Examining the Structural Relationships among Components of Strategic Thinking and Their Consequences for Creating Competitive Advantage in Primary Schools (Modeling Using a Mixed-Methods Approach)
Keywords:
Strategic thinking, principals, competitive advantage, and educationAbstract
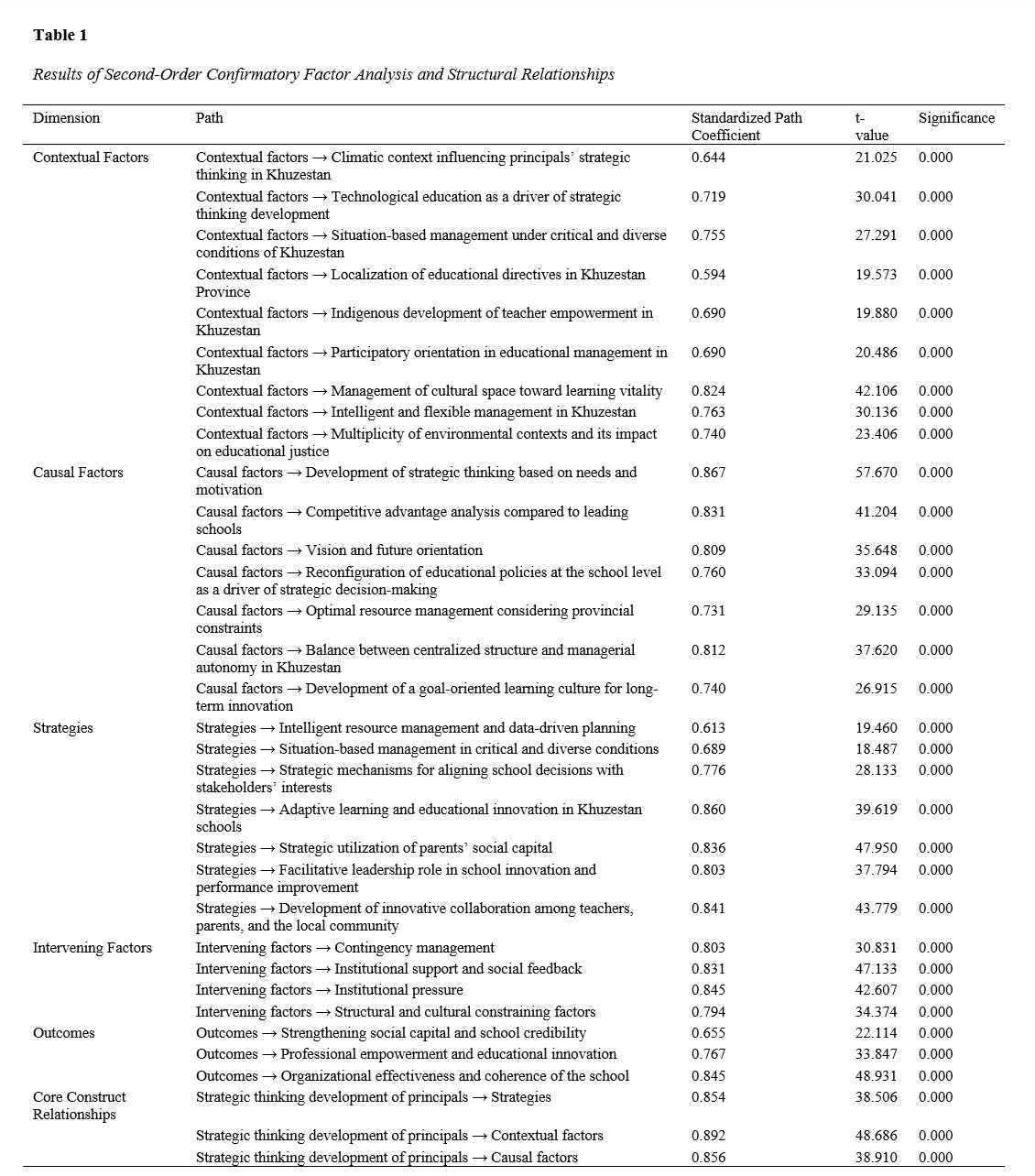
The present study was applied–developmental in terms of purpose and quantitative in terms of implementation. The statistical population consisted of all principals of primary schools under the Department of Education in Khuzestan Province. From a population of 1,688 individuals, approximately 322 participants were selected using cluster and random sampling methods. The research instrument was a researcher-developed questionnaire on principals’ strategic thinking with a competitive advantage approach in education. Data analysis methods included a one-sample t-test using SPSS software, as well as confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling (SEM). The results showed that the causal factors influencing the development of strategic thinking among primary school principals with a competitive advantage approach in the education system of Khuzestan Province include the development of strategic thinking based on needs and motivation, analysis of competitive advantage in comparison with leading schools, vision and future orientation, and the reconfiguration of educational policies at the school level. Contextual factors include the climatic context affecting the strategic thinking of principals in Khuzestan Province, technological education as a facilitator of strategic thinking growth, situation-based management under the critical and diverse conditions of Khuzestan, and the localization of educational directives in the province. Intervening factors include “institutional and organizational support” from education authorities and the extent of “structural pressures and administrative bureaucracy,” which constitute the most significant interventions. The strategies identified in this study include “intelligent resource management,” “adaptive learning and educational innovation,” and “localization of communicated strategies.” Successful principals, by leveraging “parents’ social capital” and performing the role of a “facilitative leader,” achieve outcomes that include “strengthening social capital and school branding” as the first major result, leading to increased trust among families. At the internal level, this approach results in “professional empowerment of teachers” and “innovation in teaching methods.” Ultimately, “enhancement of organizational effectiveness” and the multidimensional development of students in a joyful and dynamic environment represent the most significant outcomes, stabilizing the school’s position within the educational system of Khuzestan Province.
Downloads