Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Various Play Therapies on Aggression in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Keywords:
Play therapy, aggression, Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity DisorderAbstract
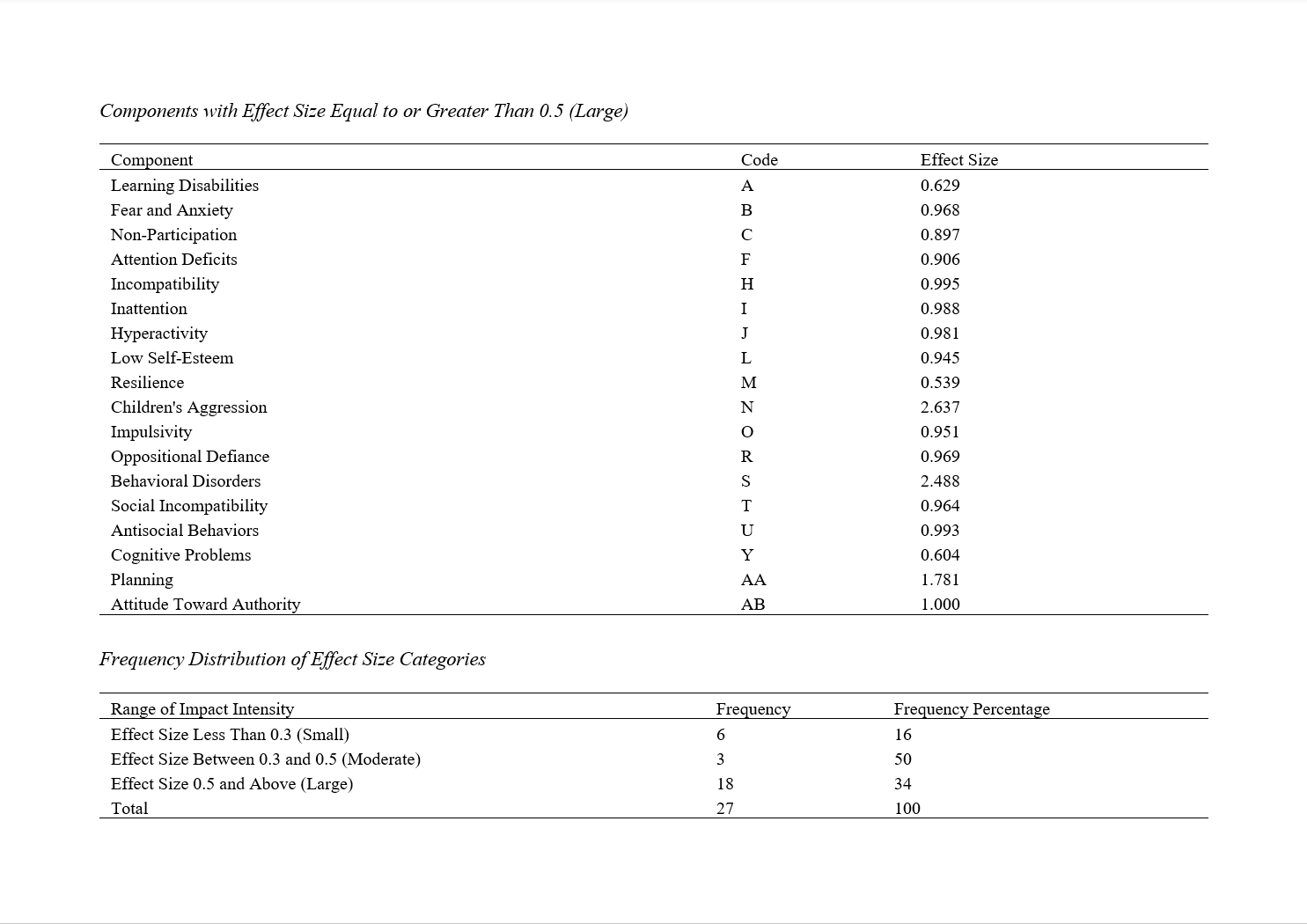
The aim of this study was to conduct a meta-analysis on the effectiveness of various play therapies on aggression in children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). This research utilized a meta-analytic method due to the nature of the study. The research population consisted of articles and studies conducted in this field. Keywords such as "Attention Deficit Disorder," "Hyperactivity," "Aggression," "Behavioral Symptoms," and "Play Therapy" were searched in various databases. A theoretical sampling method was used for selecting the studies. To search for Iranian research, only Persian sources and studies conducted in Iran were considered. These studies, published in scientific-research journals in the last ten years (2012–2022), focused on different types of play therapy for aggression in children with ADHD. The selected studies had appropriate sample sizes and met methodological criteria (such as hypothesis formulation, research method, sample population, sample size, sampling method, measurement tools, statistical hypotheses, statistical analysis method, and correct statistical calculations). The sample was a subset of the population that was chosen based on a pre-determined method. In the second phase of the research, for internal validation, the population included all specialists and experts in the field of play therapy for children with ADHD. The sample size in this phase consisted of four experts, and the sampling method was purposive. A content analysis checklist was used in this research. The results indicated that regarding the causal impact of play therapy on aggression in children, all effect sizes were extracted, ranked based on Cohen's index, and to confirm significance, two statistical significance indicators, p-value and t-value, were reported. For all these components, both indicators showed values below 0.05 (p < 0.05) and above 1.96, indicating statistical significance. Therefore, this therapeutic program can be used to reduce aggression in these children.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Azam Baktashian (Author); Mansure Shahriari (Corresponding Author); Masoud Ghasemi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







