Comparison of the Effectiveness of Brain Gym and Educational Games on the Improvement of Social Skills in 8-10 Year-Old Students
Keywords:
Brain Gym, educational games, social skills, studentsAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to compare the effectiveness of Brain Gym and educational games on improving the social skills of 8-10 year-old students with a two-month follow-up study.
Methods and Materials: The present study was a quasi-experimental research with a pre-test, post-test, and two-month follow-up design, including a control group and two experimental groups. The research population consisted of all 8-10 year-old female students in Ahvaz, among whom 120 were selected as the research sample. Nine students were excluded from the study due to irregular attendance at the educational sessions. In this study, the Matson Social Skills Questionnaire was used to assess social skills at three time points: before the intervention, after the intervention, and during the two-month follow-up. The Brain Gym group underwent 20 sessions, with sessions held twice a week for 20 minutes each. The educational games group participated in an 8-week program, with sessions held twice a week for 30-45 minutes each. The control group did not receive any intervention.
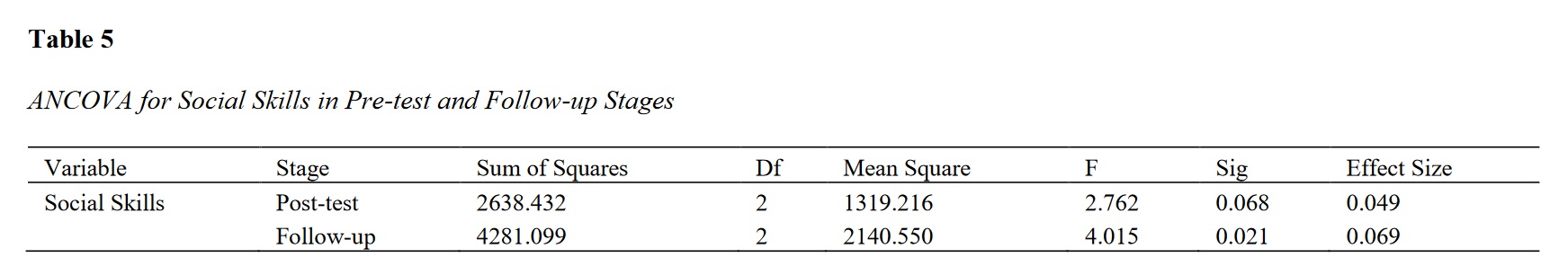
Findings: The results of the Bonferroni post-hoc test showed no significant difference between the effects of Brain Gym and educational games on improving the social skills of 8-10 year-old students (p > 0.05). However, there was a significant difference between the post-test scores and the pre-test scores for each intervention (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Overall, the results of this study indicate that interventions involving Brain Gym and educational games can be beneficial methods for improving the social skills of elementary school students.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Bahareh Rostaminejad (Author); Negar Arazeshi (Corresponding Author); Keyvan Molanorouzi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.


































