Effectiveness of Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on Perceived Stress and Alexithymia in Single Women
Keywords:
Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, perceived stress, alexithymia.Abstract
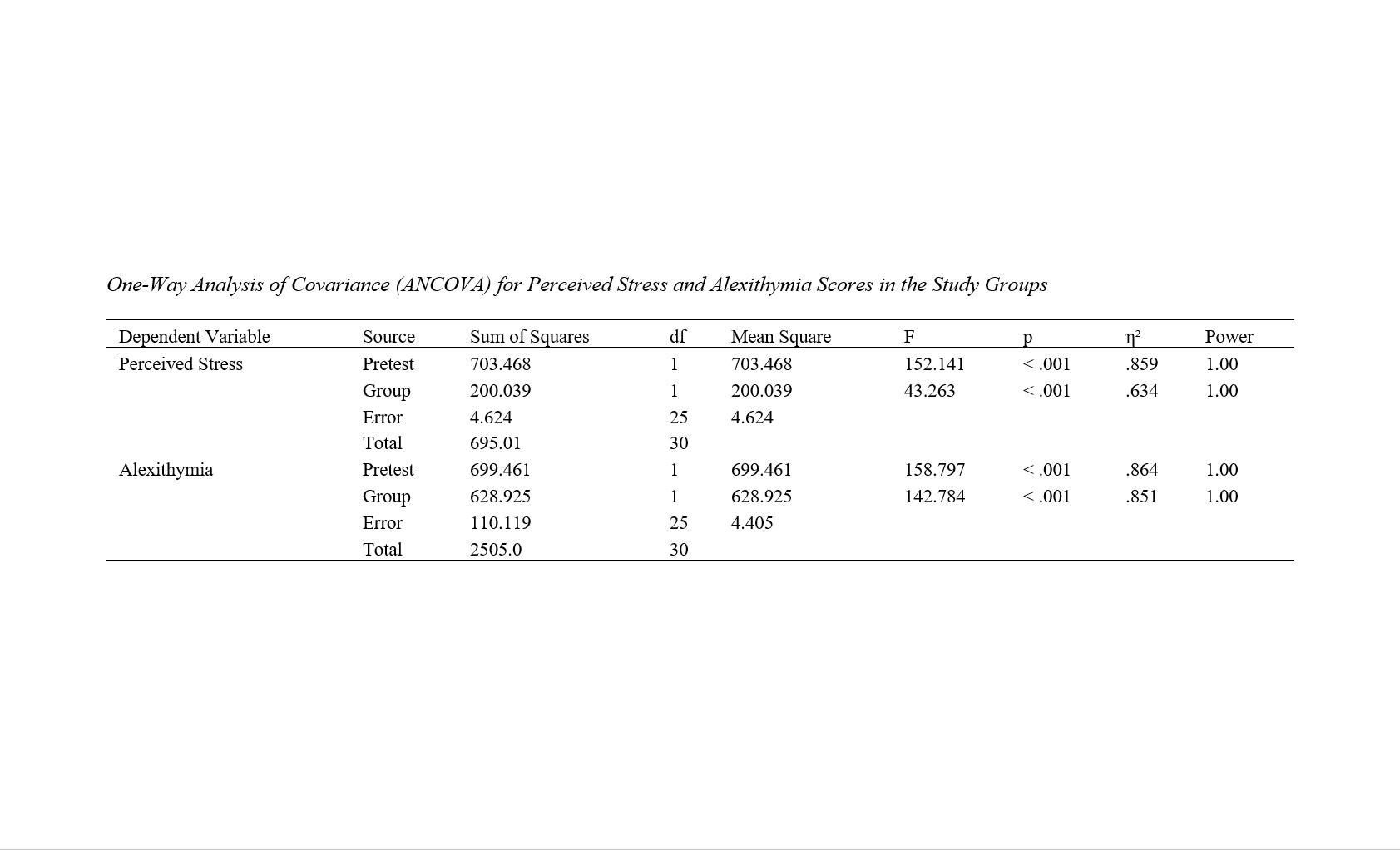
The aim of the present study was to determine the effectiveness of Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) on perceived stress and alexithymia. This study employed a quasi-experimental design with a pretest–posttest control group. Questionnaire administration was conducted in person. The statistical population of this study included all undergraduate female psychology students enrolled in the 2022 academic year at Islamic Azad University, Khomeini Shahr Branch. Sampling in this study was conducted using convenience sampling, and 30 undergraduate female psychology students from Islamic Azad University, Khomeini Shahr Branch, were selected. From this group of 30 participants, 15 were randomly assigned to the experimental group and 15 to the control group. The data were collected using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS; Cohen et al., 1983) and the Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20; Bagby et al., 1994). The results indicated that Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy had a statistically significant effect on perceived stress and alexithymia. In addition, Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy had a statistically significant effect on the subscales of alexithymia, including difficulty identifying feelings, difficulty describing feelings, and externally oriented thinking (p < .05). Therefore, it can be concluded that Ellis’s Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy can be used to improve perceived stress and alexithymia.
Downloads
References
Aktaş Terzioğlu, M., & Büber, A. (2025). Alexithymia, internet addiction, and cyber-victimisation among high school students in Turkey: an exploratory study. Behaviour & Information Technology, 44(7), 1350-1361. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2024.2353273
Cao, C., Chen, D., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Perceived stress and academic procrastination among higher vocational nursing students: the mediating roles of positive and negative emotions. BMC Nursing, 24(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02672-8
Ellis, A. (2013). Rational emotive therapy. In Albert Ellis Revisited (pp. 25-37). Routledge.
Elvins, M., Miller, A., & Turner, M. J. (2025). Examining the Effects Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy (REBT) with Embedded Athlete Rational Resilience Credo (ARRC) on the Irrational Beliefs, Motivation Regulation, and Mental Health in Student-Athletes. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 43(4), 55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-025-00619-9
G, F., & Y, C. (2022). Are Nomophobia and Alexithymia Related? The Case of Health Students. Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences, 12, 46-52. https://doi.org/10.33808/clinexphealthsci.781664
Han, L., Ban, Z., & Zhao, N. (2025). Impact of Alexithymia on Nomophobia in College Students: Chain Mediating Role of Mindfulness and Self-efficacy. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 34(4), 1353-1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-024-00948-w
Hu, C., Huang, W., & Zhang, W. (2025). Childhood emotional abuse and suicidal ideation in college students: exploring the mediating role of alexithymia and the moderating effect of physical exercise. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 16, 1660164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1660164
Liu, X., Li, Y., & Cao, X. (2024). Bidirectional reduction effects of perceived stress and general self-efficacy among college students: a cross-lagged study. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02785-0
Liu, Y., Duan, L., Shen, Q., Xu, L., & Zhang, T. (2024). The relationship between childhood psychological abuse and depression in college students: internet addiction as mediator, different dimensions of alexithymia as moderator. BMC public health, 24(1), 2744. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-20232-2
Lu, X., Li, Z., Zhu, X., Li, D., & Wei, J. (2024). The role of alexithymia and moral disengagement in childhood physical abuse and depressive symptoms: A comparative study among rural and urban Chinese college students. Psychology research and behavior management, 3197-3210. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S466379
Mafi, S., Tajvar, N., & Jalalvand, S. (2025). The Role of Emotional Intelligence, Academic Burnout, and Alexithymia in Shaping Academic Outcomes for Dental Students. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6376846/v1
Marendić, M., Aranza, D., Aranza, I., Vladislavić, S., & Kolčić, I. (2024). Differences between health and non-health science students in lifestyle habits, perceived stress and psychological well-being: a cross-sectional study. Nutrients, 16(5), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050620
Ocheni, C. A., Nwatu, U. L., Vita, B., Ezugwu, I. J., Agah, J. J., Oguguo, B. C. E., & Nwatu, J. O. (2025). Application of Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT) in the Treatment of Examination Cheating Behavior among Students. Journal of Academic Ethics, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-025-09596-1
Onuigbo, L. N., Eseadi, C., Ugwoke, S. C., Nwobi, A. U., Anyanwu, J. I., Okeke, F. C., & Eze, P. (2018). Effect of rational emotive behavior therapy on stress management and irrational beliefs of special education teachers in Nigerian elementary schools. Medicine, 97(37), e12191. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000012191
Sun, F., Wang, F., Hu, X., Xue, J., Zheng, S., Su, J., & Lu, Q. (2024). Alexithymia and negative emotions among nursing students: a moderated mediation model. BMC Nursing, 23(1), 167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01832-0
Tams, S., Legoux, R., & Léger, P. M. (2018). Smartphone withdrawal creates stress: A moderated mediation model of nomophobia, social threat, and phone withdrawal context. Computers in human Behavior, 81, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.11.026
Wen, J., Xu, Q., Jiang, Y., & Li, M. (2024). The effects of student bullying on non-suicidal self-injurious behavior in rural adolescents: the chain-mediated effects of alexithymia and ruminate thinking. Frontiers in psychology, 15, 1483408. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1483408
Xu, A., Long, F., Teng, M., Zhang, W., & Hou, L. (2025). Latent Profiles of Childhood Maltreatment and Their Associations with Emotional Reactivity, Alexithymia, and Emotion Regulation in Chinese College Students. Psychology research and behavior management, 1759-1774. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S539441
Zhang, Y. (2025). Impact of arts activities on psychological well-being: Emotional intelligence as mediator and perceived stress as moderator. Acta Psychologica, 254, 104865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2025.104865