Development of a Healthy Lifestyle Promotion Protocol for Individuals with Binge Eating
Keywords:
Binge eating, Healthy lifestyle, Protocol development, Lifestyle promotion, Eating behavior regulationAbstract
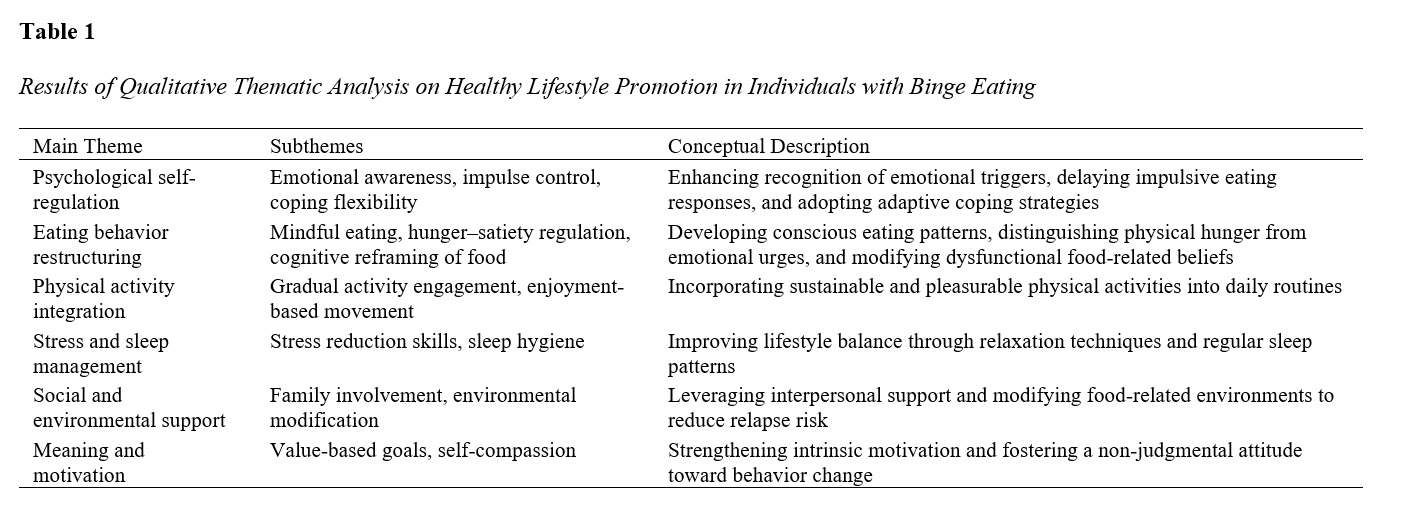
The objective of this study was to develop and validate a comprehensive, evidence-based protocol for promoting a healthy lifestyle among individuals with binge eating, grounded in empirical data and aligned with contemporary behavioral and psychological models. This applied mixed-methods study followed a sequential exploratory design. In the qualitative phase, semi-structured interviews were conducted with adults with binge eating from Tehran using purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was achieved, and data were analyzed through thematic analysis. In the quantitative phase, the extracted components were examined in a larger sample to assess content validity and internal consistency, and the finalized protocol was structured into a session-based intervention model. Thematic analysis yielded six core domains of healthy lifestyle promotion: psychological self-regulation, eating behavior restructuring, physical activity integration, stress and sleep management, social and environmental support, and meaning and motivation. Content validity indices and ratios exceeded acceptable thresholds for all components, and reliability analysis demonstrated strong internal consistency, with high Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for individual domains and excellent overall protocol reliability. The findings support the conceptualization of binge eating as a multidimensional lifestyle-related condition and indicate that the developed protocol is theoretically coherent, empirically grounded, and psychometrically sound. The protocol provides a structured yet flexible framework that integrates emotional, behavioral, and lifestyle components, offering a promising approach for promoting sustainable healthy lifestyle change among individuals with binge eating.
Downloads
References
Abalorio, B., & Turner, S. (2025). Mindfulness and Health Behavior Change: Insights from Individuals Managing Hypertension. KMAN Counseling & Psychology Nexus, 3, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.hp.psynexus.3.15
Akdeniz Kudubes, A., Ayar, D., Bektas, İ., & Bektas, M. (2022). Predicting the effect of healthy lifestyle belief on attitude toward nutrition, exercise, physical activity, and weight-related self-efficacy in Turkish adolescents. Archives de Pédiatrie, 29(1), 44-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcped.2021.11.001
Arend, I., & Yuen, K. S. (2025). Association Between Healthy Neuroticism and Eating Behavior as Revealed by the NKI Rockland Sample. Scientific reports, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-85750-4
Atanda-Ogunleye, O., Hua, S., Borsarini, B., Duck, S. A., Jansen, E., & Carnell, S. (2025). The Impact of COVID-19-Related Stress on Diet and Eating Behaviors in US College Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6196663/v1
Ayunin, E. N., Mustakim, M., & Arumsari, I. (2024). Adolescents’ Unhealthy Eating Behavior and Customer Engagement on Social Media in Sub Urban Areas. Amerta Nutrition, 8(4), 549-556. https://doi.org/10.20473/amnt.v8i4.2024.549-556
Bulut, S., Rostami, M., Hajji, J., Boltivets, S., Saadati, N., Yang, J., McDonnell, M., Chikwe, C., & William, E. (2024). Psychological and Social Factors Influencing Eating Behaviors in College Athletes. Hn, 2(1), 99-105. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.hn.2.1.11
Carraça, E. V. (2024). A Healthier Movement Behavior Profile Is Associated With Body‐congruent Food Choices Through Self‐determined Motivations to Exercise and Regulate Eating. European Journal of Sport Science, 24(3), 352-363. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsc.12092
George, B., & Ravola, M. (2024). Fighting Fire With Fire: Reclaiming Social Media to Promote Healthy Eating Behaviors Among Children. Hem, 5(3), 40-52. https://doi.org/10.61093/hem.2024.3-03
Gidugu, V., & Jacobs, M. L. (2019). Empowering individuals with mental illness to develop healthy eating h abits through mindful eating: results of a program evaluation. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 24(2), 177-186. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2018.1516295
Irandoust, K., Parsakia, K., Estifa, A., Zoormand, G., Knechtle, B., Rosemann, T., Weiss, K., & Taheri, M. (2024). Predicting and comparing the long-term impact of lifestyle interventions on individuals with eating disorders in active population: a machine learning evaluation [Original Research]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1390751
Kibayashi, E. (2022). Association of Self-Esteem With Dietary and Lifestyle Habit Self-Efficacy, Stage of Eating Behavior Change, and Dietary Intake in High School Students. The Japanese Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics, 80(1), 21-31. https://doi.org/10.5264/eiyogakuzashi.80.21
Mazzeo, S. E., Weinstock, M., Vashro, T. N., Henning, T., & Derrigo, K. (2024). Mitigating harms of social media for adolescent body image and eating disorders: a review. Psychology research and behavior management, 2587-2601. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S410600
Mortaz Hajri, A., & Mashhadi, A. (2016). The Effectiveness of Emotion-Focused Group Therapy on Depression in Women with Eating Disorders. The Third International Conference on Psychology, Educational Sciences and Lifestyle,
Nishitani, N., Sakakibara, H., & Akiyama, I. (2009). Eating behavior related to obesity and job stress in male Japanese workers. Nutrition, 25(1), 45-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2008.07.008
Patil, A., Salimath, G., & Angolkar, M. (2024). Impact of Social Media Influence on Eating Behavior in Mid and Late Adolescent Children a Cross-Sectional Study. Indian Journal of Health Sciences and Biomedical Research (Kleu), 17(2), 125-130. https://doi.org/10.4103/kleuhsj.kleuhsj_551_23
Rahmani, M., Omidi, A., & Rahmani, F. (2018). The Effect of Unified Therapy on Quality of Life in Patients with Eating Disorder. International Journal of Body, Mind and Culture, 5(1), 39-45. https://doi.org/10.22122/ijbmc.v5i1.115
Rejeski, W. J., Mihalko, S. L., Ambrosius, W. T., Bearon, L. B., & McClelland, J. W. (2011). Weight Loss and Self-Regulatory Eating Efficacy in Older Adults: The Cooperative Lifestyle Intervention Program. The Journals of Gerontology Series B, 66B(3), 279-286. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbq104
Şentürk, G. (2025). The Relationship Between Perceived Stress, Body Image and Eating Behaviors in Athletes. Research in Sport Education and Sciences, 27(2), 77-87. https://doi.org/10.62425/rses.1521040
Vakili, M., Bagherzadeh Golmakani, Z., & Bolghan-Abadi, M. (2024). Comparing the effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy with acceptance and commitment therapy on psychological coherence in binge eating patients. medical journal of mashhad university of medical sciences, 67(2), 556-570. https://mjms.mums.ac.ir/article_24678.html