Predicting Addiction Proneness Based on Emotional Intelligence, Moral Intelligence, Mental Health, and the Mediation of Life Stressful Events in Working Children
Keywords:
Addiction Potential, Emotional Intelligence , moral intelligence, mental health, stressful events, Child LaborAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to predict addiction proneness based on emotional intelligence, moral intelligence, mental health, and the mediation of life stressful events in working children in Tehran.
Methods and Materials: This correlational study employed structural equation modeling. The statistical population included all working children aged 12 to 18 in Tehran in 2024. A total of 215 participants were selected using a non-random convenience sampling method. Data were collected using a demographic questionnaire, the Addiction Proneness Scale (APS), the Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ), the 25-Symptom Checklist (SCL-25), the Lennick and Kiel Moral Intelligence Questionnaire (MIQ), and the Life Stressful Events Questionnaire by Khodayari Fard and colleagues. The reliability of the tools was assessed through internal consistency, using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. Data were analyzed using SPSS-24 and AMOS-24.
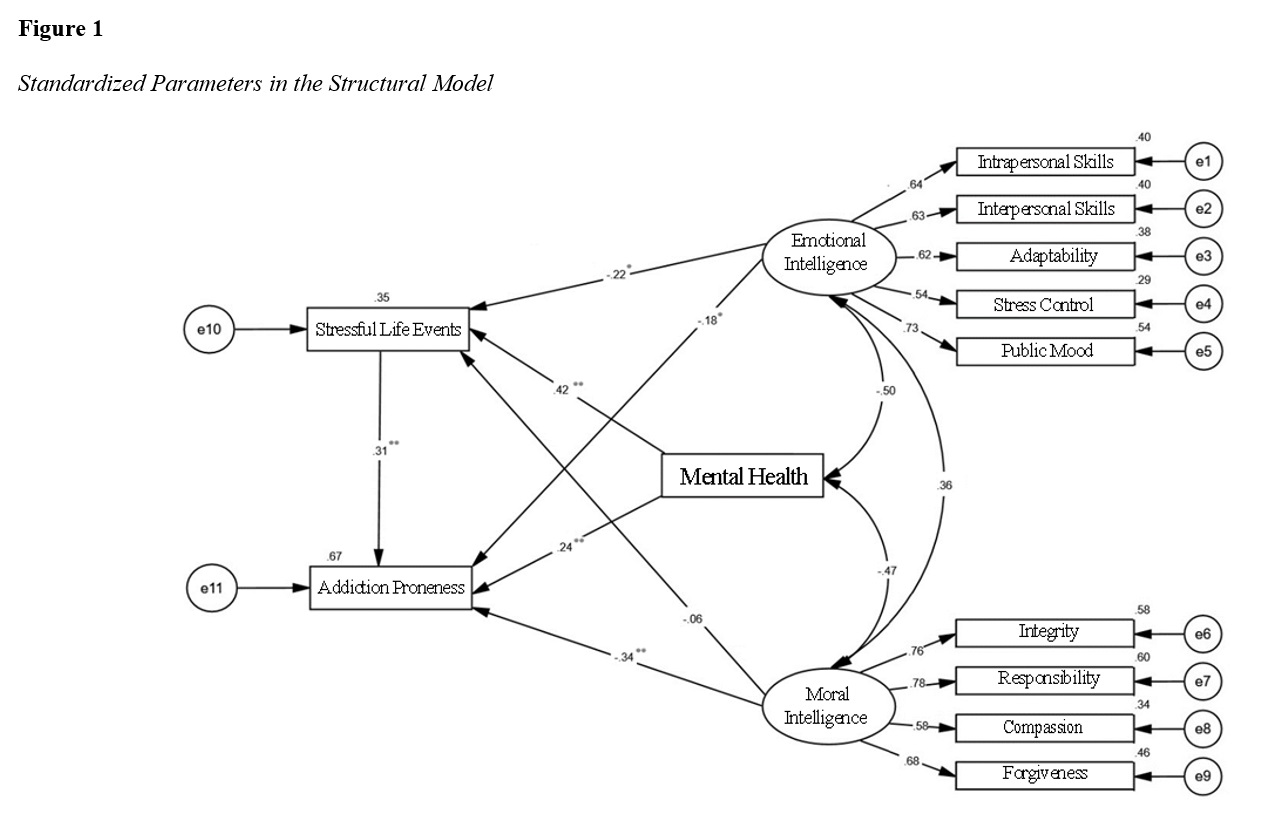
Findings: The findings indicated that mental health (P = 0.001, β = 0.365), emotional intelligence (P = 0.005, β = -0.251), and moral intelligence (P = 0.001, β = -0.359) predict addiction proneness in working children. Life stressful events mediated the correlation between mental health (P = 0.001, β = 0.128) and addiction proneness. Life stressful events also mediated the correlation between emotional intelligence and addiction proneness (P = 0.029, β = -0.067). Notably, the indirect path coefficient between moral intelligence and addiction proneness was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Based on the study findings, there is a significant relationship between addiction proneness and emotional intelligence, moral intelligence, and mental health. Life stressful events mediate the relationship between addiction proneness, emotional intelligence, and mental health.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hosna Karimi (Author); Marjan Jafari Roshan (Corresponding Author); Azin Taghipour (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



































