Exploring the Impact of Exercise Motivation and Perceived Health Competence on Emotional Eating
Keywords:
Emotional eating, exercise motivation, perceived health competence, intrinsic motivation, health behavior, psychological well-being, cross-sectional studyAbstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate the relationships between emotional eating, exercise motivation, and perceived health competence among adults.
Methods and Materials: The study employed a cross-sectional design with a sample of 193 adults, determined based on the Morgan and Krejcie table. Participants completed validated questionnaires measuring emotional eating, exercise motivation, and perceived health competence. Data were analyzed using Pearson correlation to assess the relationships between variables and multiple linear regression to determine the predictive power of exercise motivation and perceived health competence on emotional eating. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 27.
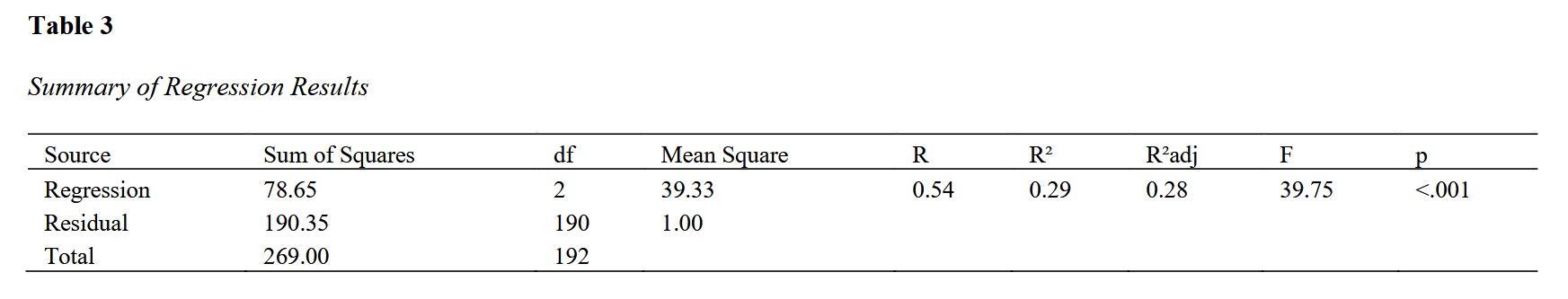
Findings: The regression analysis indicated that exercise motivation and perceived health competence together explained 29% of the variance in emotional eating behaviors (R² = 0.29, adjusted R² = 0.28, F(2, 190) = 39.75, p < .001). Both exercise motivation (B = -0.40, p < .001) and perceived health competence (B = -0.35, p < .001) were significant predictors of emotional eating.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that higher levels of exercise motivation and perceived health competence are associated with lower levels of emotional eating.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nayelli Muñoz (Corresponding Author); Bridget Abalorio (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














