Effectiveness of Schema-Based Parenting on Emotion Regulation, Reflective Functioning, and the Parent-Child Relationship of Mothers with Children Under 6 Years Old
Keywords:
Schema-based parenting, Emotion regulation, Reflective functioning, Parent-child relationshipAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine schema-based parenting on emotion regulation, reflective functioning, and the parent-child relationship of mothers with children under 6 years old.
Methods and Materials: The present study is a quantitative research with a pretest-posttest and follow-up design, including two experimental groups and one control group. The statistical population of this study consisted of all mothers with children under 6 years old in the city of Isfahan. For sampling purposes, kindergartens in Isfahan were purposefully selected, and from among them, based on the cut-off point of questionnaires and inclusion and exclusion criteria, 30 participants were chosen. They were randomly assigned equally into two groups: an experimental group (15 individuals) and a control group (15 individuals). Subsequently, schema-based parenting training sessions (competent parenting) based on the protocol by Mehrabi Nia et al. (2022) were conducted for the experimental group, while the control group received no intervention. The research tools included the Parent-Child Relationship Scale by Pianta (1992), the Parental Reflective Functioning Questionnaire by Fonagy et al. (1991), and the Emotion Regulation Checklist by Shields and Cicchetti (1995). The data collected through questionnaires were analyzed using appropriate statistical tests (repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test) and SPSS software.
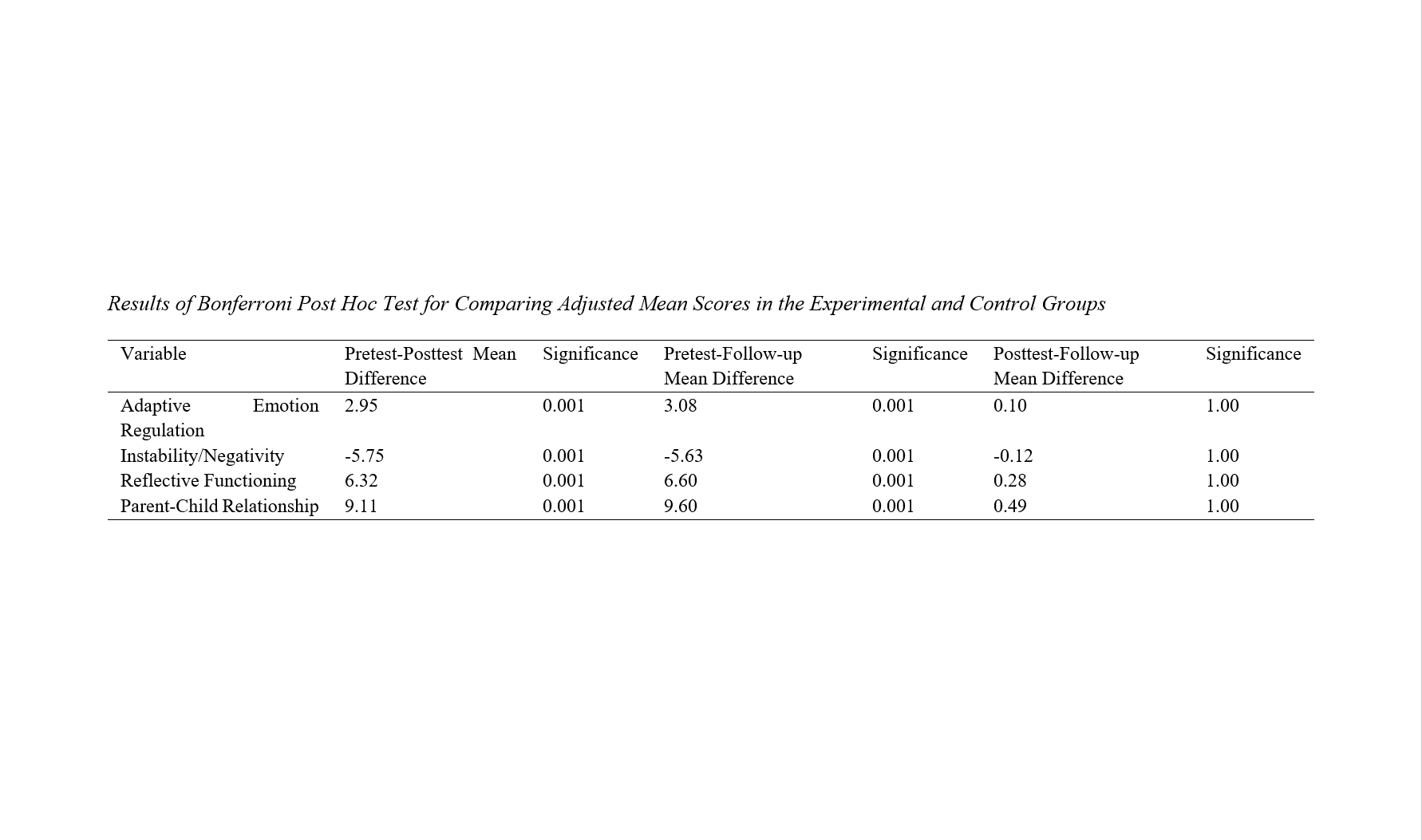
Findings: Given that the calculated F value for intergroup (group membership effect) and intragroup (time effect) as well as the interactive effect of group and time is significant at a 99% confidence level (P < 0.01), these results indicate a significant difference between the two groups. Furthermore, the results show that this significant difference exists at least during one of the intervention times among the research groups. The Bonferroni post hoc test results indicated a significant difference between the scores of adaptive emotion regulation, instability/negativity, reflective functioning, and parent-child relationship during the research stages between the experimental and control groups (p < 0.01). In other words, schema-based parenting training has had a significant impact on improving the research variables (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: These results confirm that this approach can be used as an effective strategy in enhancing parental abilities and reducing psychological challenges for mothers during the parenting period.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Reyhaneh karimnejad Isfahani (Author); Mojtaba Ansari Shahidi (Corresponding Author); Akram Dehghani (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.