Predicting the Emotional Social Adjustment of Children with Autism Based on Mother-Child Anxiety and the Adaptability of Maternal Parenting
Keywords:
Emotional social adjustment, Anxiety, Parenting adaptability, Reflective functioning, Mindful parenting, Family relations, Autism, Children, MothersAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to predict the emotional social adjustment of children with autism based on mother-child anxiety and the adaptability of maternal parenting.
Methods and Materials: The research was descriptive and correlational. The population consisted of all mothers with autistic children in the city of Kut. The sample consisted of 200 mothers with autistic children, selected through convenient sampling. The research instruments included the Mother and Child Anxiety Scale (Ataabadi et al., 2021), the Social Emotional Skills Questionnaire for Children (Payton et al., 2008), and the Parenting Adaptability Scale (Yousefi, 2021). Descriptive statistics (mean and standard deviation) and inferential statistics (Pearson correlation coefficient and stepwise regression) were used for data analysis.
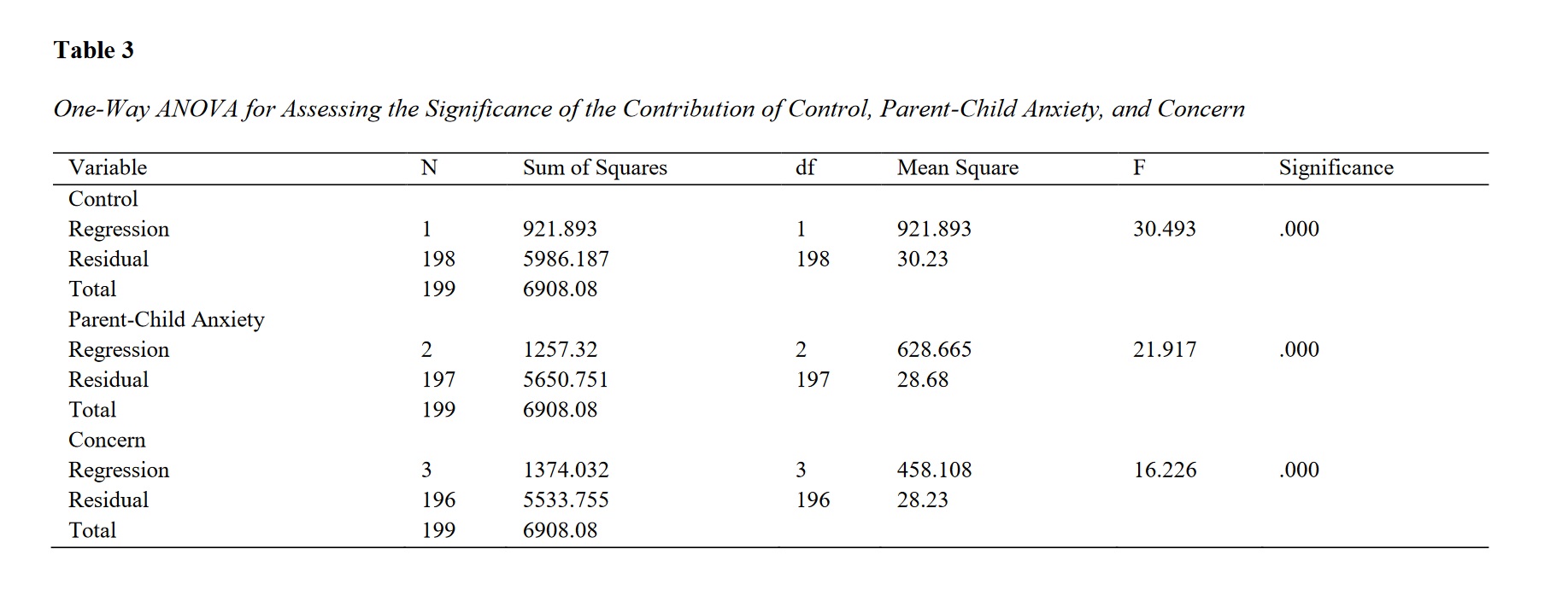
Findings: The results showed that among the predictor variables, mother-child anxiety and its dimensions, and parenting adaptability and its dimensions, were significantly correlated with emotional social adjustment. Among these variables and their dimensions, parental control, parenting concerns, and parent-child anxiety had predictive power for the emotional social adjustment of children.
Conclusion: Based on these results, it can be said that improving parenting variables is beneficial for the improvement of children's emotional social adjustment.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Alaa Najm Abed Alhammashi (Author); Zahra Yousefi (Corresponding Author); Abboud Jawad Radhi , Floor Khayatan (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.