The Effect of Neuromuscular Training on Mental Health, Depression, and Quality of Life among Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Keywords:
Neuromuscular exercises, , Mental health,, Quality of life, , Elderly womenAbstract
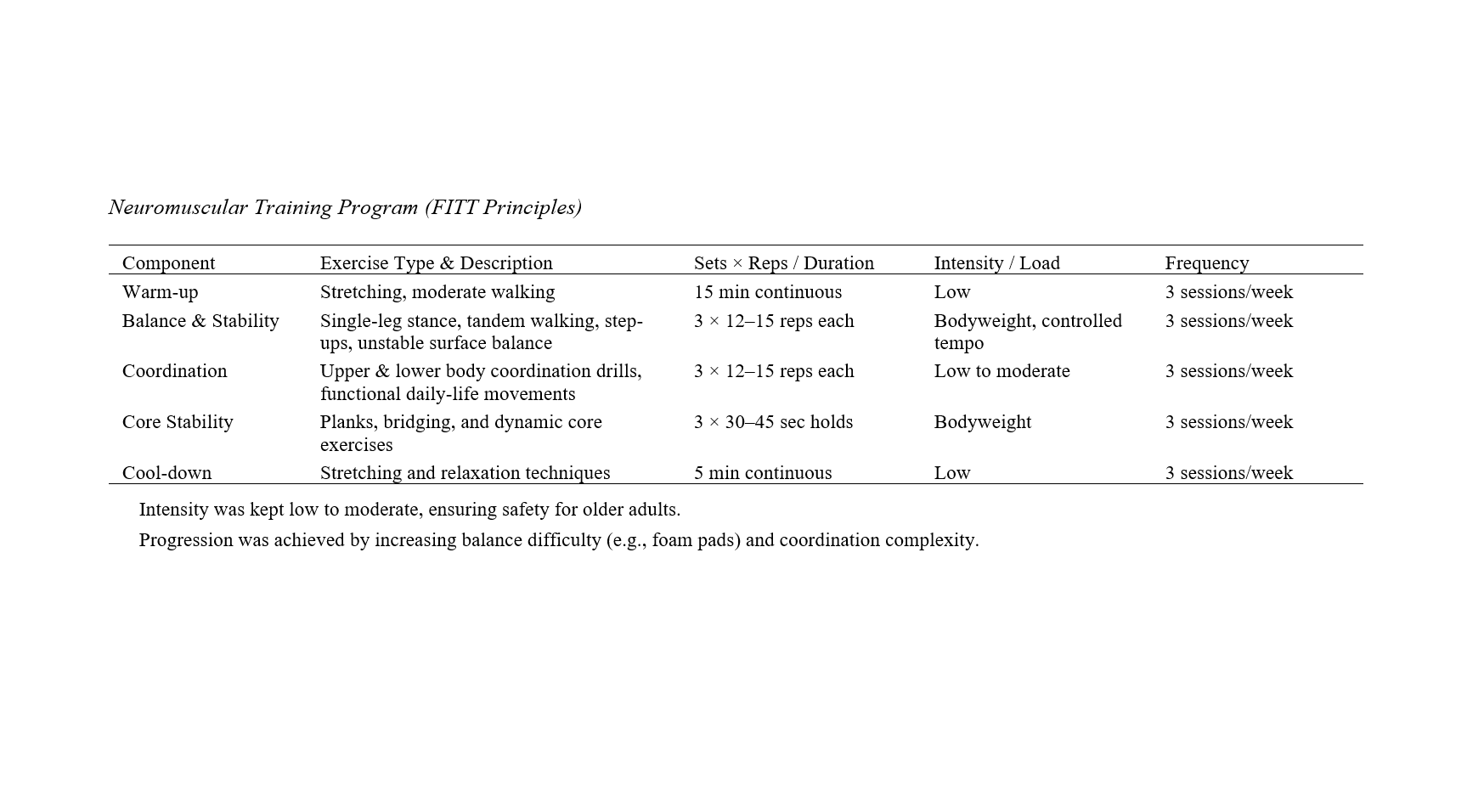
The rapid growth of the global aging population has intensified concerns regarding the physical, psychological, and social well-being of older adults, particularly women, as age-related declines in neuromuscular control, balance, and mental health contribute substantially to reduced functional independence and quality of life. Neuromuscular training (NMT) has emerged as a promising multimodal approach to counteract these effects. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of a structured six-week NMT program on mental health, depression, and quality of life in older women. This quasi-experimental study employed a pretest–posttest design with a control group. Thirty women aged 60–70 years were randomly assigned to either an experimental group (n=15) or a control group (n=15). The experimental group participated in an 18-session NMT program over six weeks, while the control group maintained their usual activities. Mental health, depression, and quality of life were measured using the GHQ-28, Beck Depression Inventory-II, and WHOQOL-BREF questionnaires, respectively. Data were analyzed using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) in SPSS26, with the level of statistical significance set at P<0.05. Preliminary analyses confirmed baseline equivalence between groups (p>0.05), and all ANCOVA assumptions were met. After the intervention, NMT produced significant improvements in mental health (F (1, 27) =7.93, p<0.001, η²=0.38), depression (F (1, 27) =2.29, p=0.004, η²=0.27), and quality of life (F (1, 27) =10.26, p=0.001, η²=0.32). These findings indicate that NMT accounted for a substantial proportion of variance in the measured outcomes. Neuromuscular training significantly improved mental health and quality of life while reducing depressive symptoms among older women. As a safe, low-cost, and accessible form of exercise, NMT may serve as an effective strategy to promote psychological well-being and healthy aging in this population.
Downloads
References
1. Cloak N, Al Khalili Y. Behavioral and psychological symptoms in dementia. 2019.
2. Aghaei N, Sadeghi R, Koosheshi M, Eini Zeinab H. A 100-Year Projection of Population Aging Trends in Iran: Decomposition of Population Momentum. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2026;20(4).
3. Oliveira JS, Gilbert S, Pinheiro MB, Tiedemann A, Macedo LB, Maia L, et al. Effect of sport on health in people aged 60 years and older: a systematic review with meta-analysis. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2023;57(4):230-6.
4. Almeida OP, Khan KM, Hankey GJ, Yeap BB, Golledge J, Flicker L. 150 minutes of vigorous physical activity per week predicts survival and successful ageing: a population-based 11-year longitudinal study of 12 201 older Australian men. British journal of sports medicine. 2014;48(3):220-5.
5. Nosratabadi I, Jahansaz S, Norouzimoghaddam E, Pourramzani N, Saeidi S, Kazemnejad leily E. Relationship between Health-Promoting Lifestyle and Quality of Life in Urolithiasis Patients. Journal of Iranian Medical Council. 2025;8(3):545-52.
6. Vaux-Bjerke A, John DH, Piercy KL. Systematic Review Protocol to Evaluate the Evidence Informing the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans Midcourse Report: Implementation Strategies for Older Adults. J Healthy Eat Act Living. 2023;3(1):36-45.
7. Hemmatadadi M, Sharafi E, Abkar A, Kashani L, Shirzad N. Comparison of Mental Health Status in Infertile Women with or without Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Journal of Iranian Medical Council. 2025;8(3):503-9.
8. Li L. Mental health interventions with older adults and the policy implications. Public Policy & Aging Report. 2025;35(2):53-6.
9. Stenner BJ, Buckley JD, Mosewich AD. Reasons why older adults play sport: A systematic review. Journal of sport and health science. 2020;9(6):530-41.
10. Shahlaee J, Nasiri A. Analysis of the Level of Physical Activity of University Faculty Members during the Coronavirus Pandemic. Journal of New Studies in Sport Management. 2022;3(2):466-73.
11. Lichtenstein E, Held S, Rappelt L, Zacher J, Eibl A, Ludyga S, et al. Agility training to integratively promote neuromuscular, cardiorespiratory and cognitive function in healthy older adults: a one-year randomized-controlled trial. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2023;20(1):21.
12. Izquierdo M, Merchant RA, Morley JE, Anker SD, Aprahamian I, Arai H, et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. The Journal of nutrition, health and aging. 2021;25(7):824-53.
13. Aminirakan D, Losekamm B, Wollesen B. Effects of combined cognitive and resistance training on physical and cognitive performance and psychosocial well-being of older adults ≥65: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2024;14(4):e082192.
14. McLafferty CL, Jr., Wetzstein CJ, Hunter GR. Resistance training is associated with improved mood in healthy older adults. Percept Mot Skills. 2004;98(3 Pt 1):947-57.
15. West J, Otte C, Geher K, Johnson J, Mohr DC. Effects of Hatha yoga and African dance on perceived stress, affect, and salivary cortisol. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2004;28(2):114-8.
16. Nguyen TM, Nguyen VH, Kim JH. Physical exercise and health-related quality of life in office workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(7):3791.
17. Çolak H, Başkan AH. The effect of exercise on quality of life in middle-aged individuals. International Journal of Applied Exercise Physiology. 2020;9(5):253-8.
18. Williams MD, Ramirez-Campillo R, Chaabene H, Moran J. Neuromuscular training and motor control in youth athletes: a meta-analysis. Perceptual and motor skills. 2021;128(5):1975-97.
19. Sterling M. General health questionnaire–28 (GHQ-28). Journal of physiotherapy. 2011;57(4):259.
20. Malakouti SK, Fatollahi P, Mirabzadeh A, Zandi T. Reliability, validity and factor structure of the GHQ-28 used among elderly Iranians. International Psychogeriatrics. 2007;19(4):623-34.
21. Hamidi R, Fekrizadeh Z, Azadbakht M, Garmaroudi G, Taheri Tanjani P, Fathizadeh S, et al. Validity and reliability Beck Depression Inventory-II among the Iranian elderly Population. Journal of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences. 2015;22(1):189-98.
22. Kalfoss MH, Reidunsdatter RJ, Klöckner CA, Nilsen M. Validation of the WHOQOL-Bref: psychometric properties and normative data for the Norwegian general population. Health and quality of life outcomes. 2021;19:1-12.
23. Paralikas T, Maria M, Dimitrios T, Christina B, Nikolaos C, Antigoni F, et al. Physical and Mental Health Level of the Elderly Living in Central Greece. Mater Sociomed. 2021;33(1):16-20.
24. Graham M, Hodgson P, Fleming L, Innerd A, Clibbens N, Hope W, et al. Effectiveness of Physical Activity Interventions on Acute Inpatient Mental Health Units on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing. 2025;34(1):e70017.
25. Ahmadi M, Kazemi-Arpanahi H, Nopour R, Shanbehzadeh M. Factors influencing quality of life among the elderly: An approach using logistic regression. Journal of Education and Health Promotion. 2023;12(1):215.
26. Seddighian SF, Hakim Javadi M, Rezaei S, Zebardast A. The effect of aerobic exercise training program on mental health and body image concern of women with obesity stigma. Health Psychology. 2020;9(34):137-54.
27. Marinkovic D, Macak D, Madic DM, Sporis G, Kuvacic D, Jasic D, et al. Effect of neuromuscular training program on Quality of Life after COVID-19 Lockdown among Young Healthy participants: a Randomized Controlled Trial. Frontiers in psychology. 2022;13:844678.
28. Fusco IA, Donath L, Nebiker L, Lichtenstein E, Minghetti A, Zahner L, et al. Background: Exercise training is a beneficial treatment strategy for depression. Previous meta-analytical reviews mainly examined the effect of aerobic exercise on depressive symptoms neglecting comparisons with neuromuscular training and meta-regression considering relevant exercise training prescriptors such as exercise duration, intensity, number of exercise sessions (volume) and frequency.
29. Mahmoudi A, Amirshaghaghi F, Aminzadeh R, Mohamadi Turkmani E. Effect of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise training on depressive symptoms, quality of life, and muscle strength in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Biological Research for nursing. 2022;24(4):541-59.
30. Cunha PM, Werneck AO, Nunes JP, Stubbs B, Schuch FB, Kunevaliki G, et al. Resistance training reduces depressive and anxiety symptoms in older women: a pilot study. Aging & mental health. 2022;26(6):1136-42.
31. Khodadad Kashi S, Mirzazadeh ZS, Saatchian V. A systematic review and meta-analysis of resistance training on quality of life, depression, muscle strength, and functional exercise capacity in older adults aged 60 years or more. Biological Research For Nursing. 2023;25(1):88-106.
32. Niazi M, malekyian fini E, Shafaiei Moghadam E. Physical Activity and Quality of Life of the Elderly. Iranian Journal of Culture and Health Promotion. 2022;6(3):457-63.
33. Ahmadi M, Noudehi M, Esmaeili M, Sadrollahi A. Comparing the Quality of Life Between Active and Non-Active Elderly Women With an Emphasis on Physical Activity. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2017;12(3):262-75.
34. Leinonen R, Heikkinen E, Hirvensalo M, Lintunen T, Rasinaho M, Sakari‐Rantala R, et al. Customer‐oriented counseling for physical activity in older people: study protocol and selected baseline results of a randomized‐controlled trial (ISRCTN 07330512). Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports. 2007;17(2):156-64.
35. Valtueña-Gimeno N, Ferrer-Sargues FJ, Fabregat-Andrés O, Martínez-Hurtado I, Martínez-Olmos FJ, Lluesma-Vidal M, et al. The impact of a neuromuscular rehabilitation programme on the quality of life of patients with acute coronary syndrome and its relationship with sexual dysfunction: a randomised controlled trial. Quality of Life Research. 2024;33(2):433-42.