The Role of Problem-Solving Ability in Work-Life Balance and Job Stressors in Employed Women
Keywords:
Problem-solving ability, Work-life balance, Dual pressures, Working womenAbstract
Objective: This study examines the role of problem-solving ability in managing work-life balance and job stressors among employed women.
Methods and Materials: The present study is applied and descriptive-correlational in nature. Data were collected from a sample of employed women using the Heppner Problem-Solving Inventory (1987), the Work-Life Balance Scale by Wang and Kou (2009), and the Job Stressors Scale by Staines (2000). Statistical analysis was performed using multiple regression analysis with a simultaneous method. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 23.
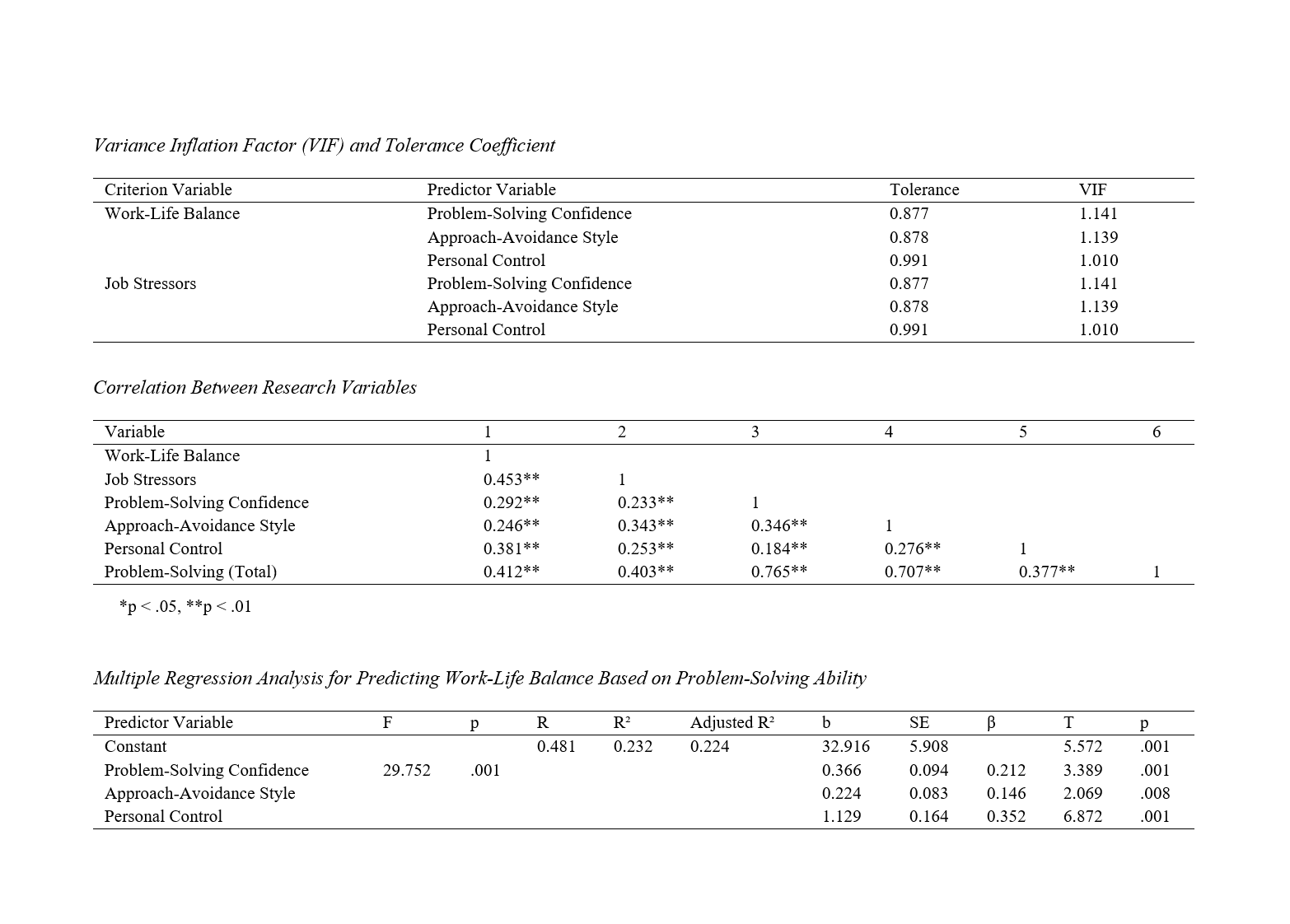
Findings: According to the data from the present study, problem-solving ability significantly predicts work-life balance in women. The dimensions of problem-solving explain 2.23% of the variance in work-life balance among employed women, with personal control having the greatest impact. Additionally, problem-solving ability significantly predicts women's job stressors. The dimensions of problem-solving explain 1.18% of the variance in job stressors among employed women. Confidence in problem-solving, approach-avoidance style, and personal control significantly predict women's job stressors, with the approach-avoidance style having the greatest impact.
Conclusion: The results showed that problem-solving ability plays an important role in managing work-life balance and dual pressures among employed women. Women with higher problem-solving ability experienced greater improvement in work-life balance and were better able to cope with job stressors.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohammadreza Choupani (Corresponding Author); Parisa Akbari, Sahar Taghavi, Mahdieh Tabatabaee mohseni , Ghazaleh Tarnas (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.