Evaluating the Efficacy of a Multifaceted Health Behavior Training Program on Psychological Distress
Keywords:
Psychological distress, Health behavior training, Cognitive behavioral therapy, Mindfulness, Randomized controlled trial, Mental health interventionAbstract
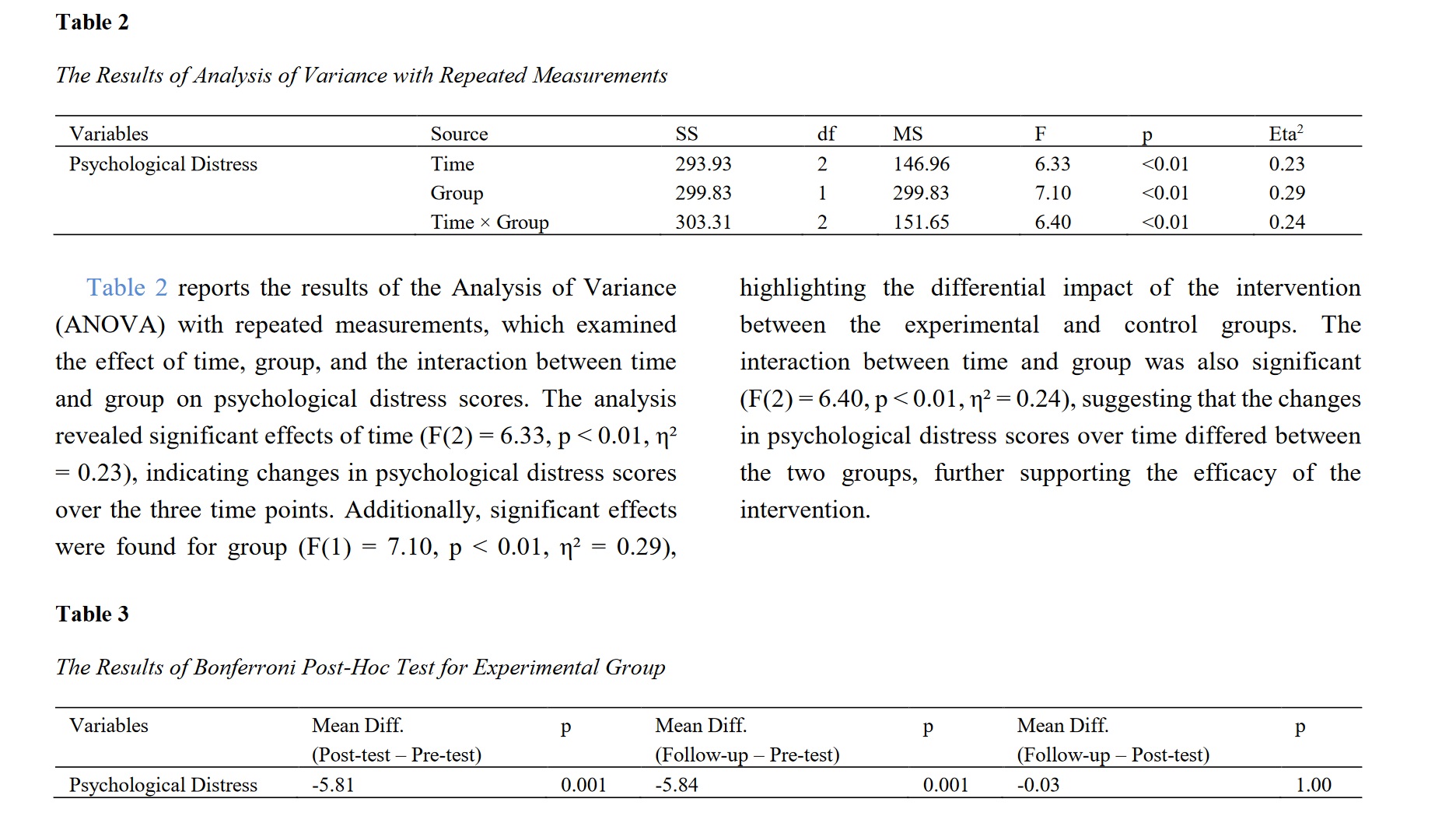
This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of a comprehensive Health Behavior Training Program in reducing psychological distress among adults. The program, integrating cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, stress management, and health education, sought to provide participants with effective tools to manage distress and improve overall well-being. A randomized controlled trial design was employed, involving 50 participants with mild to moderate psychological distress, randomly assigned to either the experimental group receiving the Health Behavior Training Program or a control group receiving no intervention. The intervention consisted of 8 weekly sessions, each lasting 90 minutes. Psychological distress was measured at baseline, post-intervention, and at a three-month follow-up using the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K10). The experimental group exhibited a significant reduction in psychological distress scores from pre-test (Mean = 33.81, SD = 4.19) to post-test (Mean = 27.44, SD = 4.42) and maintained these improvements at the three-month follow-up (Mean = 27.39, SD = 4.37). In contrast, the control group showed no significant changes in distress scores over time. Analysis of variance with repeated measurements indicated significant effects of time (F(2) = 6.33, p < 0.01), group (F(1) = 7.10, p < 0.01), and their interaction (F(2) = 6.40, p < 0.01) on psychological distress scores, underscoring the effectiveness of the intervention. The Health Behavior Training Program significantly reduced psychological distress among participants compared to a control group, with sustained effects at a three-month follow-up. These findings support the implementation of multifaceted health behavior interventions as effective tools for managing psychological distress and enhancing mental health outcomes.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Farzaneh Mardani (Corresponding Author); Nancy Parra Vázquez, Jinashree Rajendrakumar, Seyed Milad Saadati (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







