Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Various Play Therapy Types on Behavioral Symptoms of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Keywords:
play therapy, behavioral symptoms, Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderAbstract
Objective: The purpose of the present study was to conduct a meta-analysis on the effectiveness of various types of play therapy on the behavioral symptoms of children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
Methods and Materials: A meta-analysis method was employed based on the nature of the study. The statistical population consisted of articles and research conducted in this area. ADHD, behavioral symptoms, and play therapy were searched in various databases. The sampling method from this population was theoretical sampling. To search for Iranian research, only Persian sources and studies conducted in Iran were considered. These studies were published in scientific-research journals over the past decade (2011–2021) and examined various forms of play therapy on the behavioral symptoms of children with ADHD. They had an appropriate sample size and met methodological requirements (including hypothesis formulation, research design, statistical population, sample size and sampling method, measurement tools, statistical hypotheses, statistical analysis methods, and the correctness of statistical computations). A subset of the population under review was selected using a predetermined method. The statistical population in the second phase of the study, focusing on internal validation, included all specialists and experts in child play therapy for ADHD. The sample size in this section consisted of 8 specialists, selected through purposive sampling. A content analysis checklist was used in this study.
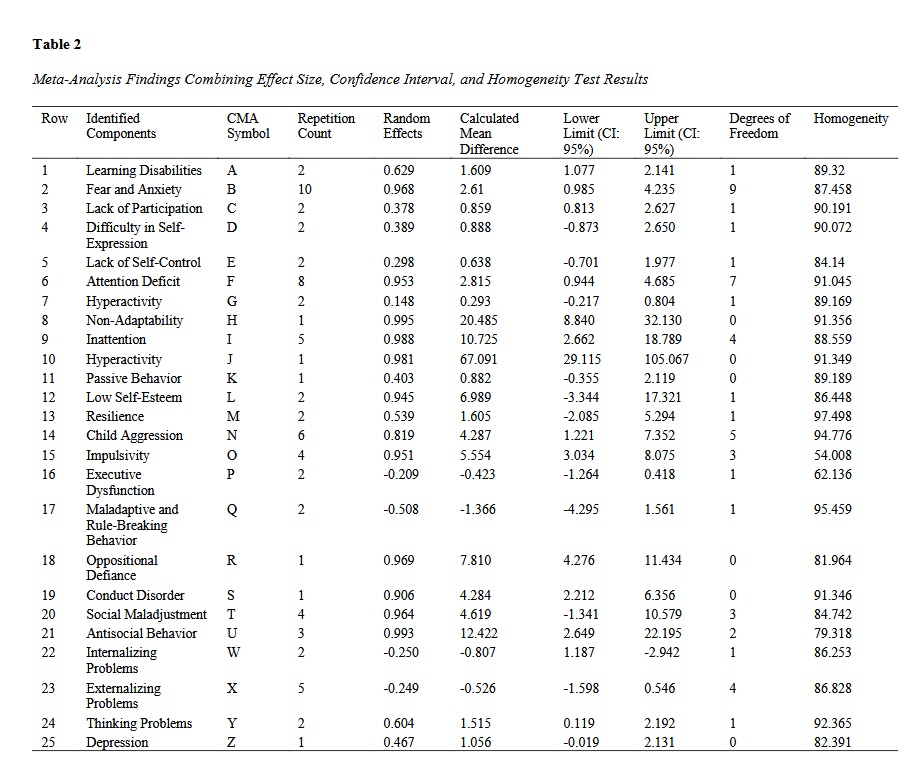
Findings: Results indicated that in the causal relationship between play therapy and children's behavioral symptoms, all effect sizes extracted were ranked based on Cohen's index, and to confirm significance, the statistical values p-value and t-value were reported. For all components, these indices were less than 0.05 (P < 0.05) and greater than 1.96, respectively.
Conclusion: Therefore, this therapeutic program can be utilized to reduce behavioral problems in these children.
Downloads
References
Akbari, B., & Rahmati, F. (2015). The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Play Therapy in Reducing Aggression in Preschool Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Child Psychological Development Quarterly, 2(2), 93-100. https://childmentalhealth.ir/article-1-53-en.html
Amiri Morchgani, F., & Lahrabi, B. (2020). Examining the Effect of Short-Term Structured Play Therapy on Reducing Symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Behavioral Disorders in Students with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. New Approaches in Educational Sciences Quarterly, 2(1), 96-108. https://journal.iocv.ir/article_106857.html?lang=en
Amouzadeh, F., Hassanvand, S., Hashemian, K., & Hemayat Talab, R. (2016). Comparison of the Effect of Play Therapy and Medication on the Development of Motor Skills and Attention Span in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Motor Behavior, 8(23), 97-110. https://mbj.ssrc.ac.ir/article_660.html?lang=en
Asghari Nekah, S. M., & Abedi, Z. (2014). Investigating the Effectiveness of Play Therapy Based on Executive Functions in Improving Response Inhibition, Planning, and Working Memory of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Cognitive Psychology Quarterly, 2(1), 41-51. https://jcp.khu.ac.ir/article-1-2005-en.html
Ashouri, M., & Abedi, A. (2020). Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Play Therapy-Based Interventions on Adaptive Behavior in Children with Intellectual Disabilities. Child Mental Health Quarterly, 7(1), 91-105. https://doi.org/10.29252/jcmh.7.1.9
Ashouri, M., & Dalalzadeh Beigi, F. (2018). The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Model-Based Play Therapy on Behavioral Problems and Social Skills in Preschool Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Rehabilitation Quarterly, 19(2), 103-115. https://doi.org/10.32598/rj.19.2.102
Ashouri, M., Ghasemzadeh, S., & Dalalzadeh, F. (2019). The Impact of Cognitive-Behavioral Model-Based Play Therapy on Social Skills in Preschool Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Child Mental Health Quarterly, 6(2), 28-39. https://doi.org/10.29252/jcmh.6.2.4
Cartabia, M., Finazzi, S., & Bonati, M. (2023). Differences between centers in functional outcome of patients with ADHD after 1 year from the time of diagnosis. Scientific reports, 13(1), 18738. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-48487-6
Cochran, N. H., Nordling, W. J., & Cochran, J. L. (2022). Child-Centered Play Therapy: A Practical Guide to Therapeutic Relationships with Children. Taylor & Francis. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003260431
Delavar, A., Ganji, K., & Taghavi, S. (2015). Analysis of Studies on the Effectiveness of Non-Medication Therapies in Reducing Symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Educational Measurement, 19, 67-98. http://ensani.ir/fa/article/353574/%D9%81%D8%B1%D8%A7%D8%AA%D8%AD%D9%84%DB%8C%D9%84-%D9%85%D8%B7%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%AB%DB%8C%D8%B1-%D8%AF%D8%B1%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86-%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D8%BA%DB%8C%D8%B1%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%88%DB%8C%DB%8C-%D8%A8%D8%B1-%DA%A9%D8%A7%D9%87%D8%B4-%D9%86%D8%B4%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%87-%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%84-%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3%D8%A7%DB%8C%DB%8C-%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%AC%D9%87-%D8%A8%DB%8C%D8%B4-%D9%81%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84
Fabiano, G. A., Pelham, W. E., Gangy, E. M., Burrows-MacLean, L., Coles, E. K., & Chaco, A. (2009). The single and combined effects of multiple intensities of behavior modification and methylphenidate for children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in a classroom setting. School Psychology Review, 36, 195-216. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.2007.12087940
Fabiano, G. A., Schatz, N. K., Aloe, A. M., Chacko, A., & Chronis-Tuscano, A. (2015). A systematic review of meta-analyses of psychosocial treatment for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 18(1), 77-97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-015-0178-6
Fabiano, G. A., Schatz, N. K., Aloe, A. M., Pelham Jr, W. E., Smyth, A. C., Zhao, X., & Coxe, S. (2021). Comprehensive meta-analysis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder psychosocial treatments investigated within between group studies. Review of Educational Research, 91(5), 718-760. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543211025092
Feizollahi, J., Rezaei, F., & Sadeghi, M. (2019). A Study on the Effect of Cognitive-Behavioral Play Therapy Combined with Parent Management Training on Symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children Aged 7-11 with ADHD. Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences Journal, 19(2), 155-172. https://doi.org/10.29252/jrums.19.2.155
Ganji, K., Zabihi, R., & Taghavi, S. (2015). Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Play Therapy on Behavioral Disorders in Children. Behavioral Sciences, 9(2), 111-120. https://www.behavsci.ir/article_67911.html
Geurts, D. E., Schellekens, M. P., Janssen, L., & Speckens, A. E. (2021). Mechanisms of change in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy in adults with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 25(9), 1331-1342. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054719896865
Glenn, M. (2024). Childhood ADHD: Treated vs. Untreated—Treatments, Implications, & Outcomes. https://digitalcommons.csp.edu/human-services_masters/6/
Haugan, A. L. J., Sund, A. M., Young, S., Thomsen, P. H., Lydersen, S., & Nøvik, T. S. (2022). Cognitive behavioural group therapy as addition to psychoeducation and pharmacological treatment for adolescents with ADHD symptoms and related impairments: a randomised controlled trial. BMC psychiatry, 22(1), 375. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-022-04019-6
Heydarian, M., Mirzaei, M., Shah Owisi, S., & Akbari, M. (2021). The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Model-Based Play Therapy on Behavioral Problems, Responsibility, and Self-Esteem of Male Students with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Early Childhood Health and Education Quarterly, 2(3), 124-143. https://jeche.ir/article-1-54-en.html
Horton, E., Romito, M., Frawley, C., & Schoonover, T. J. (2024). A size-inclusive playroom: Play therapy considerations to promote healing for children of diverse body shapes and sizes. International Journal of Play Therapy, 33(3), 154. https://doi.org/10.1037/pla0000218
Jensen, S. A., Biesen, J. N., & Graham, E. R. (2017). A meta-analytic review of play therapy with emphasis on outcome measures. Professional psychology: Research and practice, 48(5), 390. https://doi.org/10.1037/pro0000148
Lambert, S. F., LeBlanc, M., Mullen, J. A., Ray, D., Baggerly, J., White, J., & Kaplan, D. (2007). Learning more about those who play in session: The national play therapy in counseling practices project (Phase I). Journal of Counseling & Development, 85(1), 42-46. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2007.tb00442.x
Najafi, M., & Sarpoolaki, B. (2016). The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Play Therapy on Aggression and Behavioral Disorders in Elementary School Children. Exceptional Individuals Quarterly, 6(21), 103-121. https://jpe.atu.ac.ir/article_5283.html?lang=en
Nimmo-Smith, V., Merwood, A., Hank, D., Brandling, J., Greenwood, R., Skinner, L., & Rai, D. (2020). Non-pharmacological interventions for adult ADHD: a systematic review. Psychological medicine, 50(4), 529-541. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291720000069
Nursanaa, W. O., & Ady, I. N. C. (2020). Play therapy for children with anxiety disorders. 5th ASEAN Conference on Psychology, Counselling, and Humanities (ACPCH 2019),
Obiweluozo, P. E., Ede, M. O., Onwurah, C. N., Uzodinma, U. E., Dike, I. C., & Ejiofor, J. N. (2021). Impact of cognitive behavioural play therapy on social anxiety among school children with stuttering deficit: a cluster randomised trial with three months follow-up. Medicine, 100(19). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000024350
Post, P. B., Phipps, C. B., Camp, A. C., & Grybush, A. L. (2019). Effectiveness of child-centered play therapy among marginalized children. International Journal of Play Therapy, 28(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.1037/pla0000096
Pyle, K., & Fabiano, G. A. (2017). Daily report card intervention and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis of single-case studies. Exceptional Children, 83(4), 378-395. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402917706370
Robinson, A., Simpson, C., & Hott, B. L. (2017). The effects of child-centered play therapy on the behavioral performance of three first grade students with ADHD. International Journal of Play Therapy, 26(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.1037/pla0000047
Roozeh, F., & Ahmadi, A. (2015). Types of Play and Play Therapy in Psychology.International Conference on Humanities, Psychology, and Social Sciences
Sabet, M., Hashemi, N., & Jafari, F. (2020). The Effectiveness of Group Play Therapy in Reducing Behavioral Disorders and Aggression in Preschool Children with Hyperactivity Disorders. Journal of Advances in Modern Psychology, 30(3), 46-62. http://ensani.ir/fa/article/442092/%D8%A7%D8%AB%D8%B1%D8%A8%D8%AE%D8%B4%DB%8C-%D8%A8%D8%A7%D8%B2%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D8%B1%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86%DB%8C-%DA%AF%D8%B1%D9%88%D9%87%DB%8C-%D8%A8%D8%B1-%DA%A9%D8%A7%D9%87%D8%B4-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%B1%D9%81%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%B1%DB%8C-%D9%88-%D9%BE%D8%B1%D8%AE%D8%A7%D8%B4%DA%AF%D8%B1%DB%8C-%DA%A9%D9%88%D8%AF%DA%A9%D8%A7%D9%86-%D9%BE%DB%8C%D8%B4-%D8%AF%D8%A8%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%86%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%A8%DB%8C%D8%B4-%D9%81%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%DB%8C
Sibley, M. H., Graziano, P. A., Coxe, S. J., Bickman, L., Martin, P., & Flores, S. (2023). A Randomized Community-Based Trial of Behavior Therapy vs. Usual Care for Adolescent ADHD: Secondary Outcomes and Effects on Comorbidity. Behavior therapy, 54(5), 839-851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beth.2023.03.001
Veronesi, G. F., Gabellone, A., Tomlinson, A., Solmi, M., Correll, C. U., & Cortese, S. (2024). Treatments in the pipeline for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105774
Wong, T. Y., Chang, Y. T., Wang, M. Y., & Chang, Y. H. (2023). The effectiveness of child-centered play therapy for executive functions in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 28(3), 877-894. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591045221128399
Wu, C., Wu, D., Fang, Y., & Song, H. (2024). Efficacy of Integrated Neurofeedback and Virtual Reality Training in Children with ADHD: A Randomized Controlled Trial. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379892579_Efficacy_of_Integrated_Neurofeedback_and_Virtual_Reality_Training_in_Children_with_ADHD_A_Randomized_Controlled_Trial
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Azam Baktashian (Author); Mansure Shahriari (Corresponding Author); Masoud Ghasemi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














