Personality-Driven Adaptive Psychosomatic Treatment Planning via Artificial Intelligence
Keywords:
psychosomatic medicine, personality traits, artificial intelligence, adaptive treatment planning, personalized healthcareAbstract
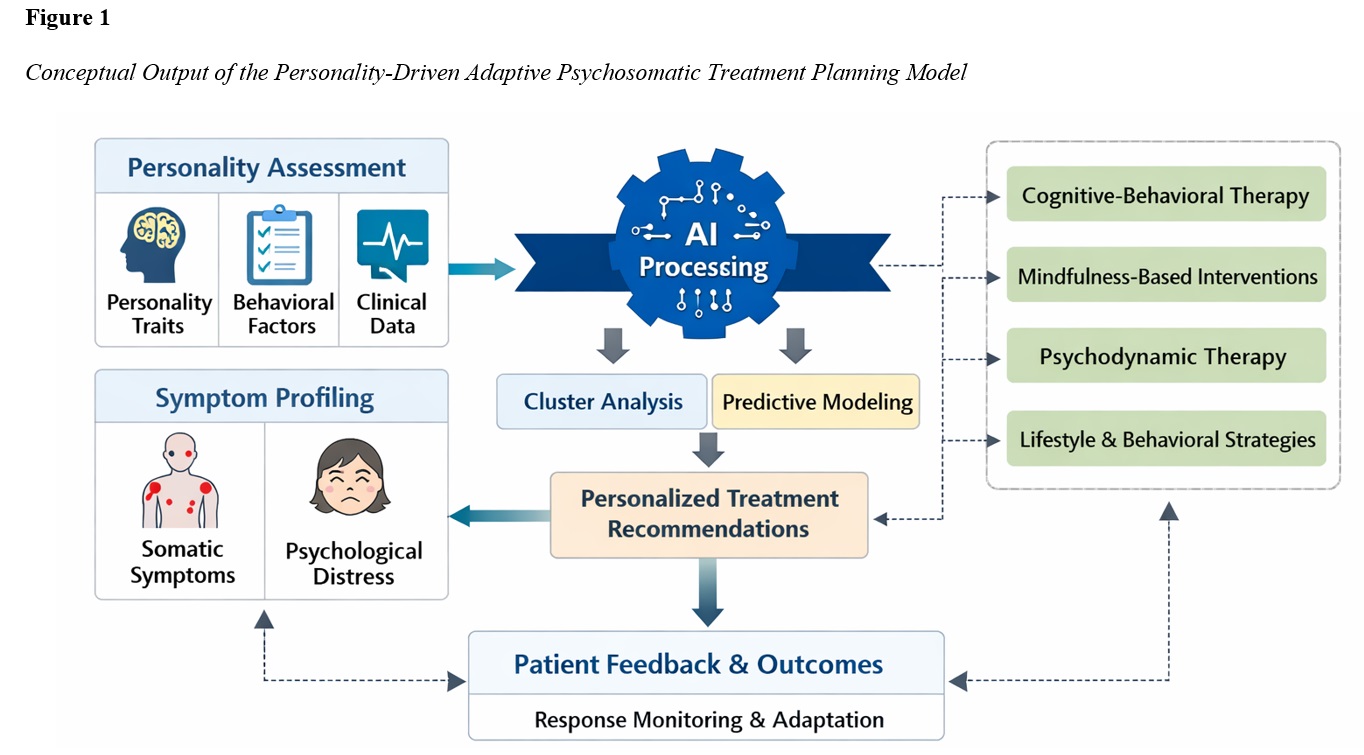
The objective of this study was to develop and empirically evaluate an artificial intelligence–based framework that integrates personality traits with psychosomatic symptom profiles to generate adaptive, personalized treatment plans in psychosomatic medicine. A mixed-methods, model-development study was conducted using clinical data from adult patients with psychosomatic complaints recruited from outpatient psychosomatic and psychological services in Taiwan. Standardized personality assessments, psychosomatic symptom measures, clinician-rated evaluations, and behavioral indicators were collected and integrated into a secure digital dataset. Machine learning techniques, including unsupervised clustering and supervised predictive modeling, were applied to identify latent personality–symptom patterns and to generate individualized treatment recommendations across multiple psychosomatic intervention modalities. Model performance was evaluated using cross-validation procedures, and explainable AI methods were employed to enhance interpretability and clinical transparency. Unsupervised learning identified four distinct personality–psychosomatic clusters characterized by differential trait configurations and symptom profiles. Predictive modeling demonstrated high classification accuracy and strong discriminative capacity in matching patients to optimal treatment modalities. Inferential analyses indicated that personality traits significantly contributed to treatment recommendation variance beyond symptom severity alone, and adaptive recommendations differed systematically across clusters, supporting the model’s capacity for clinically meaningful personalization. The findings suggest that integrating personality traits into AI-driven psychosomatic treatment planning enables robust patient stratification, improves personalization of intervention strategies, and offers a scalable decision-support approach aligned with contemporary precision medicine principles. This framework represents a promising step toward adaptive, person-centered psychosomatic care that complements clinical expertise and supports iterative treatment optimization.
Downloads
References
Abdolkarimi, M., Sadeghi‐Yarandi, M., & Sakari, P. (2024). Investigating the Relationship Between Personality Traits of Hardiness and Perfectionism With Stress and Psychosomatic Symptoms: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Nurses in Iran. BMC psychology, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01832-4
Adegoke, B. O., Odugbose, T., & Adeyemi, C. (2024). Harnessing Big Data for Tailored Health Communication: A Systematic Review of Impact and Techniques. International Journal of Biology and Pharmacy Research Updates, 3(2), 01-010. https://doi.org/10.53430/ijbpru.2024.3.2.0024
Bajestani, A. B., Shahabizadeh, F., Vaziri, S., & Kashani, F. L. (2022). Effectiveness of Integrative Therapy on Distress and Psychosomatic Symptoms in Female Patients With Gastrointestinal Dysfunction With Type D Personality. Journal of Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, 24(2), 70-77. https://doi.org/10.34172/jsums.2022.12
Bulut, S., Bukhori, B., & Bhat, R. H. (2023). The Experience of Psychosomatic Disorders Among Adolescents: Challenges and Coping Strategies. JPPR, 2(2), 19-25. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jppr.2.2.4
Doering, S., Herpertz, S., Pape, M., Hofmann, T., Rose, M., Imbierowicz, K., Geiser, F., Bierling, A. L., Weidner, K., Rademacher, J., Michalek, S., Morawa, E., Erim, Y., Teigelack, P., Teufel, M., Hartmann, A., Lahmann, C., Peters, E. M., Kruse, J., . . . Kessler, H. (2023). The Multicenter Effectiveness Study of Inpatient and Day Hospital Treatment in Departments of Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy in Germany. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1155582
Dong, W., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Wang, S., Zhong, Y., Chen, H., Dong, X., Saripan, M. I., & Zhou, Y. (2021). Electronic Science Games Used to Enhance Cognitive Ability: Opinion of Design From Personalization and Adaptation. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.789547
Efremov, A. (2023). Eliminating Psychosomatic Pain and Negative Emotions With Dehypnosis. Journal of Organizational Behavior Research, 8(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.51847/rnrhuqmtqy
Fava, G. A. (2022). Clinimetric Integration of Diagnostic Criteria for a Personalized Psychiatry. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 91(6), 373-381. https://doi.org/10.1159/000527493
Fazekas, C. (2022). Diagnostic Approaches in Psychosomatic Medicine. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift, 134(15-16), 559-560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-022-02066-3
Floris, H. P. v. V., & Geus‐Oei, L. F. d. (2022). Editorial on Special Issue “Quantitative PET and SPECT”. Diagnostics, 12(8), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081989
Frumkin, M., & Rodebaugh, T. L. (2021). The Role of Affect in Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review of Within-Person Symptom Dynamics. Journal of psychosomatic research, 147, 110527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110527
Goli, F. (2023). Beyond Biology: The Personality Underpinnings of Chronic Pain. JPPR, 2(2), 1-3. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jppr.2.2.1
Gostoli, S., Subach, R., Guolo, F., Bernardini, F. P., Cammarata, A., Gigante, G., Belnap, B. H., Riva, D. D., Urbinati, S., & Rafanelli, C. (2024). Care Manager Role for Older Multimorbid Heart Failure Patients’ Needs in Relation to Psychological Distress and Quality of Life: A Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1432588
Hall, P. A., Sheeran, P., Fong, G. T., Cheah, C. S. L., Oremus, M., Liu‐Ambrose, T., Sakib, M. N., Butt, Z. A., Ayaz, H., Jandu, N., & Morita, P. P. (2021). Biobehavioral Aspects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review. Psychosomatic Medicine, 83(4), 309-321. https://doi.org/10.1097/psy.0000000000000932
Huang, W. L., Chiu, Y.-T., Wu, C. S., Löwe, B., & Liao, S. C. (2025). Integrating DCPR-R and DSM-5 Into Clinical Psychosomatic Practice in Taiwan: Their Relationship With Psychopathologies and Quality of Life. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 94(4), 232-246. https://doi.org/10.1159/000545409
Incorvaia, C., Al‐Ahmad, M., Ansotegui, I. J., Arasi, S., Bachert, C., Bos, C., Bousquet, J., Bożek, A., Caimmi, D., Calderón, M. A., Casale, T. B., Ćustović, A., Blay, F. d., Démoly, P., Devillier, P., Didier, A., Fiocchi, A., Fox, A., Gevaert, P., . . . Canonica, G. W. (2020). Personalized Medicine for Allergy Treatment: Allergen Immunotherapy Still a Unique and Unmatched Model. Allergy, 76(4), 1041-1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14575
Incorvaia, C., Ridolo, E., Bagnasco, D., Scurati, S., & Canonica, G. W. (2021). Personalized Medicine and Allergen Immunotherapy: The Beginning of a New Era? Clinical and Molecular Allergy, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12948-021-00150-z
Johnson, K. B., Wei, W. Q., Weeraratne, D., Frisse, M. E., Misulis, K. E., Rhee, K., Zhao, J., & Snowdon, J. (2020). Precision Medicine, AI, and the Future of Personalized Health Care. Clinical and Translational Science, 14(1), 86-93. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12884
Kessler, H. (2025). Long-Term Effectiveness of Inpatient and Day Hospital Treatment in Departments of Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy in Germany. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1531504
Kop, W. J. (2021). Biopsychosocial Processes of Health and Disease During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychosomatic Medicine, 83(4), 304-308. https://doi.org/10.1097/psy.0000000000000954
Leaviss, J., Davis, S., Ren, S., Hamilton, J. A., Scope, A., Booth, A., Sutton, A., Parry, G., Buszewicz, M., Moss‐Morris, R., & White, P. D. (2020). Behavioural Modification Interventions for Medically Unexplained Symptoms in Primary Care: Systematic Reviews and Economic Evaluation. Health Technology Assessment, 24(46), 1-490. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta24460
Lee, A., Wong, Y., & Neo, X. S. (2023). Personality and Psychoneuroimmunology: Patient Perspectives on Mind-Body Health. JPPR, 1(3), 34-40. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jppr.1.3.6
Matz, S., Teeny, J. D., Vaid, S. S., Peters, H., Harari, G. M., & Cerf, M. (2024). The Potential of Generative AI for Personalized Persuasion at Scale. Scientific reports, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53755-0
Oparin, A., Balaklytska, I. O., Morozova, O. G., Oparin, A. G., & Khomenko, L. O. (2020). Mechanisms of Insomnia Formation With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Taking Into Account the Psychosomatic Status in Young People. Wiadomości Lekarskie, 73(7), 1365-1369. https://doi.org/10.36740/wlek202007111
Parekh, A.-D. E., Shaikh, O. A., Kaur, S., Manan, S., & Hasibuzzaman, M. A. (2023). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Personalized Medicine: AI-generated Personalized Therapy Regimens Based on Genetic and Medical History: Short Communication. Annals of medicine and surgery, 85(11), 5831-5833. https://doi.org/10.1097/ms9.0000000000001320
Renau, R. R., Palacios, B., Varela, L., Fernández, R. M., Correa, S. C., Estupiñán, M. F., Calvo, E., Jose, N., Muñoz, M. R., Yun, S., Jiménez‐Marrero, S., Alcoberro, L., Garay, A., Moliner, P., Sánchez-Fernández, L., Gómez, M. T. S., Hidalgo, E., Enjuanes, C., Calero-Molina, E., . . . Comín‐Colet, J. (2021). Quality of Life and Disease Experience in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction in Spain: A Mixed-Methods Study. BMJ open, 11(12), e053216. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053216
Romaniello, C., Romanazzo, S., & Cosci, F. (2023). Clinimetric Properties of the Diagnostic Criteria for Psychosomatic Research Among the Elderly. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 30(3), 611-619. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2822
Salvi, F., Ribeiro, M. H., Gallotti, R., & West, R. (2024). On the Conversational Persuasiveness of Large Language Models: A Randomized Controlled Trial. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4429707/v1
Schoenthaler, A., Leon, M., Butler, M., Steinhaeuser, K., & Wardzinski, W. (2020). Development and Evaluation of a Tailored Mobile Health Intervention to Improve Medication Adherence in Black Patients With Uncontrolled Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes: Pilot Randomized Feasibility Trial. Jmir Mhealth and Uhealth, 8(9), e17135. https://doi.org/10.2196/17135
Simchon, A., Edwards, M., & Lewandowsky, S. (2024). The Persuasive Effects of Political Microtargeting in the Age of Generative Artificial Intelligence. Pnas Nexus, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae035
Šnele, M. S., Todorović, J., & Nikolić, M. (2024). Personality Traits and Tendency Towards Psychosomatics. https://doi.org/10.36315/2024inpact107
Taylor, G. J., & Bagby, R. M. (2020). Examining Proposed Changes to the Conceptualization of the Alexithymia Construct: The Way Forward Tilts to the Past. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 90(3), 145-155. https://doi.org/10.1159/000511988
Vagni, M., Maiorano, T., Giostra, V., & Pajardi, D. (2020). Coping With COVID-19: Emergency Stress, Secondary Trauma and Self-Efficacy in Healthcare and Emergency Workers in Italy. Frontiers in psychology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.566912
Wagner‐Skacel, J., Matzer, F., Kohlhammer-Dohr, A., Dalkner, N., & Jauk, E. (2022). Assessment of Personality Functioning in Psychosomatic Medicine. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift, 134(15-16), 602-610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-021-01993-x
Werling, A. M., Walitza, S., Eliez, S., & Drechsler, R. (2022). Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Mental Health and Family Situation of Clinically Referred Children and Adolescents in Switzerland: Results of a Survey Among Mental Health Care Professionals After 1 Year of COVID-19. Journal of Neural Transmission, 129(5-6), 675-688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-022-02512-6
Wortman, M. S. H., Hartman, T. o., Johannes, C. v. d. W., Dankers, S., Visser, B., Assendelft, W. J., & Henriëtte, E. v. d. H. (2022). Perceived Working Mechanisms of Psychosomatic Therapy in Patients With Persistent Somatic Symptoms in Primary Care: A Qualitative Study. BMJ open, 12(1), e057145. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-057145
Yamanaka, Y., Yoshiuchi, K., Kubo, C., Fukudo, S., Kusumi, I., Sato, K., Ebana, S., Kawai, K., Takeuchi, T., Nakao, M., Hashizume, M., Maruoka, S., Kaneko, H., Kawasaki, Y., Fukunaga, M., Koyama, A., Hashizume, M., Okada, H., Harada, T., . . . Matsubayashi, S. (2023). A Nationwide Questionnaire Survey of Physicians Regarding the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Patients and Treatment System of Psychosomatic Medicine. BioPsychoSocial Medicine, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13030-023-00279-0
Zhang, B., Tu, N., Angrave, L., Zhang, S., Sun, T., Tay, L., & Li, J. (2023). The Generalized Thurstonian Unfolding Model (GTUM): Advancing the Modeling of Forced-Choice Data. Organizational Research Methods, 27(4), 713-747. https://doi.org/10.1177/10944281231210481
Žídková, R., Maliňáková, K., Dijk, J. P. v., & Tavel, P. (2021). The Coronavirus Pandemic and the Occurrence of Psychosomatic Symptoms: Are They Related? International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(7), 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073570