The Impact of Dialectical Behavior Therapy in Reducing Emotional Exhaustion and Enhancing Empathy
Keywords:
Dialectical Behavior Therapy, Emotional Exhaustion, Empathy, Randomized Controlled Trial, Psychological Resilience, Burnout, Mindfulness, Emotional RegulationAbstract
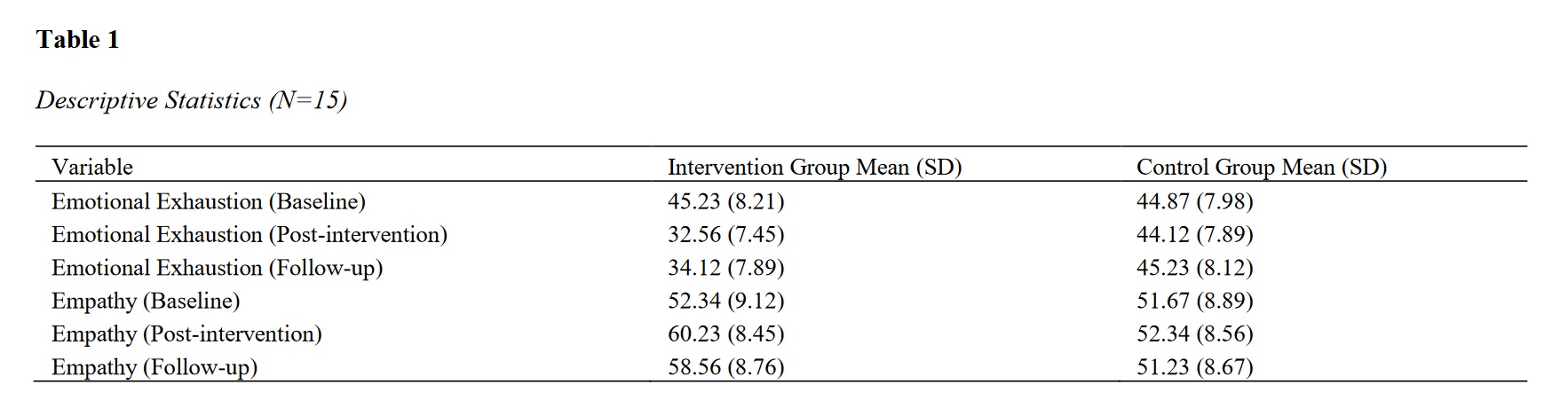
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) in reducing emotional exhaustion and enhancing empathy among participants. This randomized controlled trial included 30 participants, randomly assigned to either the DBT intervention group or a control group, with 15 participants in each group. The intervention group underwent eight 75-minute DBT sessions over three months, while the control group received no intervention. Emotional exhaustion and empathy were measured at baseline, post-intervention, and at a three-month follow-up using the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI) and the Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI), respectively. Data analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measurements and the Bonferroni post-hoc test, with statistical analyses performed using SPSS-27. The intervention group showed a significant reduction in emotional exhaustion from a baseline mean of 45.23 (SD = 8.21) to 32.56 (SD = 7.45) post-intervention and 34.12 (SD = 7.89) at follow-up. In contrast, the control group's emotional exhaustion remained relatively stable (baseline: 44.87, SD = 7.98; post-intervention: 44.12, SD = 7.89; follow-up: 45.23, SD = 8.12). Empathy scores in the intervention group increased significantly from 52.34 (SD = 9.12) at baseline to 60.23 (SD = 8.45) post-intervention, with a slight decrease to 58.56 (SD = 8.76) at follow-up. The control group showed minimal changes in empathy (baseline: 51.67, SD = 8.89; post-intervention: 52.34, SD = 8.56; follow-up: 51.23, SD = 8.67). ANOVA results confirmed the significance of these changes (F = 31.15, p < 0.001), with Bonferroni post-hoc tests indicating significant differences between baseline and subsequent time points in the intervention group (p < 0.001). The study demonstrates that DBT is significantly effective in reducing emotional exhaustion and enhancing empathy among participants. These findings suggest that DBT can be a valuable intervention for improving psychological resilience and interpersonal effectiveness, particularly in populations at risk for burnout and empathic distress.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Farzaneh Mardani (Corresponding Author); Nancy Parra Vázquez, Seyed Milad Saadati (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






