Investigating the Effectiveness of an Intervention Protocol Based on Grounded Theory on the Quality of Life and Worry of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Keywords:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Quality of Life, Grounded Theory, WorryAbstract
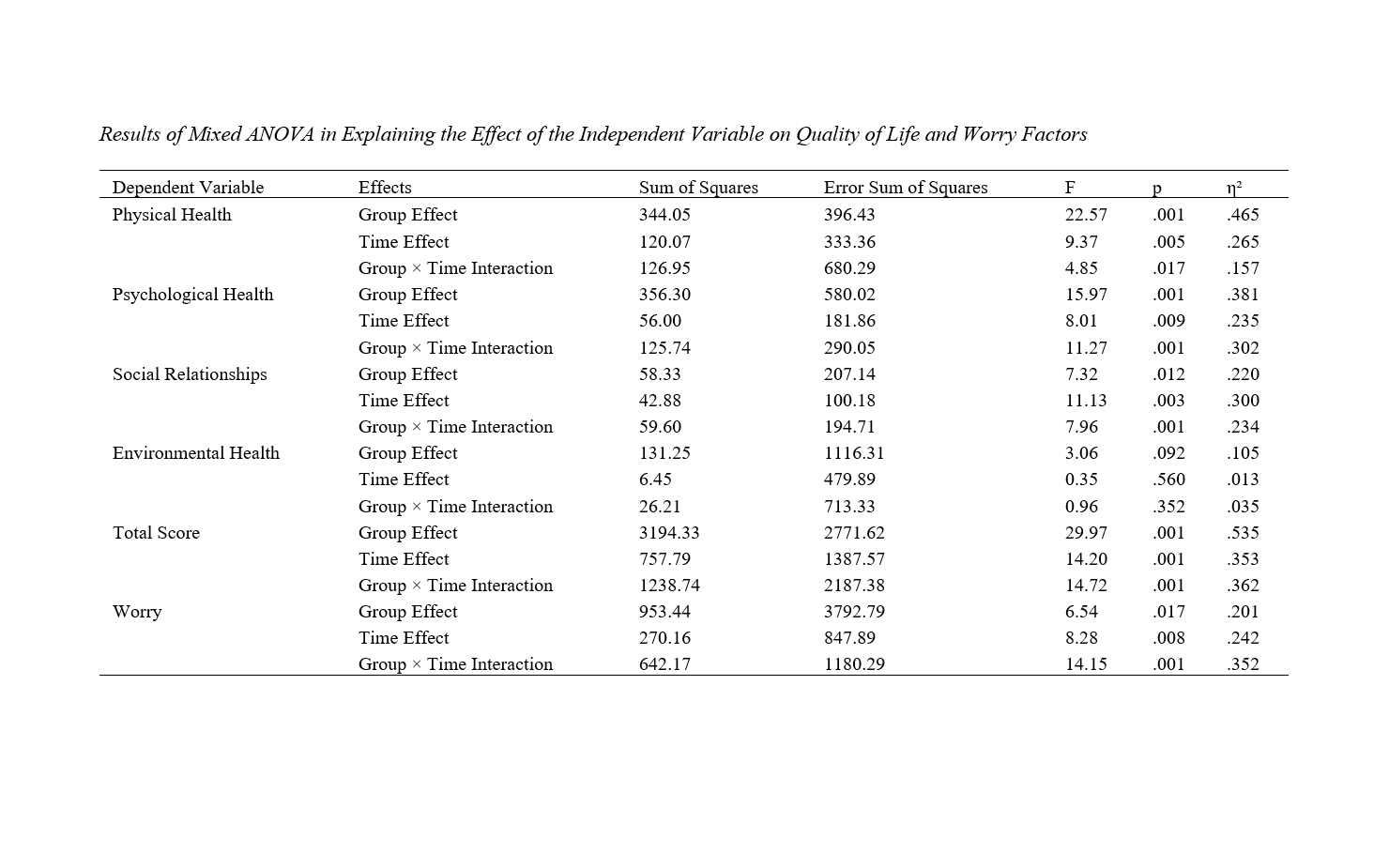
The present study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of an intervention protocol based on grounded theory on the quality of life and worry of patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The research method of the present study was mixed-methods, implemented in an exploratory design with a two-phase sequential strategy. The qualitative part of the research, considering its grounded theory basis, was phenomenological based on the Strauss and Corbin (1997) theory. The quantitative part employed a quasi-experimental method with a pretest-posttest control group design and a 2-month follow-up phase. The qualitative study population included books, articles, and theses in the field of IBS patients, and IBS patients visiting the Rāh-e Ehyā Psychiatry Clinic, Shahid Tajrish Hospital, and Behboud Gastroenterology Clinic in Tehran during the fall and winter of 2022. The quantitative study population consisted of all IBS patients visiting the Rāh-e Ehyā Psychiatry Clinic, Shahid Tajrish Hospital, and Behboud Gastroenterology Clinic in Tehran during the fall and winter of 2022. In the quantitative part, 28 IBS patients meeting the inclusion criteria were randomly assigned to either the control or experimental groups. Worry was measured using the Penn State Worry Scale. After eight intervention sessions, the research data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA and SPSS software, with a significance level of 0.05. The interaction effect of group×time for the components of physical health (η² = 0.157, P = 0.017, F = 4.85), psychological health (η² = 0.302, P = 0.001, F = 11.27), social health (η² = 0.234, P = 0.001, F = 7.96), and total quality of life score (η² = 0.362, P = 0.001, F = 14.72) was significant. Additionally, the effect of the independent variable on worry (η² = 0.352, P = 0.001, F = 14.15) was significant. The results indicated that the intervention protocol designed based on grounded theory is effective in improving the quality of life and reducing worry in patients with irritable bowel syndrome.
Downloads
References
1. Dear BF, Fogliati VJ, Fogliati R, Gandy M, McDonald S, Talley N, et al. Transdiagnostic internet-delivered cognitive-behaviour therapy (CBT) for adults with functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGID): A feasibility open trial. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2018;108:61-9. [PMID: 29602327] [DOI]
2. Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. gastroenterology. 2006;130(5):1377-90. [PMID: 16678553]
3. Alqahtani NH, Mahfouz MEM. The Prevalence and Risk Factors of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Saudi Arabia in 2019. Int J Prev Med. 2022;13:13. [PMID: 35281979] [PMCID: PMC8883680] [DOI]
4. Caes L, Orchard A, Christie D. Connecting the Mind–Body Split: Understanding the Relationship Between Symptoms and Emotional Well-Being in Chronic Pain and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Healthcare. 2017;5(4):93. [PMID: 29206152] [PMCID: PMC5746727] [DOI]
5. Brenner DM, Ladewski AM, Kinsinger SW. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2023. [DOI]
6. Weaver KR, Melkus GDE, Henderson WA. Irritable Bowel Syndrome. AJN The American Journal of Nursing. 2017;117(6):48-55. [PMID: 28541989] [PMCID: PMC5453305] [DOI]
7. Porcelli P, De Carne M, Leandro G. Distinct associations of DSM-5 Somatic Symptom Disorder, the Diagnostic Criteria for Psychosomatic Research-Revised (DCPR-R) and symptom severity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2020;64:56-62. [PMID: 32199282] [DOI]
8. Quattropani MC, Lenzo V, Filastro A, Fries W. Metacognitions and basic emotions in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. Psicoterapia Cognitiva e Comportamentale. 2019;25(1):35-51.
9. Koloski NA, Jones M, Talley NJ. Evidence that independent gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut pathways operate in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia: a 1-year population-based prospective study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44(6):592-600. [PMID: 27444264] [DOI]
10. Edebol-Carlman H, Schrooten M, Ljótsson B, Boersma K, Linton S, Brummer RJ. Cognitive behavioral therapy for irritable bowel syndrome: the effects on state and trait anxiety and the autonomic nervous system during induced rectal distensions–An uncontrolled trial. Scandinavian journal of pain. 2018;18(1):81-91. [PMID: 29794287]
11. Jadallah KA, Khatatbeh MM, Sarsak EW, Sweidan AN, Alzubi BF. Irritable bowel syndrome and its associated factors among Jordanian medical students: A cross-sectional study. Medicine. 2022;101(33):e30134. [PMID: 35984126] [PMCID: PMC9387975] [DOI]
12. Tosic-Golubovic S, Miljkovic S, Nagorni A, Lazarevic D, Nikolic G. Irritable bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression and personality characteristics. Psychiatr Danub. 2010;22(3):418-24.
13. Shahkaram H, Yaztappeh JS, Sadeghi A, Kianimoghadam AS, Soltanabadi S, Bakhtiari M, et al. Comparing the effectiveness of transdiagnostic treatment with acceptance and commitment therapy on emotional disorders, rumination, and life satisfaction in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024;24(1):66. [PMID: 38321387] [PMCID: PMC10845775] [DOI]
14. Shirvan AA, Nikoogoftar M, Ahadi H. The Effectiveness of Schema Therapy Intervention on Somatic Symptom Experience, Medication Adherence, and Perceived Stress in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Hormozgan Medical Journal. 2022. [DOI]
15. Solati-Dehkordy K, Kalantari M, Molavi H, Afshar H, Adibi P. The Effects of Relaxation with Drug Therapy on the Quality of Life and Symptoms of IBS. GOVARESH. 2011;14(2):6.
16. Jo M, Son C. Effects of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) on IBS-symptoms, stress, quality of life, and acceptance-action of people with irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2018;16(11):501-9.
17. Ford AC, Quigley EMM, Lacy BE, Lembo AJ, Saito YA, Schiller LR, et al. Effect of Antidepressants and Psychological Therapies, Including Hypnotherapy, in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG. 2014;109(9):1350-65. [DOI]
18. Fukudo S, Kaneko H, Akiho H, Inamori M, Endo Y, Okumura T, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for irritable bowel syndrome. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2015;50(1):11-30. [PMID: 25500976] [DOI]
19. Ali R, Alshareef F, Al-Qahtani M, Almuqrin O, Aloraini H, Alshibani A, et al. Migraine: Prevalence, Predisposing Factors, and Impact on Quality of Life among Saudi Board Family Medicine Residents in Riyadh, KSA. International Neuropsychiatric Disease Journal. 2023;20(1):29-43. [DOI]
20. Jandaghi G, Zia-Tohidi A, Firoozi M. Psychological Interventions for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Iranian Randomized Trials. Arch Iran Med. 2021;24(6):496-504. [PMID: 34488313] [DOI]
21. Aftab R, Shams A. Relationship Between Integrated Self-Knowledge and Resilience with Anxiety of Being Infected by COVID-19: The Mediating Role of Intolerance of Ambiguity, Worry, and Physical Activity. Sport Psychology Studies. 2020;9(32):201-26. [DOI]
22. Babaei K, Issazadegan A, Pirnabikhah N, Tajoddini E. On the Role of Brain-Behavioral Systems (BAS/BIS), Novelty Seeking, Reward Dependency, and Pathological Worry in Predicting Addiction Tendency of. etiadpajohi. 2016;10(37):259-75.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yasaman Ghorbani Ashin (Author); Mohammadreza Seirafi (Corresponding Author); Khadijeh Abolmaali Alhosseini, Morvarid Ahadi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















