Predictors of Self-Care Behavior: The Roles of Type D Personality and Locus of Control in Adults
Keywords:
Type D personality, locus of control, self-care behaviors, chronic health conditions, psychological factorsAbstract
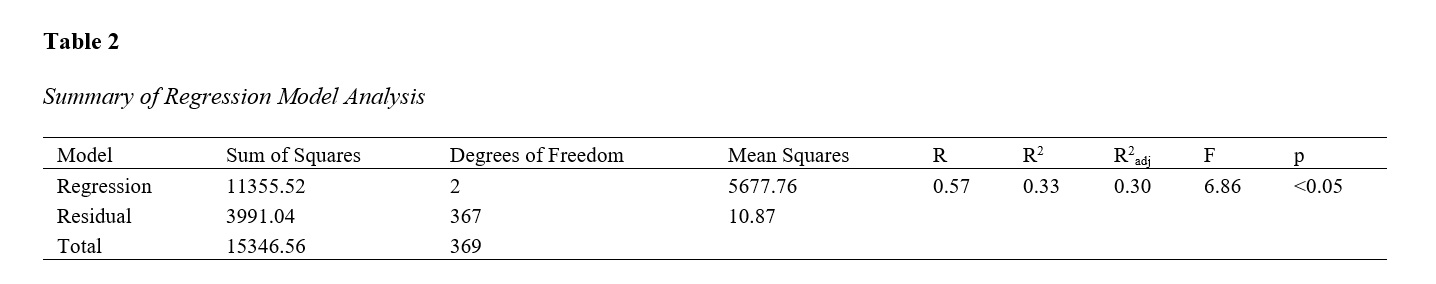
This study aimed to examine the predictive role of Type D personality and locus of control on self-care behaviors among adults, particularly those managing chronic health conditions. Utilizing a cross-sectional design, data were collected from 370 participants through standardized instruments measuring Type D personality, locus of control, and self-care behaviors. Linear regression analysis was performed using SPSS-27 to assess the predictive relationships between the variables. The results indicated that both Type D personality and locus of control significantly predict self-care behaviors, accounting for 33% of the variance in self-care engagement. Specifically, Type D personality and an external locus of control were associated with poorer self-care practices. The study underscores the significant influence of psychological factors on self-care behaviors. Tailored interventions that consider individuals' psychological profiles may enhance self-care practices, particularly among those with chronic health conditions.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Shokouh Navabinejad (Author); Mehdi Rostami (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






