Presentation of a Model of Relationships between Cognitive Emotion Regulation, Metacognitive Beliefs, and Metacognitive Awareness: The Mediating Role of Goal Orientation and Self-Efficacy among Young Female Students
Keywords:
Metacognitive Awareness, Metacognitive Beliefs, Cognitive Emotion Regulation, Goal Orientation, Self-EfficacyAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to present a model of the relationships between cognitive emotion regulation, metacognitive beliefs, and metacognitive awareness, considering the mediating role of goal orientation and self-efficacy among young female students at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences.
Methods and Materials: This applied research utilized a descriptive correlational method of path analysis. The statistical population comprised all undergraduate female students (School of Public Health and Environment) at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, totaling approximately 2,422 individuals. A sample size of 480 students was selected using stratified random sampling based on Morgan's table. The data collection tool was a standardized questionnaire whose validity was confirmed by experts, and its reliability was verified through a pilot study and Cronbach's alpha calculation.
Findings: The findings indicated that four factors—metacognitive beliefs, cognitive emotion regulation, goal orientation, and self-efficacy—had a significant impact on students' metacognitive awareness in the English language course. Among the endogenous variables, self-efficacy had the greatest effect (0.19), while metacognitive beliefs had the least effect (0.164) on the variable of metacognitive awareness.
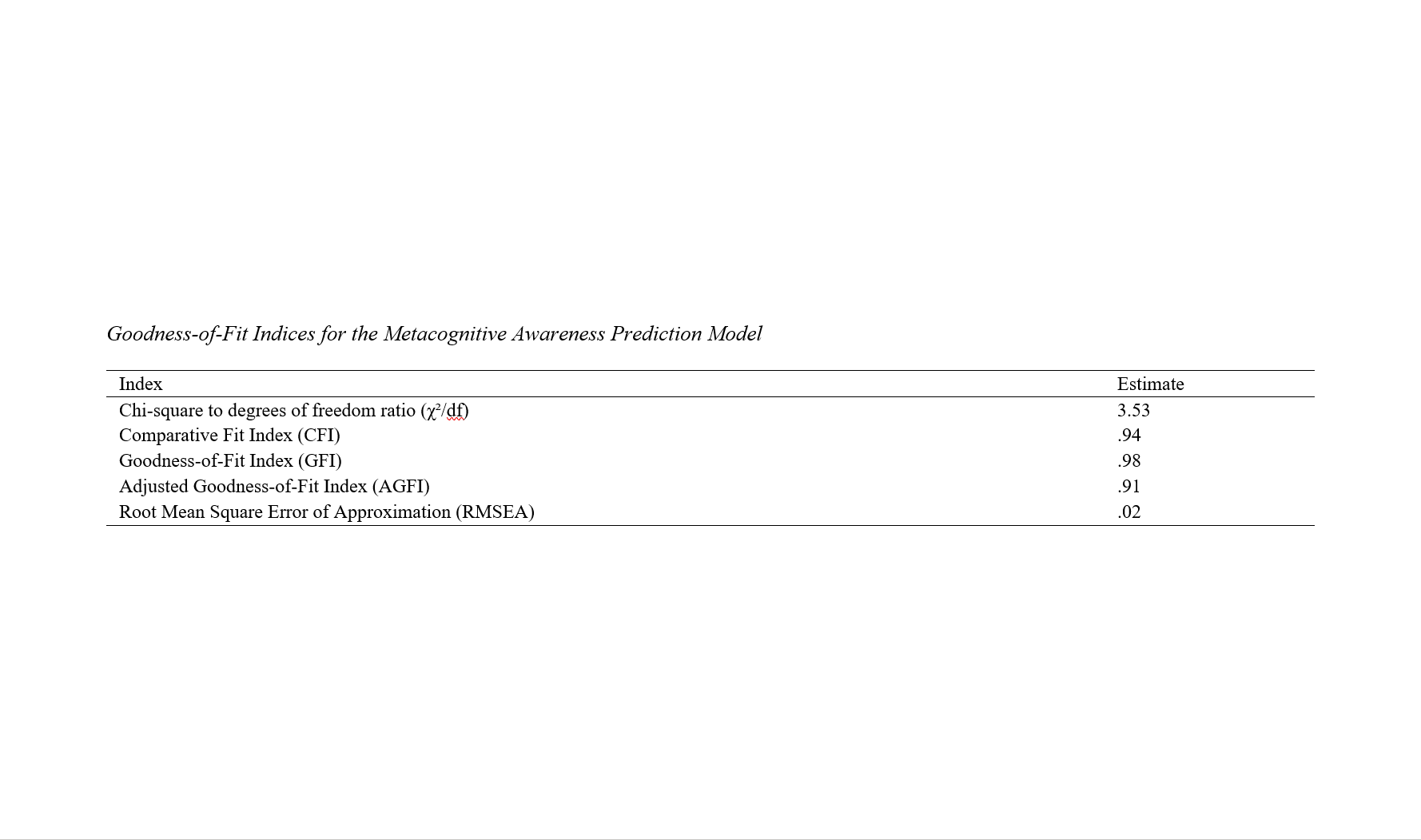
Conclusion: Overall, it must be acknowledged that given the goodness-of-fit indices and the comprehensive evaluation of the model within the studied group, the proposed model demonstrated suitable fit indices and can be utilized in decision-making and policy-making processes.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fahimeh Rajabi, Horeye Bayramnejad, Parvaneh Doodman, Sadegheh Salmanpour (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.