisms protecting adolescents from substance abuse.
Downloads
References
Agwogie, M. O., & Kliewer, W. (2024). Parenting and Other Potential Protective Factors Associated With Polysubstance Use Among Public School Students in Lagos, Nigeria. International journal of psychology, 59(3), 432-440. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijop.13122
Brincks, A. M., Perrino, T., Estrada, Y., & Prado, G. (2023). Preventing Alcohol Use Among Hispanic Adolescents Through a Family-Based Intervention: The Role of Parent Alcohol Misuse. Journal of Family Psychology, 37(1), 105-109. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0001038
Cox, R. B., Washburn, I. J., Croff, J. M., & Ringwalt, C. L. (2021). Parental School‐Involvement and Substance Use? A Novel Family‐Based Prevention Strategy for Latino Youth. Family Relations, 70(4), 1178-1189. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12533
Crabtree, M. A., Emery, N. N., Stanley, L. R., Prince, M. A., & Swaim, R. C. (2023). Intersecting Sex and American Indian Identity Moderates School and Individual Correlates of Binge Drinking Among Reservation-Area Adolescents. Journal of Psychopathology and Clinical Science, 132(5), 555-566. https://doi.org/10.1037/abn0000817
Fire, G., Barak, S., Shlomi, H., Tirtzha, C., Ben-Meir, L., Giladi, A., Harel‐Fisch, Y., & Tesler, R. (2023). After School: Volunteering in Community Emergency Services and Substance Use Among Israeli Adolescents. Psychology in the Schools, 60(7), 2579-2591. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22878
Gentzke, A. S., Wang, T. W., Cornelius, M. E., Park‐Lee, E., Ren, C., Sawdey, M. D., Cullen, K. A., Loretan, C., Jamal, A., & Homa, D. M. (2022). Tobacco Product Use and Associated Factors Among Middle and High School Students — National Youth Tobacco Survey, United States, 2021. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 71(5), 1-29. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.ss7105a1
Halvorson, M. A., Epstein, M., Caouette, J. D., Danzo, S., Satchell, A. K., Oesterle, S., & Kuklinski, M. R. (2024). General and Specific Risk and Protective Factors for Cigarette and Electronic Nicotine Delivery System (ENDS) Use. Prevention Science, 25(8), 1298-1309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-024-01752-0
Hoots, B. E., Li, J., Hertz, M., Esser, M. B., Rico, A., Zavala, E., & Jones, C. M. (2023). Alcohol and Other Substance Use Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among High School Students — Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2021. MMWR supplements, 72(1), 84-92. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.su7201a10
Jackson, K. M., Merrill, J. E., Stevens, A. K., Hayes, K. L., & White, H. R. (2021). Changes in Alcohol Use and Drinking Context Due to the COVID‐19 Pandemic: A Multimethod Study of College Student Drinkers. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 45(4), 752-764. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.14574
Kristjánsson, Á. L., Santilli, A. M., Mills, R., Layman, H. M., Smith, M. L., Mann, M. J., MacKillop, J., James, J. E., Lilly, C., & Kogan, S. M. (2022). Risk and Resilience Pathways, Community Adversity, Decision-Making, and Alcohol Use Among Appalachian Adolescents: Protocol for the Longitudinal Young Mountaineer Health Study Cohort. Jmir Research Protocols, 11(8), e40451. https://doi.org/10.2196/40451
Layman, H. M., Þórisdóttir, I. E., Halldorsdottir, T., Sigfúsdóttir, I. D., Allegrante, J. P., & Kristjánsson, Á. L. (2022). Substance Use Among Youth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. Current psychiatry reports, 24(6), 307-324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-022-01338-z
Le, T. T. T. (2023). Key Risk Factors Associated With Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems Use Among Adolescents. JAMA Network Open, 6(10), e2337101. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37101
Lee, E., & Santiago, A. M. (2021). Cumulative Exposure to Neighborhood Conditions and Substance Use Initiation Among Low-Income Latinx and African American Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(20), 10831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010831
McGovern, R., Bogowicz, P., Meader, N., Kaner, E., Alderson, H., Craig, D., Geijer‐Simpson, E., Jackson, K., Muir, C., Salonen, D., Smart, D., & Newham, J. (2023). The Association Between Maternal and Paternal Substance Use and Child Substance Use, Internalizing and Externalizing Problems: A Systematic Review and Meta‐analysis. Addiction, 118(5), 804-818. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.16127
Mereish, E. H., Fish, J. N., & Watson, R. J. (2023). Intersectional Minority Stress and Alcohol, Tobacco, and Cannabis Use Among Sexual and Gender Minority Adolescents of Color: Moderating Role of Family Support. LGBT Health, 10(1), 18-25. https://doi.org/10.1089/lgbt.2021.0430
Merrin, G. J., Bailey, J. A., Kelly, A. B., Le, V. T., Heerde, J. A., Doery, E., Batmaz, E. A., & Toumbourou, J. W. (2024). Continuity and Change in Substance Use Patterns During the Transition From Adolescence to Young Adulthood: Examining Changes in Social Roles. International journal of mental health and addiction, 23(6), 4155-4177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-024-01342-9
Montero‐Zamora, P., López-Soto, A., Cordoba, J., & Ramirez, E. (2025). Adolescent Substance Use in Costa Rica: Findings From a National Survey Among Secondary School Students. Frontiers in Public Health, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1655355
Nath, A., Choudhari, S. G., Dakhode, S. U., Rannaware, A., & Gaidhane, A. (2022). Substance Abuse Amongst Adolescents: An Issue of Public Health Significance. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.31193
Nawi, A. M., İsmail, R., Ibrahim, F., Hassan, M. R., Manaf, M. R. A., Amit, N., Ibrahim, N., & Shafurdin, N. S. (2021). Risk and Protective Factors of Drug Abuse Among Adolescents: A Systematic Review. BMC public health, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11906-2
Okine, L., & Unger, J. B. (2024). Substance Use Among Latinx Youth: The Roles of Sociocultural Influences, Family Factors, and Childhood Adversity. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 34(4), 1562-1572. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.13025
Pelham, W. E., Tapert, S. F., Gonzalez, M. R., McCabe, C., Lisdahl, K. M., Alzueta, E., Baker, F. C., Breslin, F. J., Dick, A. S., Dowling, G. J., Guillaumé, M., Hoffman, E. A., Marshall, A. T., McCandliss, B. D., Sheth, C., Sowell, E. R., Thompson, W. K., Rinsveld, A. V., Wade, N. E., & Brown, S. A. (2021). Early Adolescent Substance Use Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Longitudinal Survey in the ABCD Study Cohort. Journal of Adolescent Health, 69(3), 390-397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.06.015
Rajamani, J. B., Reshmi, Y. S., Pricilla, R. A., Prasad, J., & Baskar, M. (2024). Prevalence of Substance Use Among Adolescents Residing in Urban Slums of Vellore: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 13(11), 4831-4836. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_420_24
Rogers, A. H., Palermo, T. M., Groenewald, C. B., & Murray, C. B. (2024). Adolescent Predictors of Substance Use in Young Adulthood Among Individuals With Childhood‐onset Chronic Pain: A follow‐up Study. European Journal of Pain, 29(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.4724
Ruiz, Y., Taylor, Z., & Cavin, R. (2020). Parent-Adolescent Communication as a Protective Factor Against Adolescent Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Reported Narratives From Youth From Latinx Farmworker Families. Journal of Adolescent Research, 36(4), 315-341. https://doi.org/10.1177/0743558420906084
Ryzin, M. J. V., Cil, G., & Roseth, C. J. (2022). Costs and Benefits of Cooperative Learning as a Universal School‐based Approach to Adolescent Substance Use Prevention. Journal of Community Psychology, 51(1), 438-452. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.22916
Scholes‐Balog, K. E., Hemphill, S. A., Heerde, J. A., Toumbourou, J. W., & Patton, G. (2020). Childhood Social Environmental and Behavioural Predictors of Early Adolescent Onset Cannabis Use. Drug and Alcohol Review, 39(4), 384-393. https://doi.org/10.1111/dar.13077
Soest, T. v., Kozák, M., Rodríguez‐Cano, R., Fluit, S., Cortés‐García, L., Ulset, V., Haghish, E. F., & Bakken, A. (2022). Adolescents’ Psychosocial Well-Being One Year After the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Norway. Nature Human Behaviour, 6(2), 217-228. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01255-w
Suarez, G. L., Shaw, D. S., Wilson, M. N., Lemery‐Chalfant, K., & Hyde, L. W. (2024). Inhibitory Control in Late Childhood as a Predictor of Antisocial Behavior in Adolescence and the Role of Social Context. Prevention Science, 26(4), 568-581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-024-01754-y
Swaim, R. C., Crabtree, M. A., & Egli, M. (2025). A Structural Equation Model Test of Affect, Family Warmth, and Substance Use Among American Indian Reservation-Based Adolescents. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 39(4), 345-353. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0001068
Szoko, N., Ragavan, M. I., Khetarpal, S. K., Chu, K. H., & Culyba, A. J. (2021). Protective Factors Against Vaping and Other Tobacco Use. Pediatrics, 148(2). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-048066
Þórisdóttir, I. E., Ásgeirsdóttir, B. B., Kristjánsson, Á. L., Valdimarsdóttir, H., Tolgyes, E. M. J., Sigfússon, J., Allegrante, J. P., Sigfúsdóttir, I. D., & Halldorsdottir, T. (2021). Depressive Symptoms, Mental Wellbeing, and Substance Use Among Adolescents Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Iceland: A Longitudinal, Population-Based Study. The Lancet Psychiatry, 8(8), 663-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00156-5
Villanueva‐Blasco, V. J., Belda-Ferri, L., & Vázquez‐Martínez, A. (2025). A Systematic Review on Risk Factors and Reasons for E-Cigarette Use in Adolescents. Tobacco Induced Diseases, 23(January), 1-25. https://doi.org/10.18332/tid/196679