Exploring the Factors Influencing AI Integration in Clinical Diagnostic Decision-Making
Keywords:
Artificial intelligence, Clinical decision-making, Diagnostic medicine, Healthcare professionals, Qualitative study, Sociotechnical factors, Thematic analysis, Medical ethics, AI implementation barriersAbstract
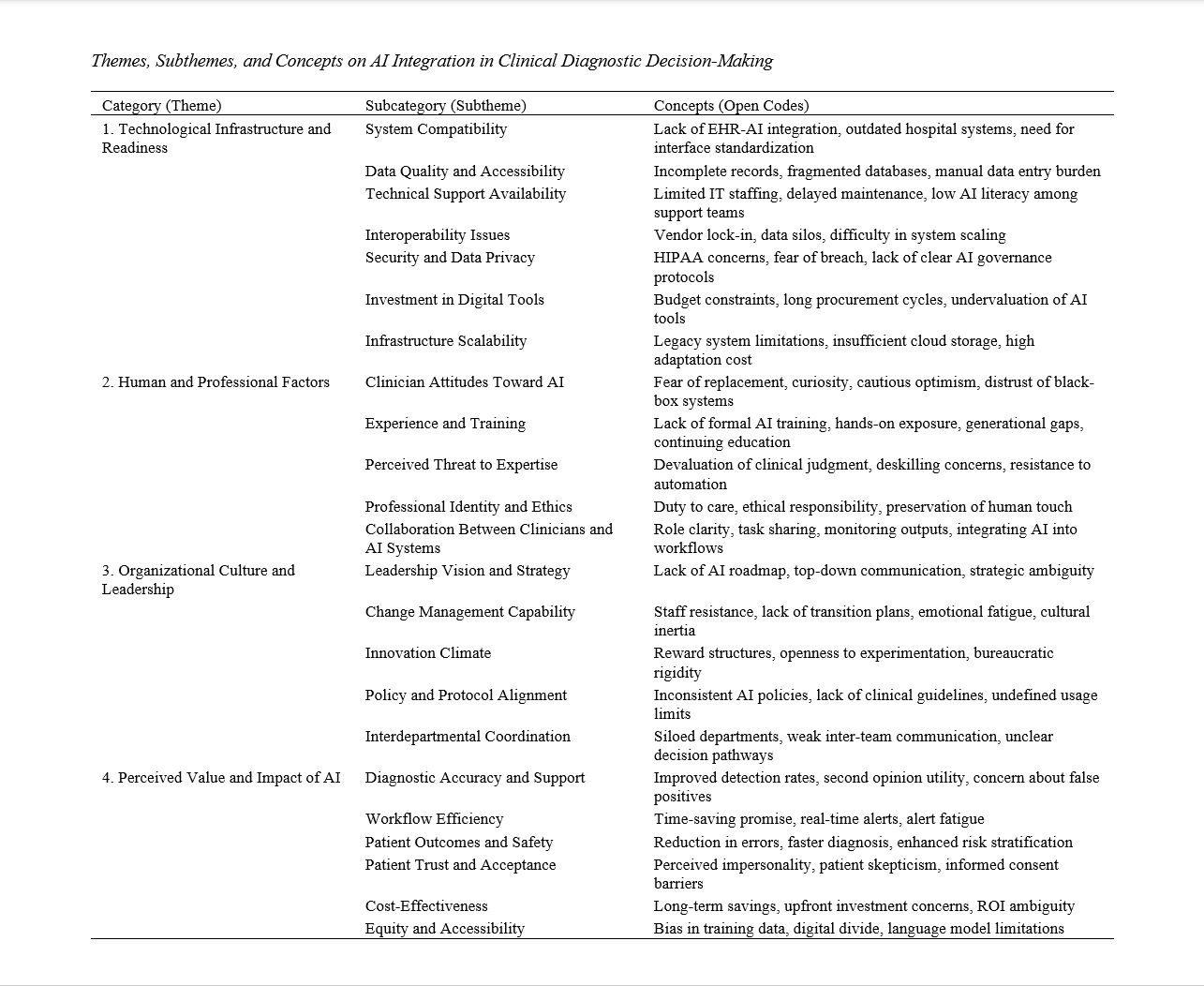
This study aimed to explore the key factors influencing the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into clinical diagnostic decision-making from the perspective of healthcare professionals. This research employed a qualitative design based on semi-structured interviews with 23 healthcare professionals in Canada, including physicians, radiologists, clinical informaticians, nurse practitioners, and administrators. Participants were selected through purposive sampling to ensure diverse perspectives, and data collection continued until theoretical saturation was achieved. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed thematically using NVivo software, with codes and themes developed iteratively through inductive analysis and constant comparison. Four major themes emerged from the data: (1) technological infrastructure and readiness, (2) human and professional factors, (3) organizational culture and leadership, and (4) perceived value and impact of AI. Participants reported that outdated systems, poor interoperability, and insufficient technical support limited integration. Attitudes toward AI varied, with concerns about trust, autonomy, and training gaps. Organizational barriers included lack of leadership strategy and unclear implementation policies. While AI was recognized for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, concerns about alert fatigue, liability, and ethical issues were prevalent. Patient trust, professional identity, and collaborative workflows also influenced AI adoption outcomes. Integrating AI into clinical diagnostics is a complex, multidimensional process shaped by technological, professional, organizational, and ethical factors. Beyond technical improvements, successful implementation requires a holistic, sociotechnical approach that addresses infrastructure, education, workflow design, and patient-clinician communication. Institutional strategies should prioritize clinician engagement, interdisciplinary collaboration, and transparent governance to foster responsible and effective AI adoption in healthcare settings.
Downloads
References
1. Basubrin O. Current Status and Future of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Cureus. 2025.
2. Kotowicz M, Bieniak-Pentchev M, Koczkodaj M. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Potential and Application Possibilities - Comprehensive Literature Review. Quality in Sport. 2025;41:60222.
3. Wheatley M. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Diagnostic Medicine. Pjai. 2024.
4. Lee KWA, Chan LKW, Lee CH, Bohórquez J, Haykal D, Wan J, et al. Artificial Intelligence Application in Diagnosing, Classifying, Localizing, Detecting and Estimation the Severity of Skin Condition in Aesthetic Medicine: A Review. Dermatological Reviews. 2025;6(1).
5. Selvakumar P, Sivaraja M, Dharmalingam S, Jeyakarthika K, Dhaaraani R, Manjunath TC. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations of AI in Nuclear Medicine. 2025:29-50.
6. Salomon I, Sibomana O. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Advantages and Disadvantages for Today and the Future. International Journal of Surgery Open. 2024;62(4):471-3.
7. Rubini A, Via RD, Pastore VP, Signore FD, Rosto M, Bonis AD, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Veterinary Sciences. 2025;12(5):404.
8. Domrös-Zoungrana D, Rajaeean N, Boie S, Fröling E, Lenz C. Medical Education: Considerations for a Successful Integration of Learning With and Learning About AI. Journal of Medical Education and Curricular Development. 2024;11.
9. Singh S, Devi J, Kumar D. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare and Medicine. 2025:68-77.
10. Cabral BP, Braga LAM, Filho CGC, Penteado BE, Sandro Luís Freire de Castro S, Castro L, et al. Future Use of AI in Diagnostic Medicine: 2-Wave Cross-Sectional Survey Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2025;27:e53892.
11. Pasupuleti MK. Revolutionizing Healthcare: AI and Big Data for Predictive Analytics and Precision Medicine. 2025:151-60.
12. Erizo JJ. Navigating the Frontier: Assessing the Extent of AI's Influence in Healthcare. Jafotik. 2024;2(1):7-12.
13. Czerwinska M, Ejdys J, Rzepka A. Understanding Patient Attitudes Towards the Use of AI in Medical Diagnosis Using Necessary Conditions Analysis. European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship. 2024;19(1):984-6.
14. Westphal A, Mrowka R. Special Issue European Journal of Physiology: Artificial Intelligence in the Field of Physiology and Medicine. Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology. 2025;477(4):509-12.
15. Rimkutė D. AI and Liability in Medicine: The Case of Assistive-Diagnostic AI. Baltic Journal of Law & Politics. 2024;16(2):64-81.
16. Li Y, Q L, Fu K, Zhou X, Zhang K. Progress in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Ultrasound-Assisted Medical Diagnosis. Bioengineering. 2025;12(3):288.
17. Miskeen E, Alfaifi J, Alhuian DM, Alghamdi M, Alharthi MH, Alshahrani NA, et al. Prospective Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Fetal Medicine: A Scoping Review of Recent Updates. International Journal of General Medicine. 2025;Volume 18:237-45.
18. Udegbe FC, Ebulue OR, Ebulue CC, Ekesiobi CS. Ai's Impact on Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments for Improved Health Outcomes. Engineering Science & Technology Journal. 2024;5(4):1386-94.
19. Zafar S, Rana N. The Convergence of Nanotechnology and Artificial Intelligence: Unlocking Future Innovations. Recent Innovations in Chemical Engineering (Formerly Recent Patents on Chemical Engineering). 2025;18.
20. Ruan C, Zhu Y, Xiong J. Applications and Prospects of Artificial Intelligence in Oral Medicine. 2024;1(2):11-5.
21. Taksøe‐Vester C, Bashir Z, Sejer EPF, Ngo ML, Pedersen LH, Friis ML, et al. Artificial Intelligence and Ultrasound in Fetal Medicine. Ugeskr Læger. 2025:1-6.
22. Pacholec C, Flatland B, Xie H, Zimmerman KA. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Veterinary Diagnostics: A Look to Quality Assurance, Part II External Validation. Veterinary Clinical Pathology. 2025.
23. Kuttan N, Pundkar A, Gadkari C, Patel A, Kumar A. Transforming Emergency Medicine With Artificial Intelligence: From Triage to Clinical Decision Support. Multidisciplinary Reviews. 2025;8(10):2025285.
24. Sitarek G, Żerek M. Artificial Intelligence in Emergency Medicine: A Literature Review. Quality in Sport. 2024;33:55839.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Seyed Amir Saadati (Corresponding Author); James Ma (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















