Machine Learning Modeling of Parental Decision-Making Under Stress and Its Impact on Child Outcomes
Keywords:
Parental stress, Decision-making, Child development, Family functioning, Machine learning, Predictive modelingAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to develop and evaluate machine learning models of parental decision-making under stress to predict child behavioral and academic outcomes among Malaysian families.
Methods and Materials: This cross-sectional predictive study was conducted among 487 parent–child dyads recruited from urban and suburban regions of Malaysia. Parents completed standardized measures of parenting stress, stress-based decision-making, emotional regulation, family functioning, and contextual characteristics, while child outcomes were assessed using validated behavioral and academic indicators obtained from parents, teachers, and school records. Data were preprocessed and analyzed using multiple supervised machine learning algorithms, including random forest, gradient boosting, support vector machine, and deep neural network models. Model performance was evaluated using nested cross-validation procedures, and feature attribution techniques were applied to identify the most influential predictors. Structural equation modeling was additionally conducted to examine theoretical pathways among core variables.
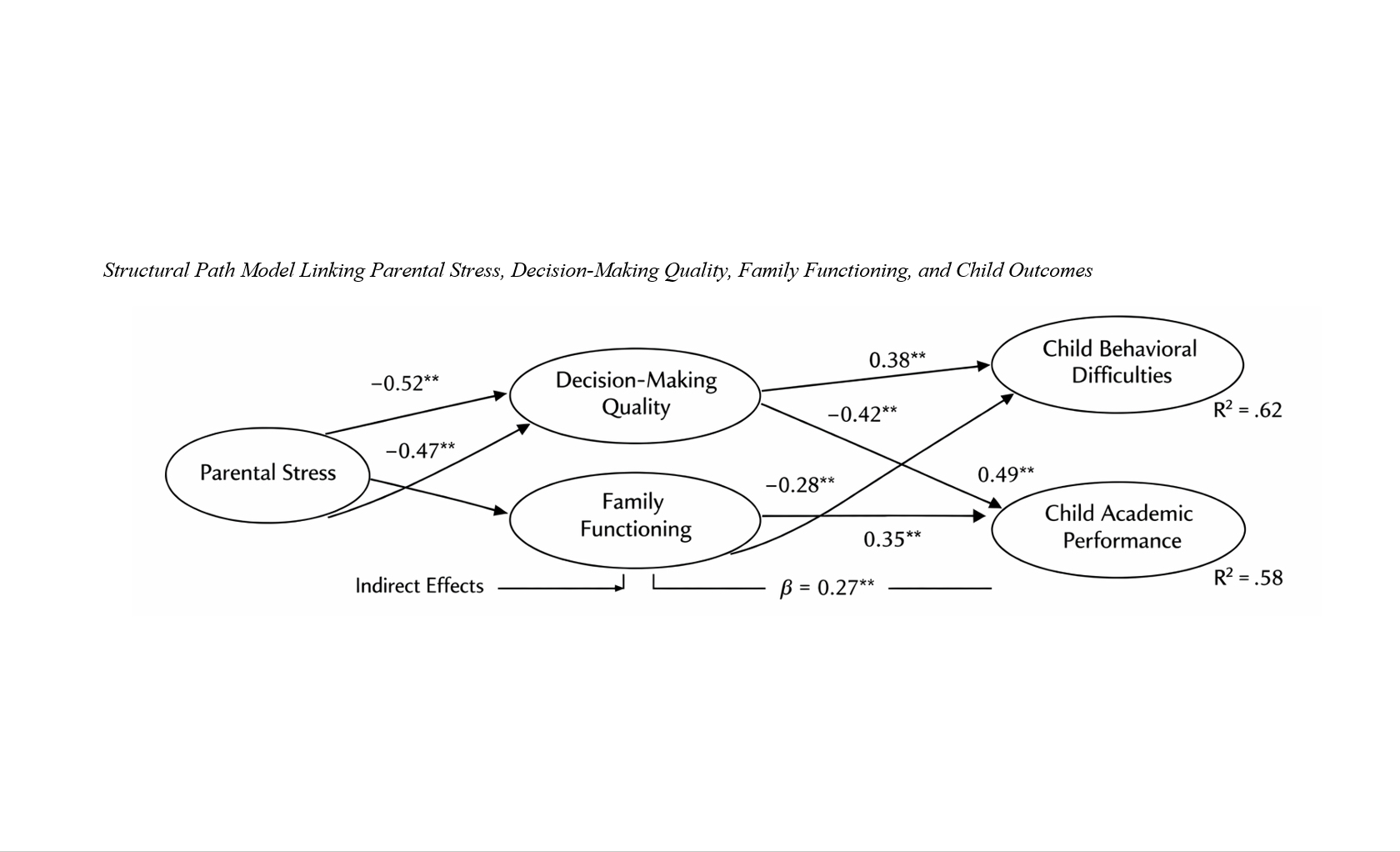
Findings: The deep neural network achieved the highest predictive accuracy for both child behavioral difficulties (AUC = 0.96, F1 = 0.91) and academic performance (AUC = 0.92, F1 = 0.85), outperforming all comparison models. Parental stress and stress-based decision consistency emerged as the strongest predictors of child outcomes, followed by family cohesion, parental emotional regulation, and economic stability. The structural model demonstrated that parental decision-making quality significantly mediated the relationship between parental stress and both child behavioral and academic outcomes, with the full model explaining 62% of the variance in behavioral difficulties and 58% of the variance in academic performance.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that parental decision-making under stress constitutes a central predictive mechanism shaping child development and that machine learning models provide powerful tools for identifying families at heightened developmental risk, thereby supporting early intervention and precision-based family support strategies.
Downloads
References
Byeon, H. (2025). Enhancing Autism Care: The Role of Remote Support in Parental Well-Being and Child Development. World journal of psychiatry, 15(4). https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.102267
Chen, Y.-C., Byrne, E., & Vélez, T. (2022). A Preliminary Study of COVID-19-related Stressors, Parenting Stress, and Parental Psychological Well-Being Among Parents of School-Age Children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 31(6), 1558-1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02321-1
Chung, G., Tilley, J. L., Netto, N., Chan, A., & Lanier, P. (2024). Parenting Stress and Its Impact on Parental and Child Functioning During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Meta-Analytical Review. International Journal of Stress Management, 31(3), 238-251. https://doi.org/10.1037/str0000329
Datu, J. A. D., Tai, A. P. L., Valdez, J. P. M., To, P. C., Fung, W. Y., Poon, K., Leung, M.-K., & Lau, W. K. (2024). Stress Mindset Relates to Better Mental Health in Parents of Children With Special Needs: A Path Analysis Study. Child & Family Social Work, 30(4), 931-938. https://doi.org/10.1111/cfs.13228
Fang, Y., Luo, J., Boele, M., Windhorst, D. A., Grieken, A. v., & Raat, H. (2022). Parent, Child, and Situational Factors Associated With Parenting Stress: A Systematic Review. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 33(6), 1687-1705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-022-02027-1
Fanta, A., Kim, S. E., Huang, C. J., Tsai, W., & Huang, C. Y. (2025). Economic Stress and Child Outcomes: The Family Stress Model Among Asian American Families During COVID-19. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1591730
Folk, J. B., Aguilera, A., Chaplin, T. M., & Tolou‐Shams, M. (2025). Stress Management Among Caregivers of Detained Youth: Protocol for Randomized Controlled Trial of the RAISE Web-Based mHealth App. Jmir Research Protocols, 14, e67511. https://doi.org/10.2196/67511
Frankel, L. A., Kuno, C. B., & Sampige, R. (2021). The Relationship Between COVID-related Parenting Stress, Nonresponsive Feeding Behaviors, and Parent Mental Health. Current Psychology, 42(13), 10706-10717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02333-y
García, M. F., Montero‐Zamora, P., Salas‐Wright, C. P., Maldonado‐Molina, M. M., Piñeros-Leaño, M., Hodges, J. C., Bates, M., Brown, E. C., Gómez, R., Calderón, I., & Schwartz, S. J. (2024). The Impact of Cultural Stress on Family Functioning Among Puerto Rican Displaced Families and the Effect on Mental Health. Family Process, 63(2), 843-864. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12998
Geprägs, A., Bürgin, D., Fegert, J. M., Brähler, E., & Clemens, V. (2023). Parental Stress and Physical Violence Against Children During the Second Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results of a Population-Based Survey in Germany. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-023-00571-5
Giannotti, M., Mazzoni, N., Bentenuto, A., Venuti, P., & Falco, S. d. (2021). Family Adjustment to COVID‐19 Lockdown in Italy: Parental Stress, Coparenting, and Child Externalizing Behavior. Family Process, 61(2), 745-763. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12686
Green, R., Linga-Easwaran, J., Goodman, C., Taylor, M., Fabiano, G. F., Miller, S. P., & Williams, T. S. (2024). Positive Parenting Practices Support Children at Neurological Risk During COVID-19: A Call for Accessible Parenting Interventions. Frontiers in psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1328476
Guessoum, S. B., Lachal, J., Radjack, R., Carretier, É., Minassian, S., Benoit, L., & Moro, M. R. (2020). Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Lockdown. Psychiatry research, 291, 113264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113264
He, Y., Ortiz, R., Kishton, R., Wood, J. N., Fingerman, M., Jacobs, L., & Šinko, L. (2022). In Their Own Words: Child and Adolescent Perceptions of Caregiver Stress During Early COVID-19. Child abuse & neglect, 124, 105452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105452
Kauhanen, L., Wan Mohd Azam Wan Mohd, Y., Lempinen, L., Peltonen, K., Gyllenberg, D., Mishina, K., Gilbert, S., Bastola, K., Brown, J. S. L., & Sourander, A. (2022). A Systematic Review of the Mental Health Changes of Children and Young People Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 32(6), 995-1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-022-02060-0
Kerr, M., Rasmussen, H. F., Fanning, K., & Braaten, S. M. (2021). Parenting During COVID‐19: A Study of Parents' Experiences Across Gender and Income Levels. Family Relations, 70(5), 1327-1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12571
Kong, C., & Yasmin, F. (2022). Impact of Parenting Style on Early Childhood Learning: Mediating Role of Parental Self-Efficacy. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.928629
Lawson, M., Piel, M. H., & Simon, M. (2020). Child Maltreatment During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Consequences of Parental Job Loss on Psychological and Physical Abuse Towards Children. Child abuse & neglect, 110, 104709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104709
Marchetti, D., Fontanesi, L., Mazza, C., Giandomenico, S. D., Roma, P., & Verrocchio, M. C. (2020). Parenting-Related Exhaustion During the Italian COVID-19 Lockdown. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 45(10), 1114-1123. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsaa093
Mestermann, S., Kleinöder, J. M., Arndt, M., Krämer, J., Eichler, A., & Kratz, O. (2023). The Father’s Part: A Pilot Evaluation of a Father-Centered Family Intervention Group in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Behavioral Sciences, 14(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14010013
Morgan, D. D., Higgins, C. D., & Rogers, C. R. (2024). The Role of Parent's Mental Health in Shaping Perceptions of Adolescent Mental Health Experiences After COVID‐19. Family Relations, 74(2), 583-601. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.13123
Moscardino, U., Dicataldo, R., Roch, M., Carbone, M., & Mammarella, I. C. (2021). Parental Stress During COVID-19: A Brief Report on the Role of Distance Education and Family Resources in an Italian Sample. Current Psychology, 40(11), 5749-5752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01454-8
Orgilés, M., Belzunegui-Pastor, À., Morales, A., & Espada, J. P. (2023). Parental Stress as a Mediator Between Parents’ Emotion Regulation and Youth’s Psychological Symptoms During the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Cross-Sectional Study. Psychology Society & Education, 15(1), 40-47. https://doi.org/10.21071/pse.v15i1.15383
Romero, E., López‐Romero, L., Domínguez-Álvarez, B., Villar, P., & Fraguela, J. A. G. (2020). Testing the Effects of COVID-19 Confinement in Spanish Children: The Role of Parents’ Distress, Emotional Problems and Specific Parenting. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(19), 6975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17196975
Russell, B. S., Hutchison, M., Tambling, R. R., Tomkunas, A. J., & Horton, A. L. (2020). Initial Challenges of Caregiving During COVID-19: Caregiver Burden, Mental Health, and the Parent–Child Relationship. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 51(5), 671-682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-020-01037-x
Saleem, F. T., Christophe, N. K., Anyiwo, N., Bernard, D. L., Jones, S. C. T., Anderson, R. E., Stein, G. L., & Kiang, L. (2025). The Talk and Walk in Black Families: Exploring Racial Socialization Content and Competency in the Context of Parental Worries About Racial Profiling and Adolescents' Internalizing Outcomes. Family Process, 64(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.13095
Scales, P. C., Roehlkepartain, E. C., & Houltberg, B. J. (2023). Effects of Developmental Relationships on the Well‐being of Youth in High‐stress Families. Family Relations, 72(5), 2800-2819. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12822
Skjerdingstad, N., Johnson, M. S., Johnson, S. U., Hoffart, A., & Ebrahimi, O. V. (2021). Parental Burnout During the COVID‐19 Pandemic. Family Process, 61(4), 1715-1729. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12740
Spinelli, M., Lionetti, F., Pastore, M., & Fasolo, M. (2020). Parents' Stress and Children's Psychological Problems in Families Facing the COVID-19 Outbreak in Italy. Frontiers in psychology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01713
Xu, M., Wu, D., Tang, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, X., Zhou, L., Li, F., & Jiang, L. (2022). From Child Social Impairment to Parenting Stress in Mothers of Children With ASD: The Role of Parental Self-Efficacy and Social Support. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1005748
Zhou, Q., Lin, C., & Guo, X. (2025). Family Dysfunction, Parenting Stress, and Child Mental Health: Associations With Bullying Involvement and the Moderating Role of Neighborhood Support. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1644696