Rumination and Identity Confusion as Predictors of Emotional Exhaustion in Emerging Adult Women
Keywords:
Emotional exhaustion, Rumination, Identity confusion, Emerging adulthood, Cognitive vulnerability, Women’s mental healthAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the predictive roles of rumination and identity confusion in emotional exhaustion among emerging adult women.
Methods and Materials: A correlational descriptive design was employed with a sample of 392 emerging adult women in Iraq, selected based on Morgan and Krejcie’s sample size table. Participants completed standardized self-report instruments measuring emotional exhaustion, rumination, and identity confusion. Descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation coefficients, and multiple linear regression analyses were conducted using SPSS version 27. All assumptions for regression, including normality, linearity, homoscedasticity, multicollinearity, and independence of residuals, were checked and confirmed prior to analysis.
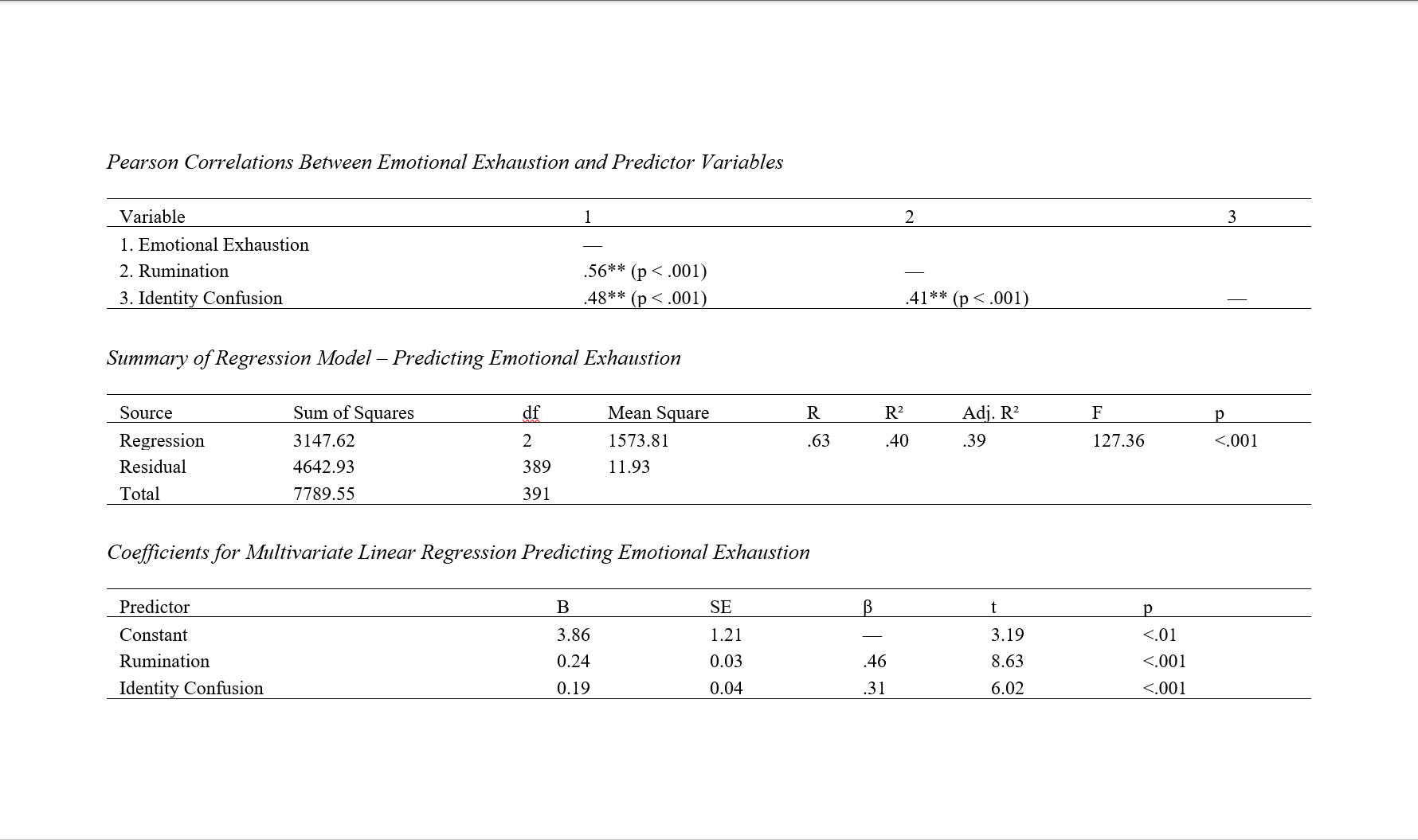
Findings: The results revealed significant and positive correlations between emotional exhaustion and both rumination (r = .56, p < .001) and identity confusion (r = .48, p < .001). Multiple linear regression analysis indicated that rumination (B = 0.24, β = .46, t = 8.63, p < .001) and identity confusion (B = 0.19, β = .31, t = 6.02, p < .001) significantly predicted emotional exhaustion. The overall regression model was statistically significant, F(2, 389) = 127.36, p < .001, accounting for 40% of the variance in emotional exhaustion (R² = .40, adjusted R² = .39).
Conclusion: This study provides empirical evidence that rumination and identity confusion are significant cognitive and developmental predictors of emotional exhaustion in emerging adult women. The findings highlight the importance of addressing maladaptive thought patterns and unresolved identity issues during this life stage to mitigate psychological fatigue and promote emotional well-being. Interventions targeting cognitive restructuring and identity coherence may be effective in reducing the risk of emotional exhaustion in this vulnerable population.
Downloads
References
Borders, A. (2020). Rumination, Anger, and Aggression. 73-100. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-812545-8.00003-6
Camacho, A., Ruiz, R. O., & Romera, E. M. (2021). Longitudinal Associations Between Cybervictimization, Anger Rumination, and Cyberaggression. Aggressive Behavior, 47(3), 332-342. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21958
Chen, S., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Teng, Z., & Luo, Y. (2025). How Does Trait Anger Associate With Aggression Among Chinese College Students? The Role of Anger Rumination and Locus of Control. Psychology in the Schools, 62(4), 1217-1227. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23386
Hardin, K. M., Contreras, I. M., Kosiak, K., & Novaco, R. W. (2022). Anger Rumination and Imagined Violence as Related to Violent Behavior Before and After Psychiatric Hospitalization. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 78(9), 1878-1895. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.23334
Hosie, J., Simpson, K., Dunne, A. L., & Daffern, M. (2022). A Study of the Relationships Between Rumination, Anger Rumination, Aggressive Script Rehearsal, and Aggressive Behavior in a Sample of Incarcerated Adult Males. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 78(9), 1925-1939. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.23341
Isaksson, J., Sukhodolsky, D. G., Koposov, R., Stickley, A., & Ruchkin, V. (2020). The Role of Gender in the Associations Among Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms, Anger, and Aggression in Russian Adolescents. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 33(4), 552-563. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22502
Ju, H.-J., & Park, J.-H. (2022). The Relation Between Perceived Stress and Aggression: The Dual Mediation Effects of Intolerance of Frustration and Anger Rumination. The Association of Korea Counseling Psychology Education Welfare, 9(6), 193-209. https://doi.org/10.20496/cpew.2022.9.6.193
Kim, Y., & Park, K.-H. (2023). The Effects of Hostile Attribution Bias and Negative Urgency on Reactive Aggression: The Mediation Effect of Anger Rumination. Korean Association for Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 23(22), 455-467. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2023.23.22.455
Koposov, R., Stickley, A., Sukhodolsky, D. G., & Ruchkin, V. (2022). Bulimia Symptoms and Anger and Aggression Among Adolescents. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2275597/v1
Plessen, K. J., Constanty, L., Ranjbar, S., Turri, F., Miano, G., Lepage, C., & Urben, S. (2023). The Role of Self-Regulatory Control Processes in Understanding Aggressive Ideations and Behaviors: An Experience Sampling Method Study. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1058814
Quan, F., Huang, J., Li, H., & Zhu, W. (2024). Longitudinal Relations Between Bullying Victimization and Aggression: The Multiple Mediation Effects of Anger Rumination and Hostile Automatic Thoughts. PsyCh Journal, 13(5), 849-859. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.760
Quan, F., Wang, L., Gong, X., Lei, X., Liang, B., & Zhang, S. (2022). Hostile Attribution Bias and Anger Rumination Sequentially Mediate the Association Between Trait Anger and Reactive Aggression. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.778695
Ruchkin, V., Stickley, A., Koposov, R., Sukhodolsky, D. G., & Isaksson, J. (2023a). Depressive Symptoms and Anger and Aggression in Russian Adolescents. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-023-00677-w
Ruchkin, V., Stickley, A., Koposov, R., Sukhodolsky, D. G., & Isaksson, J. (2023b). Depressive Symptoms and Their Associations With Anger and Aggression in Russian Adolescents. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3085432/v1
Salguero, J. M., García‐Sancho, E., Ramos‐Cejudo, J., & Kannis‐Dymand, L. (2020). Individual Differences in Anger and Displaced Aggression: The Role of Metacognitive Beliefs and Anger Rumination. Aggressive Behavior, 46(2), 162-169. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21878
Sarrate‐Costa, C., Lila, M., Comes‐Fayos, J., Moya-Albiol, L., & Romero‐Martínez, Á. (2022). Reduced Vagal Tone in Intimate Partner Violence Perpetrators Is Partly Explained by Anger Rumination. Current Psychology, 42(33), 29603-29615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03994-z
Scaini, S., Forresi, B., Torres, D., Piron, R., & Giani, L. (2024). The Role of Anger Cognitions and Anger Rumination in Predicting Externalizing and Internalizing Problems in Adolescence. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy, 39(1), 38-55. https://doi.org/10.1891/jcp-2023-0050
Stephens, A. N., Collard, J., & Koppel, S. (2023). Don’t Sweat the Small Stuff; Anger Rumination and Lack of Forgiveness Are Related to Aggressive Driving Behaviours. Current Psychology, 43(7), 6338-6349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04744-5
Sung, J., & Kim, E.-J. (2024). The Relationship Between Covert Narcissism and Reactive Aggression: The Sequential Mediation Effect of Hostile Attribution Bias and Anger Rumination. Soc Cognitive Enhancement Intervention, 15(4), 281-297. https://doi.org/10.21197/jcei.15.4.14
Tao, Y., Niu, H., Li, Y., Liu, X., Wang, S., Ma, Z., Hou, W., & Liu, X. (2023). Effects of Personal Relative Deprivation on the Relationship Between Anger Rumination and Aggression During and After the COVID‐19 Pandemic Lockdown: A Longitudinal Moderated Network Approach. Journal of adolescence, 95(3), 596-608. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12140
Tran, T. T. C., Le, T. V., Cao, C. T., Dam, A. T. V., & Nguyen, Q. T. (2024). The Relationships Between Parental Educational Practices, Pro-Aggression Beliefs, and Aggressive Behavior: A Cross-Sectional Study. Multidisciplinary Science Journal, 6(9), 2024197. https://doi.org/10.31893/multiscience.2024197
Umar, A. (2025). Anger on the Road: Moderating Role of Trait Emotional Intelligence in the Relationship Between Anger Rumination and Dangerous Driving Behaviors Among Young Motorbike Users. Res. J. Social Affairs, 3(3), 125-134. https://doi.org/10.71317/rjsa.003.03.0205
Wen, J., Wang, G., & Miao, M. (2024). The Link Between Anger and Reactive Aggression: Insights Into Anger Rumination. Aggressive Behavior, 50(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.22157
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














