Workload and Creative Performance: The Buffering Role of Intrinsic Motivation
Keywords:
Workload, Intrinsic Motivation, Creative Performance, Job Demands–Resources Model, Structural Equation ModelingAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the effect of workload on creative performance and to test whether intrinsic motivation buffers the potential negative impact of workload among employees in Colombia.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational research design was employed with a sample of 397 full-time employees from diverse organizations across Colombia, selected using Morgan and Krejcie’s sample size determination table. Data were collected using validated instruments: the Quantitative Workload Inventory, the Work Preference Inventory–Intrinsic Motivation subscale, and the Employee Creativity Scale. Descriptive statistics, Pearson’s correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling (SEM) were conducted to test the hypothesized relationships. Analyses were performed using SPSS version 27 and AMOS version 21. Model fit was assessed through multiple indices, including χ², degrees of freedom, χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA.
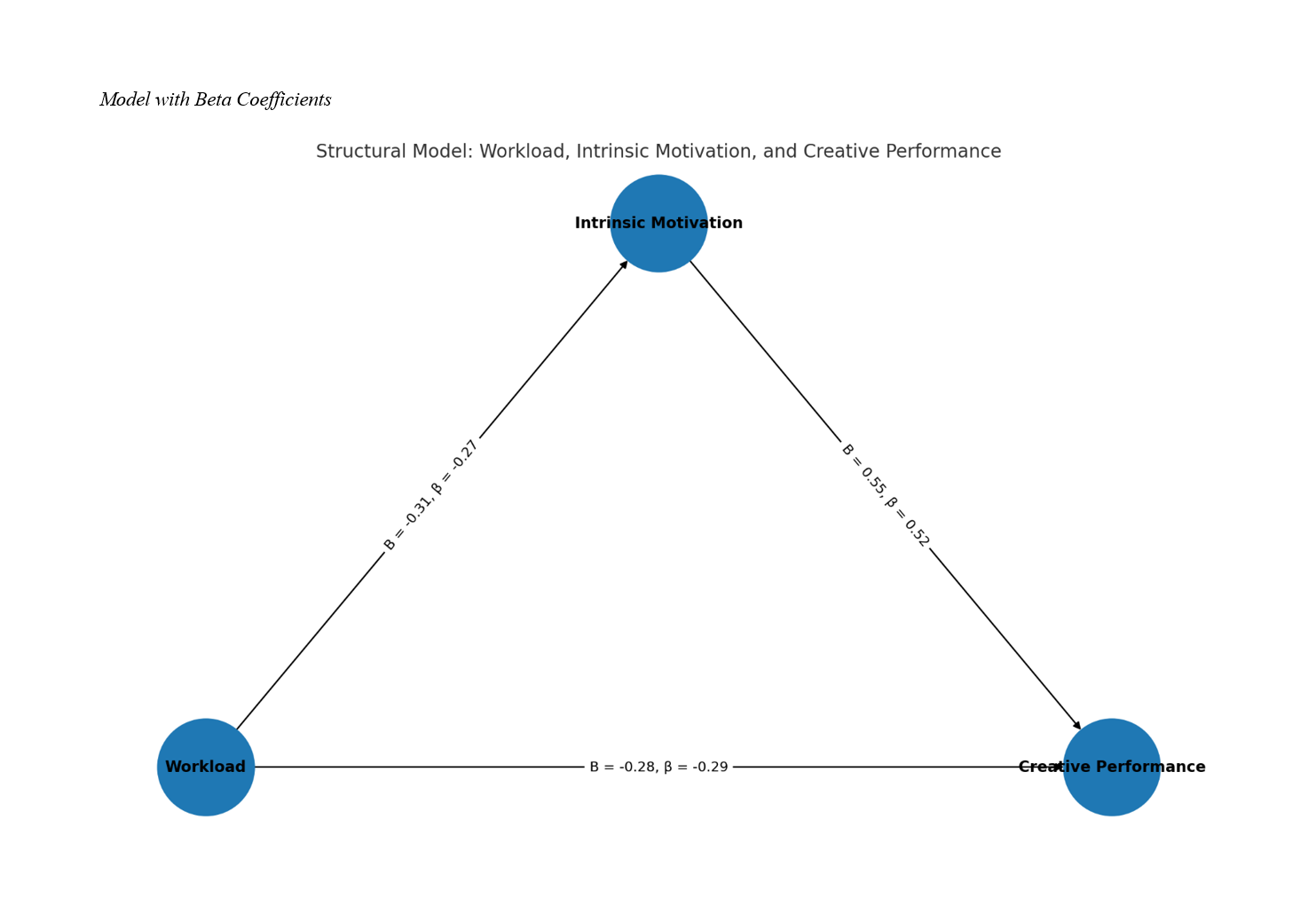
Findings: Results indicated that workload was significantly and negatively correlated with creative performance (r = –.31, p < .001) and with intrinsic motivation (r = –.27, p = .001), while intrinsic motivation was strongly and positively correlated with creative performance (r = .48, p < .001). SEM analysis confirmed good model fit (χ²/df = 1.74; GFI = .94; CFI = .97; RMSEA = .043) and revealed that workload exerted a significant direct negative effect on creative performance (β = –.29, p < .001) and on intrinsic motivation (β = –.27, p < .001). Intrinsic motivation showed a robust positive effect on creative performance (β = .52, p < .001) and buffered the negative workload–creativity relationship, partially mediating and weakening the total negative impact of workload (β total = –.15, p = .041).
Conclusion: Findings highlight that although heavy workload reduces employees’ creativity, fostering intrinsic motivation can protect and sustain innovative performance under job demands. Organizations should design roles and climates that support autonomy, curiosity, and self-driven engagement to maintain creativity despite high workload conditions.
Downloads
References
Ankhtsetseg, G., & Lee, H. (2022). The Influence of Empowering Leadership on Employee Agility: Focusing on the Mediating Effects of Role Breadth Self-Efficacy and Intrinsic Motivation. Korean Hum Resour Develop Strategy Institute, 17(4), 123-154. https://doi.org/10.21329/khrd.2022.17.4.123
Aristana, I. N., Puspitawati, N. M. D., & Ismayanthi, T. I. T. (2023). Leadership and Employee Creativity: The Mediation Role of Intrinsic Motivation. Media Ekonomi Dan Manajemen, 38(1), 161. https://doi.org/10.56444/mem.v38i1.3270
Devapriyanga, G., & Subashini, R. (2024). Enhancing Creative Excellence in the Southern Indian IT Sectors: The Role of Autonomous Motivation in Inclusive Leadership Practices. International Research Journal of Multidisciplinary Scope, 05(04), 899-911. https://doi.org/10.47857/irjms.2024.v05i04.01476
Gao, Y., & Tsai, K.-C. B. (2024). The Effect of Entrepreneurial Leadership on College Students' Creativity: The Mediating Role of Intrinsic Motivation and Emotional Intelligence. Environment and Social Psychology, 9(9). https://doi.org/10.59429/esp.v9i9.3043
Hastiti, A. P. (2025). Digital Leadership in Driving Work Innovation: The Role of Creativity, Motivation, and Gender. The Winners, 26(1), 43-57. https://doi.org/10.21512/tw.v26i1.12572
Lee, D. w. (2024). The Relationship Between College Students' Openness to Experience, Engagement in the Creative Process, Intrinsic Motivation, and Creative Performance in Dance Composition Classes. Korean Association for Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction, 24(20), 257-283. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2024.24.20.257
Li, L., Zhang, Y., & Zheng, X. (2022). Burden or Opportunity? The Role of Employees' Regulatory Focus in Shaping the Motivational Processes of Empowering Leadership. Baltic Journal of Management, 18(1), 89-103. https://doi.org/10.1108/bjm-11-2021-0410
Liu, J., & Huang, J.-H. (2024). The Influence of College Students' Perception of Green Inclusive Leadership on Green Creativity: the Mediating Role of Green Intrinsic Motivation. Journal of Ecohumanism, 3(8). https://doi.org/10.62754/joe.v3i8.5406
Mayasari, N., Suhara, A., Marlita, D., Widowati, R., & Damiyana, D. (2024). The Influence of Organizational Communication, Participative Leadership, and Work Motivation on Employee Creativity: Case Study in the Creative Industries in Bali. The Eastasouth Management and Business, 2(03), 298-309. https://doi.org/10.58812/esmb.v2i03.258
Muhammad, S., & Anshori, M. (2025). Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Kolaboratif Dan Perilaku Kreatif Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Dengan Motivasi Intrinsik Sebagai Variabel Intervening (Studi Pada BPJS Ketenagakerjaan Di Madura). Jurnal Kajian Ilmu Manajemen (Jkim), 4(3). https://doi.org/10.21107/jkim.v4i3.26941
Nguyễn, T. P. L., Nguyễn, T. T., Nguyen, T. D., & Ha, N. T. V. (2022). Psychological Empowerment and Employee Creativity in Vietnam Telecommunication Enterprises: The Mediating Role of Intrinsic Work Motivation. Journal of Organizational Behavior Research, 7(2), 132-142. https://doi.org/10.51847/0xkwbkbehe
Semedo, C., Salvador, A., Santos, N. R. d., Pais, L., & Mónico, L. (2022). Toxic Leadership and Empowering Leadership: Relations With Work Motivation. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 15, 1885-1900. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s340863
Setyono, H., Adawiyah, W. R., & Fitriani, S. (2024). Transformational Leadership and Consumer Citizenship Behavior on Employee Creativity: The Mediating Role of Intrinsic Motivation. Jurnal Fokus Manajemen Bisnis, 14(2), 256-270. https://doi.org/10.12928/fokus.v14i2.10593
Sirine, H. (2024). Leading With Insight: How Intellectual Capital Shapes Supervisory Leadership. Global, 2(7), 1377-1400. https://doi.org/10.59613/global.v2i7.218
Thu, S. H. T., & Phạm, M. (2024). How Do Transformational Leadership and Affective Trust Enhance Creativity? Emerging Science Journal, 8(5), 1847-1859. https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2024-08-05-011
Widnyani, N. M., & Dewi, K. K. (2022). Pengaruh Efikasi Diri, Pelatihan Kerja, Dan Lingkungan Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Divisi Frontliner Di PT BPR Indra Candra Singaraja. Artha Satya Dharma, 15(2), 43-48. https://doi.org/10.55822/asd.v15i2.260
Xu, W., Zhang, Y., Yan, M., Zhang, J., & Fan, X. (2023). How Empowering Leadership Promotes Millennial Employees’ Voice Behavior. Social Behavior and Personality an International Journal, 51(11), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.12525
Xue, H., Luo, Y., Luan, Y., & Wang, N. (2022). A Meta-Analysis of Leadership and Intrinsic Motivation: Examining Relative Importance and Moderators. Frontiers in psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.941161
Yuliawati, A. K. (2025). The Effect of Inclusive Leadership and Intrinsic Motivation on Innovation Work Behavior: The Mediating Role of Creative Self-Efficacy. Journal of Social Research, 4(8), 2097-2106. https://doi.org/10.55324/josr.v4i8.2736
Yusriani, S., Isham, F., Azis, E., Yulina, Y., & Kamal, N. M. (2025). Promoting Innovative Work Behaviors for Greener and Sustainable Development Among Service Sector Workers in Denmark. Icbem(2), 279-294. https://doi.org/10.47747/icbem.v2i2.2722
Zaeni, N., Maryadi, M., Salim, M., & Kitta, S. (2024). The Relationship Between Employee Motivation, Creativity and Performance. Paradoks Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi, 7(4), 466-480. https://doi.org/10.57178/paradoks.v7i4.991