Health Consciousness and Distress Tolerance as Predictors of Rehabilitation Self-Efficacy
Keywords:
Rehabilitation self-efficacy, health consciousness, distress tolerance, rehabilitation, psychological resilience, health behaviorAbstract
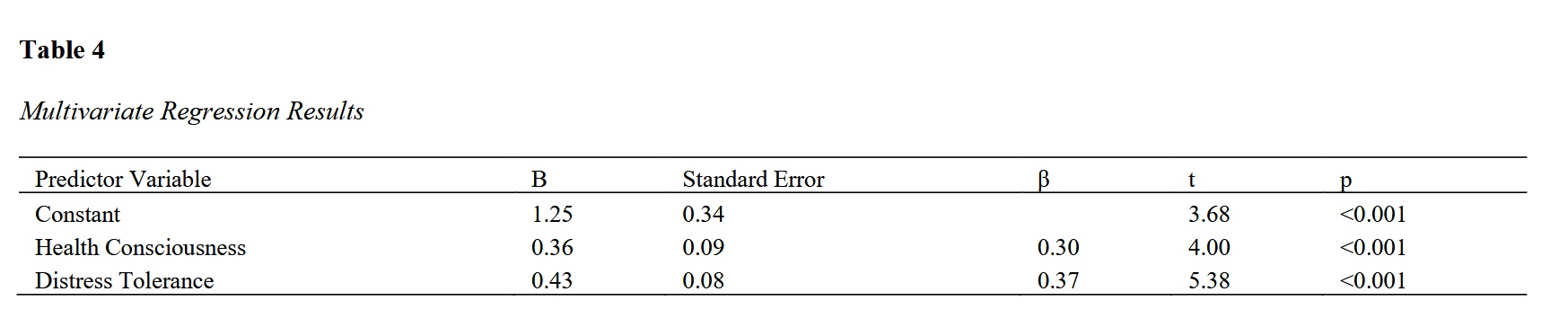
This study aimed to examine the predictive value of health consciousness and distress tolerance on rehabilitation self-efficacy. Rehabilitation self-efficacy is crucial for successful recovery, and understanding its determinants can inform the development of effective interventions. A cross-sectional design was employed, involving 217 participants recruited from rehabilitation centers. The sample size was determined based on the Morgan and Krejcie table. Standardized questionnaires were used to assess rehabilitation self-efficacy, health consciousness, and distress tolerance. Pearson correlation and linear regression analyses were conducted to examine the relationships between variables using SPSS version 27. Descriptive statistics indicated that the mean scores for rehabilitation self-efficacy, health consciousness, and distress tolerance were 3.85 (SD = 0.72), 4.10 (SD = 0.65), and 3.67 (SD = 0.80), respectively. Pearson correlation analysis showed significant positive correlations between rehabilitation self-efficacy and both health consciousness (r = 0.48, p < 0.001) and distress tolerance (r = 0.52, p < 0.001). The regression model was significant (F(2, 214) = 65.41, p < 0.001) and explained 38% of the variance in rehabilitation self-efficacy (R² = 0.38). Health consciousness (B = 0.36, β = 0.30, p < 0.001) and distress tolerance (B = 0.43, β = 0.37, p < 0.001) were both significant predictors of rehabilitation self-efficacy. The findings indicate that both health consciousness and distress tolerance significantly predict rehabilitation self-efficacy. These results underscore the importance of integrating psychological resilience and health awareness into rehabilitation programs to enhance patient outcomes. Future research should explore these relationships longitudinally and experimentally, while practitioners should focus on boosting these factors in rehabilitation settings.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Angel Lee (Corresponding Author); Syarifah Maisarah (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







