Determinants of Health-Related Quality of Life: The Roles of Time Management and Perceived Injustice
Keywords:
Health-Related Quality of Life, Time Management, Perceived Injustice, Chronic Conditions, Cross-Sectional StudyAbstract
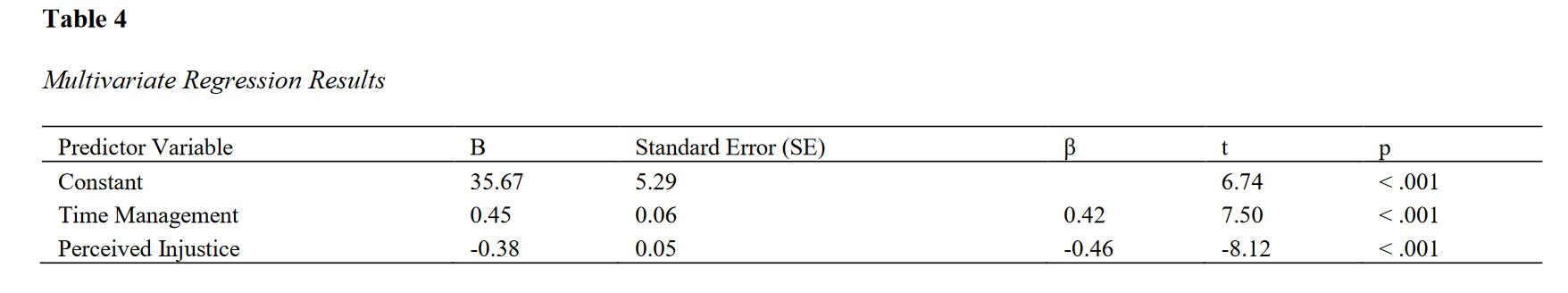
This study aims to examine the predictive roles of time management and perceived injustice on Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) among adults. By understanding these relationships, the study seeks to identify potential areas for intervention to enhance well-being, particularly for individuals with chronic health conditions. A cross-sectional design was employed with 230 participants selected through convenience sampling from community centers and healthcare facilities. The sample size was determined using the Morgan and Krejcie table. Participants completed validated questionnaires measuring HRQoL (SF-36 Health Survey), time management (Time Management Behavior Scale), and perceived injustice (Injustice Experience Questionnaire). Data were analyzed using SPSS version 27, with Pearson correlation to explore relationships between variables and linear regression to assess predictive power. Assumptions of normality, linearity, and homoscedasticity were confirmed before analysis. Descriptive statistics indicated mean scores of 70.35 (SD = 15.78) for HRQoL, 75.64 (SD = 10.24) for time management, and 45.82 (SD = 12.96) for perceived injustice. Pearson correlations revealed that time management positively correlated with HRQoL (r = 0.48, p < .001), while perceived injustice negatively correlated with HRQoL (r = -0.52, p < .001). Regression analysis showed that time management (B = 0.45, p < .001) and perceived injustice (B = -0.38, p < .001) significantly predicted HRQoL, with the model explaining 40% of the variance (R^2 = 0.40). The study highlights the significant roles of time management and perceived injustice in predicting HRQoL. Effective time management is associated with higher HRQoL, while higher perceived injustice is linked to lower HRQoL. These findings underscore the need for interventions targeting time management skills and perceptions of injustice to improve quality of life.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Elif Toktas (Corresponding Author); Neda Atapour (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







