Exploration of How Health Anxiety and Media Exposure Predict Preventive Health Actions
Keywords:
Health anxiety, Media exposure, Preventive health behaviorAbstract
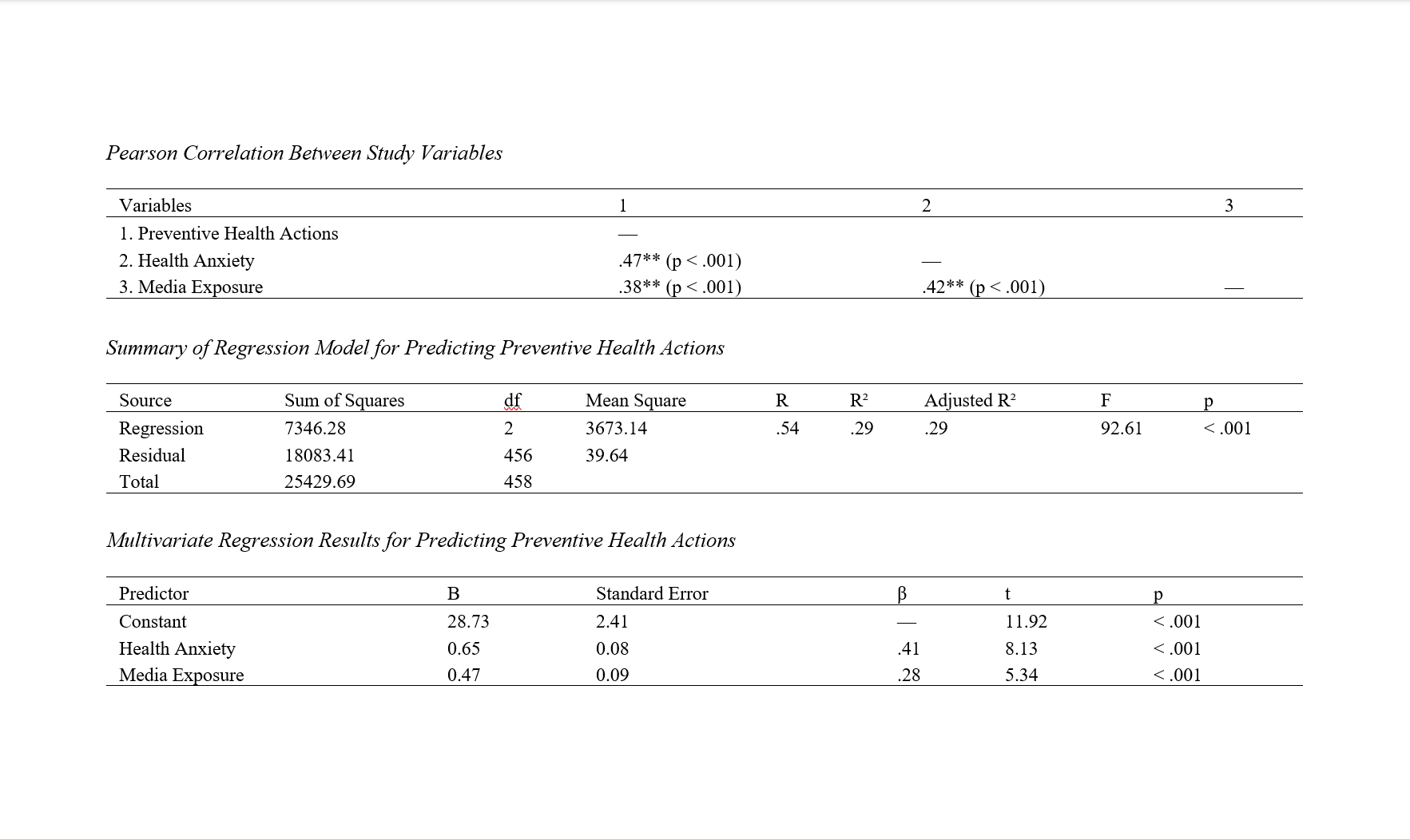
This study aimed to investigate how health anxiety and media exposure predict engagement in preventive health actions during the COVID-19 pandemic. A correlational descriptive design was used with a sample of 459 adult participants from Bulgaria, selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie sample size table. Participants completed standardized self-report questionnaires, including the Preventive Health Behavior Checklist (PHBC), the Short Health Anxiety Inventory (SHAI), and the Media Exposure Scale for Health Information (MESH). Data were collected online and analyzed using SPSS-27. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to assess the relationships between the dependent variable (preventive health actions) and each independent variable (health anxiety and media exposure). Multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the predictive power of the two independent variables on preventive behaviors. Descriptive results indicated high mean scores for preventive health actions (M = 63.27, SD = 8.41), moderate to high health anxiety (M = 38.52, SD = 7.66), and moderate media exposure (M = 29.84, SD = 5.73). Pearson correlations showed significant positive relationships between preventive health actions and both health anxiety (r = .47, p < .001) and media exposure (r = .38, p < .001). Regression analysis revealed that health anxiety (β = .41, p < .001) and media exposure (β = .28, p < .001) were both significant predictors of preventive health actions, jointly accounting for 29% of the variance (R² = .29, F(2, 456) = 92.61, p < .001). The findings highlight the important roles of psychological and informational factors in promoting health-protective behaviors. Both health anxiety and media exposure significantly influence individuals’ engagement in preventive actions, underscoring the need for balanced media messaging and supportive mental health strategies during public health crises.
Downloads
References
Alizade Moghaddam, A., Vaslehchi, T., Azimi Takami, Z., Azimi Takami, F., & Kiani, S. (2024). The Effectiveness of Schema Therapy on Health Anxiety and Health Stubbornness of People Visiting Neurology Clinics. Health Nexus, 2(1), 21-28.
Alrasheed, M. M., Alrasheed, S., & Alqahtani, A. S. (2022). Impact of Social Media Exposure on Risk Perceptions, Mental Health Outcomes, and Preventive Behaviors During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Health Systems Research, 2(3), 107-113. https://doi.org/10.1159/000525209
Brunette, M. F., Erlich, M. D., Edwards, M. L., Adler, D. A., Berlant, J., Dixon, L. B., First, M. B., Oslin, D. W., Siris, S. G., & Talley, R. M. (2023). Addressing the Increasing Mental Health Distress and Mental Illness Among Young Adults in the United States. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 211(12), 961-967. https://doi.org/10.1097/nmd.0000000000001734
Chen, Z.-j., Li, Q., Li, T., Chen, B., Wang, J., & Zhen, R. (2023). Pandemic Exposure and Adolescent Anxiety: Roles of Negative Media Exposure and Negative Coping Styles. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2901425/v1
Dwiyani, T., Kristantiningtyas, D., Apsari, H. L., & Putra, A. S. B. (2024). Board and Director Traits, Company Growth's Impact on Green Accounting Policy Moderated by Media Exposure. International Journal of Economics (Ijec), 3(1), 300-309. https://doi.org/10.55299/ijec.v3i1.769
Feng, Y., & Tong, Q. (2022). Exploring the Mediating Role of Situation Awareness and Crisis Emotions Between Social Media Use and COVID-19 Protective Behaviors: Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.793033
Gu, X., Obrenovic, B., & Wei, F. (2023). Empirical Study on Social Media Exposure and Fear as Drivers of Anxiety and Depression During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability, 15(6), 5312. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065312
Handayani, P. W., Zagatti, G. A., Kéfi, H., & Bressan, S. (2023). Impact of Social Media Usage on Users’ COVID-19 Protective Behavior: Survey Study in Indonesia. Jmir Formative Research, 7, e46661. https://doi.org/10.2196/46661
Hanine, I., Chtibi, M., Bensalah, Y., Belbachir, S., & Ouanass, A. (2022). Social Medias in Increasing Anxiety Around COVID-19 in Morocco. European Psychiatry, 65(S1), S540-S540. https://doi.org/10.1192/j.eurpsy.2022.1381
He, R., He, J., & Zhang, H. (2023). Generational Differences in the Relationship Between Media Exposure and Health Behaviors During COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1039122
Hung, S. C., Yang, S. C., & Luo, Y. F. (2021). New Media Literacy, Health Status, Anxiety, and Preventative Behaviors Related to COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Study in Taiwan. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(21), 11247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111247
Iwanowska, M., Zawadzka, A. M., & Kondratowicz, B. (2023). News Media Exposure and Life Satisfaction in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Moderated Mediation Model of COVID-19 Fear and Worries and Gender. Current Issues in Personality Psychology. https://doi.org/10.5114/cipp/156172
Liu, T., Zhang, S., & Zhang, H. (2022). Exposure to COVID‐19‐related Media Content and Mental Health During the Initial Outbreak of COVID‐19 in China. Scandinavian journal of psychology, 63(4), 283-289. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12805
Mabaso, W. S., Hein, S., Pavarini, G., & Fazel, M. (2024a). Exploring the Relationship Between Public Social Media Accounts, Adolescent Mental Health, and Parental Guidance in England: Large Cross-Sectional School Survey Study. Journal of medical Internet research, 26, e57154. https://doi.org/10.2196/57154
Mabaso, W. S., Hein, S., Pavarini, G., & Fazel, M. (2024b). Exploring the Relationship Between Public Social Media Accounts, Adolescent Mental Health, and Parental Guidance in England: Large Cross-Sectional School Survey Study (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.2196/preprints.57154
Mathkar, M., & Deshpande, S. (2022). Impact of Mass Media on the Mental Health of Individuals During the Covid-19 Pandemic. Ijar, 18-21. https://doi.org/10.36106/ijar/9305846
Mohamed, N. A., Hoda, R. N., & Osman, B. M. (2022). Psychological and Behavioral Responses to COVID-19. International journal of health sciences, 13253-13270. https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6ns1.13732
Mokhtari-Hesari, P., Yarmohammadi, H., Bahabadi, M. R., Maftoon, F., Tavousi, M., Riazi, H., & Montazeri, A. (2021). Exposure to the COVID-19 News on Social Media: Psychological and Self-Reported Behavioural Responses Among Iranian Adults. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-518988/v1
Montazeri, A., Mohammadi, S., Hesari, P. M., Yarmohammadi, H., Bahabadi, M. R., Moghari, F. N., Maftoon, F., Tavousi, M., & Riazi, H. (2023). Exposure to the COVID-19 News on Social Media and Consequent Psychological Distress and Potential Behavioral Change. Scientific reports, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-42459-6
Nakhaei Moghadam, R., Bahrainian, S. A., & Nasri, M. (2024). The effectiveness of intensive and short-term dynamic psychotherapy on attachment styles, somatization and health anxiety in patients with chronic pain. Journal of Assessment and Research in Applied Counseling (JARAC), 6(1). https://journals.kmanpub.com/index.php/jarac/article/view/1287
Neill, R. D., Blair, C., Best, P., McGlinchey, E., & Armour, C. (2021). Media Consumption and Mental Health During COVID-19 Lockdown: A UK Cross-Sectional Study Across England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Journal of Public Health, 31(3), 435-443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01506-0
Obrenovic, B., Godinić, D., Du, G., Khudaykulov, A., & Gan, H. (2024). Identity Disturbance in the Digital Era During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Adverse Effects of Social Media and Job Stress. Behavioral Sciences, 14(8), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14080648
Priyana, Y. (2023). The Effect of Social Media Use and Environment on Mental Health Among Young People in Sukabumi. West Science Interdisciplinary Studies, 1(03), 27-33. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsis.v1i03.52
Riaz, M., Wu, J., Sherani, M., Ali, S., Boamah, F. A., & Zhu, Y. (2023). An Empirical Evaluation of the Predictors and Consequences of Social Media Health-Misinformation Seeking Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Internet Research, 33(5), 1871-1906. https://doi.org/10.1108/intr-04-2022-0247
Sarfika, R., Saifudin, I. M. M. Y., Malini, H., Putri, D. E., Wicaksana, A. L., Mahathir, M., & Novrianda, D. (2023). Factors Associated With Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms Among Indonesian Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare in Low-resource Settings. https://doi.org/10.4081/hls.2023.11931
Segun-Martins, I. O. (2022). The Predictive Roles of Perceived Emotional Self-Awareness and Self-Monitoring Competence on Preventive Health Behaviour among Psychology Interns in Psychiatric Hospital in Ondo State, South-West, Nigeria. Clinical Psychology and Mental Health Care, 4(2). https://aditum.org/images/currentissue/1657607427Clinical_Psychology_and_Mental_Health_Care.pdf
Shi, C., Du, X., Chen, W., & Ren, Z. (2024). Predictive Roles of Cognitive Biases in Health Anxiety: A Machine Learning Approach. Stress and Health, 40(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.3463
Soroya, S. H., Rehman, A. U., & Faiola, A. (2023). Exploring the Impact of Internet and Media Sources Exposure On self-Care Behavior: Mediating the Role of Health Anxiety, Literacy and Information-Seeking Behavior. Kybernetes, 53(11), 4797-4817. https://doi.org/10.1108/k-06-2023-1003
Suanrueang, P., Suen, M. W., Lin, H. F., Er, T. K., & Jamora, M. M. Q. (2022). The Impact of the Covid-19 Pandemic on Anxiety, Health Literacy, and eHealth Literacy in 2020 Related to Healthcare Behavior in Thailand. Journal of Public Health and Development, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.55131/jphd/2022/200115
Weigle, P. (2024). Introduction to the Section on Digital Media and Mental Health. 117-120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-69362-5_16
Yang, Q., Wu, Z., Xie, Y., Xiao, X., Wu, J., Sang, T., Zhang, K., Song, H., Wu, X., & Xu, X. (2021). The Impact of Health Education Videos on General Public’s Mental Health and Behavior During COVID-19. Global Health Research and Policy, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-021-00211-5
Yue, Y. (2024). Exploring Role of Physical Activity and Emotional Exhaustion to Improve Preventive Health Behavior Among Students of Chinese Colleges. American Journal of Health Behavior, 48(6), 1692-1701. https://doi.org/10.5993/ajhb.48.6.20
Zhou, L., Ju, P., Li, Y., Liu, B., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., & Yin, H. (2023). Preventive health behaviors among the middle-aged and elderly in China: Does social capital matter? Preventive Medicine Reports, 35, 102329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2023.102329
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







