The Structural Model of Psychological Vulnerability Based on Object Relations and Adverse Childhood Experiences Considering the Mediating Role of Internalized Shame in Individuals Seeking Cosmetic Surgery
Keywords:
Psychological Vulnerability, Adverse Childhood Experiences, Object Relations, Internalized Shame, Cosmetic SurgeryAbstract
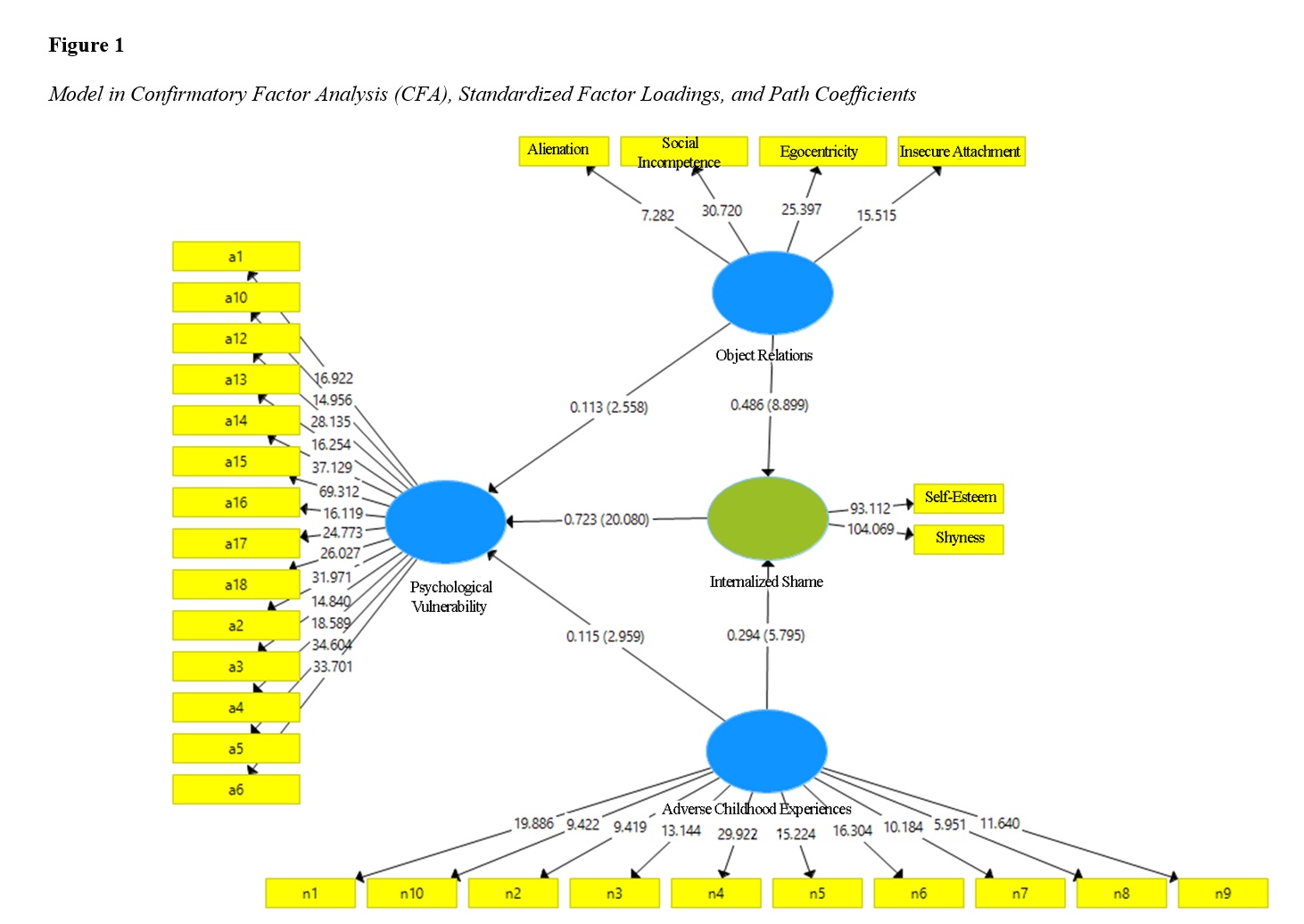
The objective of this study was to test the structural model of psychological vulnerability based on object relations and adverse childhood experiences, considering the mediating role of internalized shame in individuals seeking cosmetic surgery. This study was fundamental and quantitative, using a descriptive-correlational and structural equation modeling (SEM) approach. The statistical population included all individuals residing in Tehran who were seeking cosmetic surgery and visited aesthetic clinics during the years 2023-2024. A sample of 304 self-volunteered participants from this population was selected through convenience sampling. Data were collected using the Psychological Vulnerability Questionnaire by Derogatis (2001), the Adverse Childhood Experiences Questionnaire by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Kaiser Foundation (2018), the Object Relations Questionnaire by Bell (1986), and the Internalized Shame Questionnaire by Cook (1993). Data analysis was conducted using correlation matrices and structural equation modeling. The data analysis results indicated that the proposed model’s indices demonstrated an acceptable fit. The pathways from adverse childhood experiences to psychological vulnerability (β = 0.115, P = 0.000), from adverse childhood experiences to internalized shame (β = 0.294, P = 0.000), from internalized shame to psychological vulnerability (β = 0.723, P = 0.000), from object relations to psychological vulnerability (β = 0.113, P = 0.000), and from object relations to internalized shame (β = 0.486, P = 0.000) were significant. Additionally, the mediating role of internalized shame was confirmed at a 0.95 confidence level. Thus, it is recommended that the role of these variables be considered significant in assessment, diagnosis, and treatment. Relevant organizations should also consider implementing potential preventive programs.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ladan Nassiri (Author); Maryam Ghahremani (Corresponding Author); Shahriar Dargahi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

















