Examining the Effectiveness of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms in Adults with Attention Deficit Disorder
Keywords:
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms, Attention Deficit DisorderAbstract
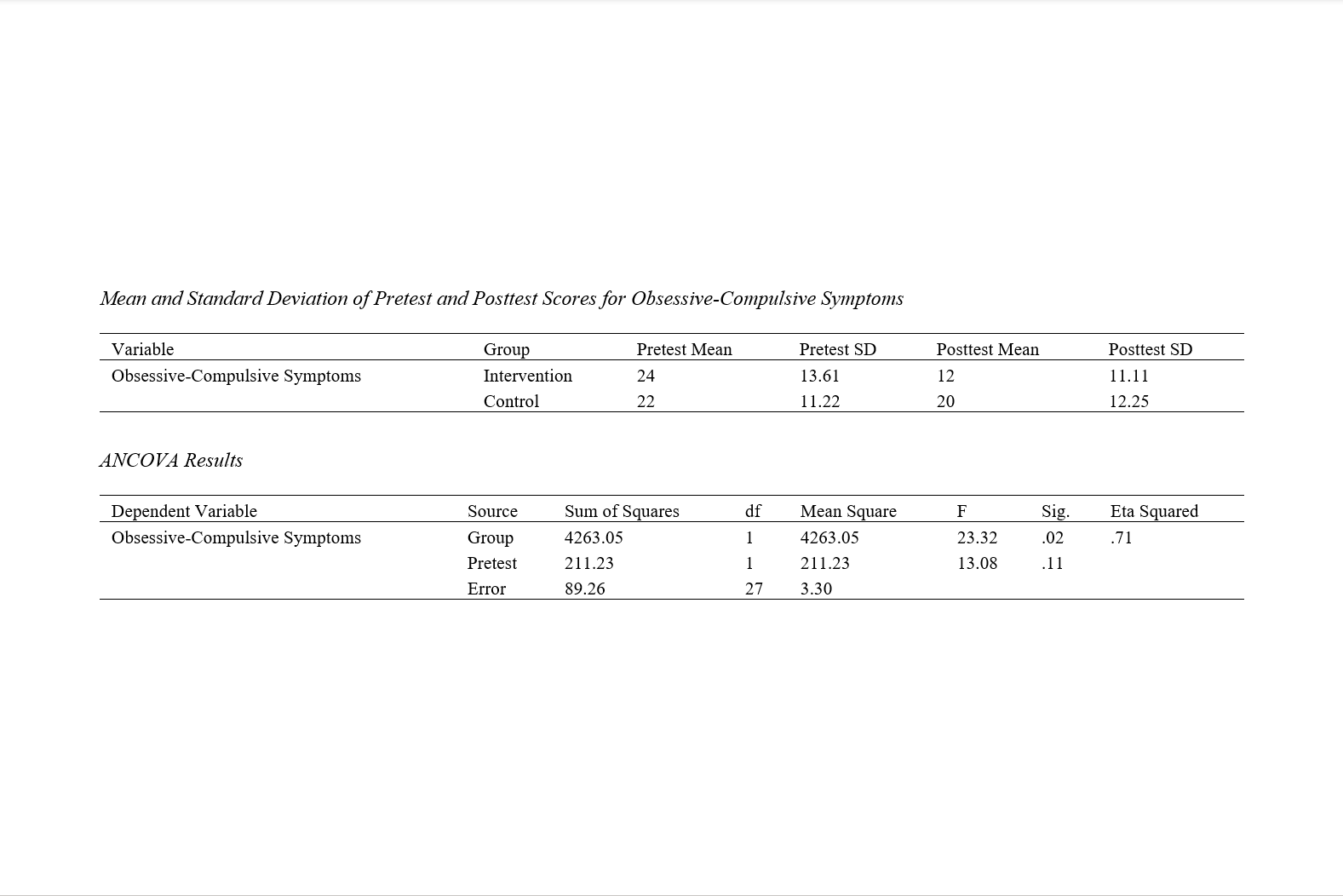
One of the disorders that has affected many individuals today is Attention Deficit Disorder. The present study aimed to examine the effectiveness of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) on obsessive-compulsive symptoms in adults diagnosed with Attention Deficit Disorder. This study utilized a quasi-experimental design with pretest-posttest and a control group. The statistical population included all adults diagnosed with Attention Deficit Disorder who visited psychological clinics in Yazd, Iran, in 2024. From this population, 30 individuals were selected through convenience sampling based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Participants were then randomly assigned to the intervention group (n = 15) and the control group (n = 15). The research instrument was the Maudsley Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory (MOCI). Participants in the experimental group received 10 sessions of rTMS, each lasting 20 minutes. Data were analyzed using ANCOVA in SPSS version 23. The results indicated a significant reduction in obsessive-compulsive symptom scores in adults with Attention Deficit Disorder in the intervention group compared to the control group after receiving treatment (F = 23.22, p < .05). According to the effect size results, 71% of the variance between the intervention and control groups in obsessive-compulsive symptoms was attributable to rTMS treatment. Given the study’s findings, rTMS may be an effective intervention for reducing obsessive-compulsive symptoms in adults with Attention Deficit Disorder.
Downloads
References
1. Frank Y. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Pediatric behavioral neurology2024. 179-202 p[DOI]
2. Song P, Zha M, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Rudan I. The prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of global health. 2021;11. [PMID: 33692893] [PMCID: PMC7916320] [DOI]
3. Dutta CN, Christov-Moore L, Ombao H, Douglas PK. Neuroprotection in late life attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A review of pharmacotherapy and phenotype across the lifespan. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2022;16. [PMID: 36226261] [PMCID: PMC9548548] [DOI]
4. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Alcohol-related disorders Kaplan and Sadock’s synopsis of psychiatry: behavioral sciences/clinical psychiatry. Philadephia (PA): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. 1472 p
5. Abramovitch A, Dar R, Mittelman A, Wilhelm S. Comorbidity between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder across the lifespan: a systematic and critical review. Harvard review of psychiatry. 2015;23(4):245-62. [PMID: 26052877] [PMCID: PMC4495876] [DOI]
6. Singh A, Anjankar VP, Sapkale B. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): a comprehensive review of diagnosis, comorbidities, and treatment approaches. Cureus. 2023;15(11). [DOI]
7. Ujjwal P, Sanjita D, Kumar FN. A Comprehensive Review on Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: An Update. Pharmacophore. 2024;15(2-2024):54-62. [DOI]
8. Chamberlain SR, Solly JE, Hook RW, Vaghi MM, Robbins TW. Cognitive inflexibility in OCD and related disorders. The neurobiology and treatment of OCD: Accelerating Progress2021. p. 125-45.[PMID: 33547598] [DOI]
9. Wu H, Hariz M, Visser-Vandewalle V, Zrinzo L, Coenen VA, Sheth SA, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): emerging or established therapy? Molecular psychiatry. 2021;26(1):60-5. [PMID: 33144712] [PMCID: PMC7815503] [DOI]
10. Öst LG, Enebrink P, Finnes A, Ghaderi A, Havnen A, Kvale G, et al. Cognitive behavior therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder in routine clinical care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2022;159. [PMID: 36302283] [DOI]
11. Lefaucheur JP, Aleman A, Baeken C, Benninger DH, Brunelin J, Di Lazzaro V, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014-2018). Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(2):474-528. [PMID: 31901449] [DOI]
12. De Risio L, Borgi M, Pettorruso M, Miuli A, Ottomana AM, Sociali A. Recovering from depression with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Translational Psychiatry. 2020;10(1). [PMID: 33173042] [PMCID: PMC7655822] [DOI]
13. asbaghi E, rafienia P, mkvand hossini S, sabahi P. The Effectiveness of rTMS on Working Memory and Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychology. 2017;3(8):29-50.
14. Li X, Hartwell KJ, Henderson S, Badran BW, Brady KT, George MS. Two weeks of image-guided left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation improves smoking cessation: a double-blind, sham-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Brain stimulation. 2020;13(5):1271-9. [PMID: 32534252] [PMCID: PMC7494651] [DOI]
15. Beynel L, Davis SW, Crowell CA, Dannhauer M, Lim W, Palmer H, et al. Site-specific effects of online rTMS during a working memory task in healthy older adults. Brain sciences. 2020;10(5). [PMID: 32349366 ] [PMCID: PMC7287855] [DOI]
16. Brabenec L, Klobusiakova P, Simko P, Kostalova M, Mekyska J, Rektorova I. Non-invasive brain stimulation for speech in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Brain Stimulation. 2021;14(3):571-8. [PMID: 33781956] [DOI]
17. Delavar A. Educational and psychological research. Tehran: Virayesh Pub; 2015.
18. Rachman S, Hodgson R. Obsessive compulsive complains. Behavior Research and Therapy. 1977;15:389-95. [PMID: 612339] [DOI]
19. Alilou MM. Worry and its relationship with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Contemporary Psychology. 2006;1(10):27-9.
20. Berlim MT, Neufeld NH, Van den Eynde F. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): an exploratory meta-analysis of randomized and sham-controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2013;47(8):999-1006. [PMID: 23615189] [DOI]
21. Dehghani-Arani F, Kazemi R, Hallajian AH, Sima S, Boutimaz S, Hedayati S, et al. Metaanalysis of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) Efficacy for OCD Treatment: The Impact of Stimulation Parameters, Symptom Subtype and rTMS-Induced Electrical Field. J Clin Med. 2024;13(18). [PMID: 39336846] [PMCID: PMC11432318] [DOI]
22. Godfrey KEM, Muthukumaraswamy SD, Stinear CM, Hoeh N. Effect of rTMS on GABA and glutamate levels in treatment-resistant depression: An MR spectroscopy study. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2021;317. [PMID: 34479176] [DOI]
23. Mahdavi M, Haji Mohammad Baqer S. Magnetic brain stimulation (rTMS) in the treatment of depression, OCD and epilepsy: the first international conference on educational sciences, psychology and humanities. 2021.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Kimia Esmaeili (Author); Samira Mollaei (Corresponding Author); Pegah Ahmadi, Mohammad Reza Yekta, Saba Rabiee (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















