The Effect of Aerobic Exercise and Ethanolic Extract of Rice Bran on The Expression of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase and HMGCR Genes in the Liver Tissue of Rats Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Keywords:
Aerobic exercise, rice bran, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, HMGCR, high-fat dietAbstract
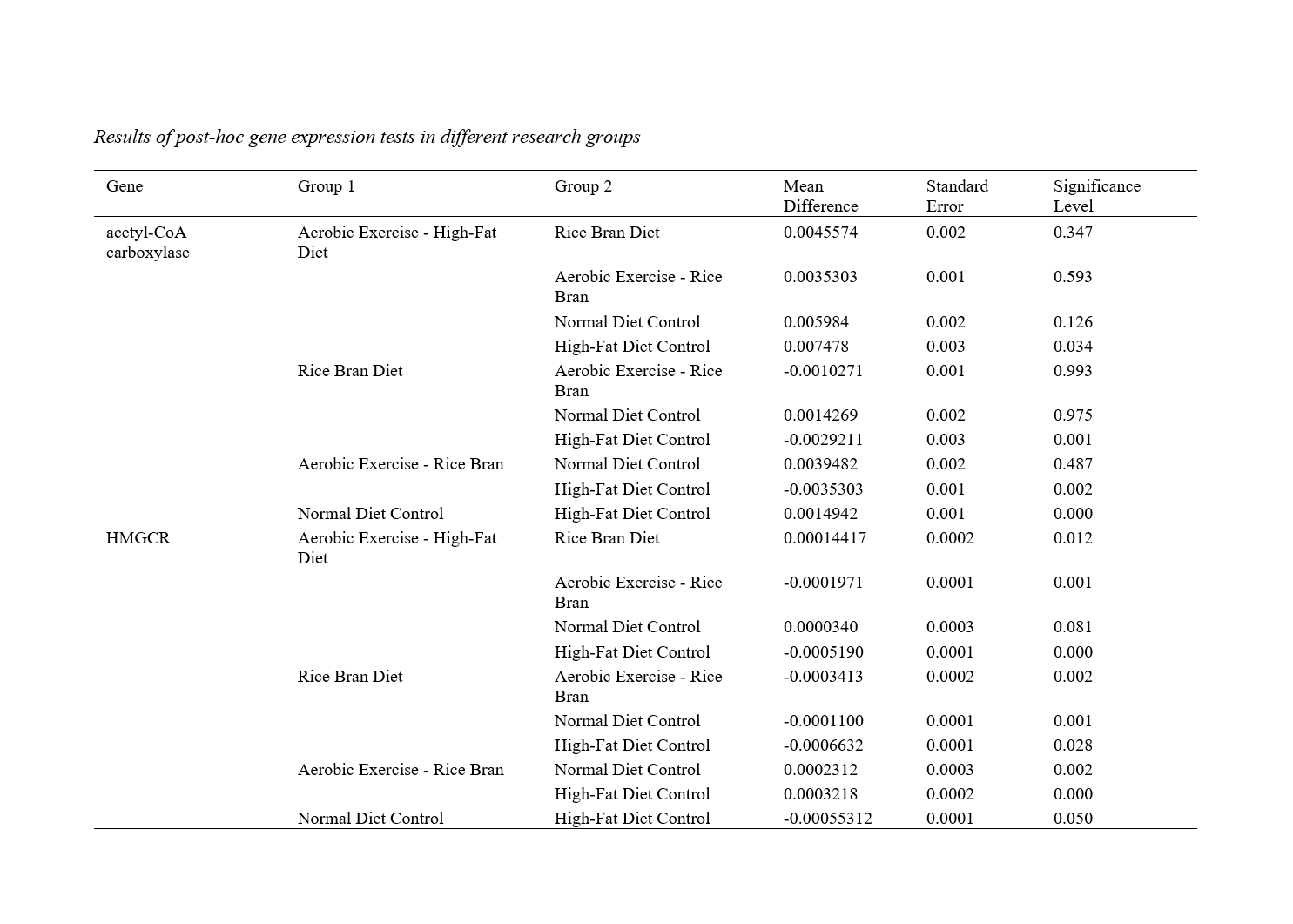
Alteration in cholesterol homeostasis is a consequence of overweight and obesity induced by diet, with the liver being one of the key organs in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. Since the effect of rice bran and aerobic exercise on the hepatic cholesterol synthesis pathway is not well understood, this study aimed to investigate the effect of aerobic exercise and ethanolic extract of rice bran on the expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase and HMGCR genes in the liver tissue of rats fed with a high-fat diet. In a preclinical trial, 30 eight-week-old female rats were randomly divided into five groups (6 rats per group): control with normal diet, control with a high-fat diet, aerobic exercise with a high-fat diet, and aerobic exercise with rice bran and a high-fat diet. The aerobic exercise program included running on a treadmill at moderate intensity (50-60% Vo2max), 5 sessions per week for 4 weeks. The ethanolic extract of rice bran was administered at a dose of 60 mg/kg via gavage to the supplement and exercise-supplement groups. The expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase in the control group with a normal diet significantly increased compared to the control group with a high-fat diet (P = 0.000), while the expression of HMGCR significantly decreased (P = 0.050). Additionally, the expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase in the aerobic exercise group with a high-fat diet showed a significant increase compared to the control group with a high-fat diet (P ≤ 0.034), and the expression of HMGCR showed a significant decrease (P = 0.000). Furthermore, intergroup comparisons revealed that the increase in the expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase in the rice bran diet group was significant compared to the control group with a high-fat diet (P ≤ 0.001), while the expression of HMGCR significantly decreased (P ≤ 0.028). Similar changes were observed in the aerobic exercise-rice bran group compared to the control group with a high-fat diet, showing a significant increase in the expression of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (P ≤ 0.002), while the decrease in HMGCR expression was significant (P = 0.000).
Downloads
References
1. Aguilar-Ballester M, Herrero-Cervera A, Vinué Á, Martínez-Hervás S, González-Navarro H. Impact of Cholesterol Metabolism in Immune Cell Function and Atherosclerosis. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):2021.
2. Alipour Talesh G, Trézéguet V, Merched A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Statins. Biochemistry. 2020;59(37):3393-400.
3. Alvarez-Jimenez L, Morales-Palomo F, Moreno-Cabañas A, Ortega JF, Mora-Rodriguez R. Statins effect on insulin resistance after a meal and exercise in hypercholesterolemic pre-diabetic individuals. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 2022;32(9):1346-55.
4. Alves JB, Rodrigues MHP, Duarte FA, Furlong EB, Christ-Ribeiro A. Rice Bran and Its Potential To Complement the Nutritional Needs of Children and Elderly. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition. 2023;78(1):86-92.
5. Aly DM, Fteah AM, Al Assaly NM, Elashry MA, Youssef YF, Hedaya MS. Correlation of serum biochemical characteristics and ABCG8 genetic variant (rs 11887534) with gall stone compositions and risk of gallstone disease in Egyptian patients. Asian Journal of Surgery. 2023;46(9):3560-7.
6. André R, Pacheco R, Alves AC, Santos HM, Bourbon M, Serralheiro ML. The Hypocholesterolemic Potential of the Edible Algae Fucus vesiculosus: Proteomic and Quantitative PCR Analysis. Foods. 2023;12(14):2758.
7. Balasubramanian R, Maideen NM. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) and their drug interactions involving CYP enzymes, P-glycoprotein and OATP transporters-an overview. Current drug metabolism. 2021;22(5):328-41.
8. Banerjee A, Moreno A, Pata J, Falson P, Prasad R. Chapter Eight - ABCG: a new fold of ABC exporters and a whole new bag of riddles! Donev R, editor: Academic Press; 2021 2021/01/01/. 163-91 p.
9. Barkas F, Nomikos T, Liberopoulos E, Panagiotakos D. Diet and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Among Individuals with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):2436.
10. Bastida MJ, Girós LM, Benito R, Janusz K, Hernández-Rivas MJ, González-Porras RJ. Sitosterolemia: Diagnosis, Metabolic and Hematological Abnormalities, Cardiovascular Disease and Management. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2019;26(37):6766-75.
11. Benn T, Kim B, Park Y-K, Wegner CJ, Harness E, Nam T-G, et al. Polyphenol-rich blackcurrant extract prevents inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 2014;25(10):1019-25.
12. Brendolan A, Russo V. Targeting cholesterol homeostasis in hematopoietic malignancies. Blood. 2022;139(2):165-76.
13. Wu N, Sarna LK, Hwang S-Y, Zhu Q, Wang P, Siow YL, O K. Activation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase during high fat diet feeding. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease. 2013;1832(10):1560-8.
14. Chatterjee A, Gerdes MW, Martinez SG. Identification of Risk Factors Associated with Obesity and Overweight—A Machine Learning Overview. Sensors. 2020;20(9):2734.
15. Galdieri L, Zhang T, Rogerson D, Lleshi R, Vancura A. Protein Acetylation and Acetyl Coenzyme A Metabolism in Budding Yeast. Eukaryotic Cell. 2014;13(12):1472-83.
16. Cardoso D, Perucha E. Cholesterol metabolism: a new molecular switch to control inflammation. Clinical Science. 2021;135(11):1389-408.
17. Cao K, Zhang K, Ma M, Ma J, Tian J, Jin Y. Lactobacillus mediates the expression of NPC1L1, CYP7A1, and ABCG5 genes to regulate cholesterol. Food Science & Nutrition. 2021;9(12):6882-91.
18. de Lima NS, De Sousa RAL, Amorim FT, Gripp F, Diniz e Magalhães CO, Henrique Pinto S, et al. Moderate-intensity continuous training and high-intensity interval training improve cognition, and BDNF levels of middle-aged overweight men. Metabolic Brain Disease. 2022;37(2):463-71.
19. Côté I, Ngo Sock ET, Lévy É, Lavoie J-M. An atherogenic diet decreases liver FXR gene expression and causes severe hepatic steatosis and hepatic cholesterol accumulation: effect of endurance training. European Journal of Nutrition. 2013;52(5):1523-32.
20. Eftekharzadeh M, Atashak S, Azarbayjani MA, Moradi L, Rahmati-Ahmadabad S. The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on SREBP-1c Gene Expression in Skeletal Muscle in Obese Female Rats. Thrita. 2023;12(1):e138382.
21. Yang A, Alrosan AZ, Sharpe LJ, Brown AJ, Callaghan R, Gelissen IC. Regulation of ABCG4 transporter expression by sterols and LXR ligands. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 2021;1865(1):129769.
22. Luo J, Yang H, Song B-L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2020;21(4):225-45.
23. Ma Z, Deng C, Hu W, Zhou J, Fan C, Di S, et al. Liver X receptors and their agonists: targeting for cholesterol homeostasis and cardiovascular diseases. Current issues in molecular biology. 2017;22(1):41-64.
24. Makhmudova U, Schulze PC, Lütjohann D, Weingärtner O. Phytosterols and Cardiovascular Disease. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. 2021;23(11):68.
25. Munkong N, Somnuk S, Jantarach N, Ruxsanawet K, Nuntaboon P, Kanjoo V, Yoysungnoen B. Red Rice Bran Extract Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Dyslipidemia in Mice. Nutrients. 2023;15(1):246.
26. Chung HR, Vakil M, Munroe M, Parikh A, Meador BM, Wu PT, et al. The Impact of Exercise on Statin-Associated Skeletal Muscle Myopathy. PLOS ONE. 2016;11(12):e0168065.
27. Ortega FJ, Mayas D, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Esteve E, et al. The Gene Expression of the Main Lipogenic Enzymes is Downregulated in Visceral Adipose Tissue of Obese Subjects. Obesity. 2010;18(1):13-20.
28. Suwannachot P, Thawornchinsombut S, Jongjareonrak A, Sringam P, Senaphan K. Supplementation with rice bran hydrolysates reduces oxidative stress and improves lipid profiles in adult dogs. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science. 2023;85(7):727-34.
29. Lei L, Chen J, Liu Y, Wang L, Zhao G, Chen Z-Y. Dietary Wheat Bran Oil Is Equally as Effective as Rice Bran Oil in Reducing Plasma Cholesterol. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2018;66(11):2765-74.
30. Kumar A, Vashist A, Kumar P, Kalonia H, Mishra J. Protective effect of HMG CoA reductase inhibitors against running wheel activity induced fatigue, anxiety like behavior, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. Pharmacological Reports. 2012;64(6):1326-36.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Shokofe Maleki (Author); Mohammad Ali Azarbayjani (Corresponding Author); Shahin Riyahi Malayeri, Maghsoud Peeri , Saleh Rahmati Ahmadabad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















