An Investigation of the Effects of Group Work Dynamics on Iranian Male and Female EFL Learners’ Motivation in Communicative Tasks
Keywords:
Group work dynamics, Group work, Motivation, EFL LearnersAbstract
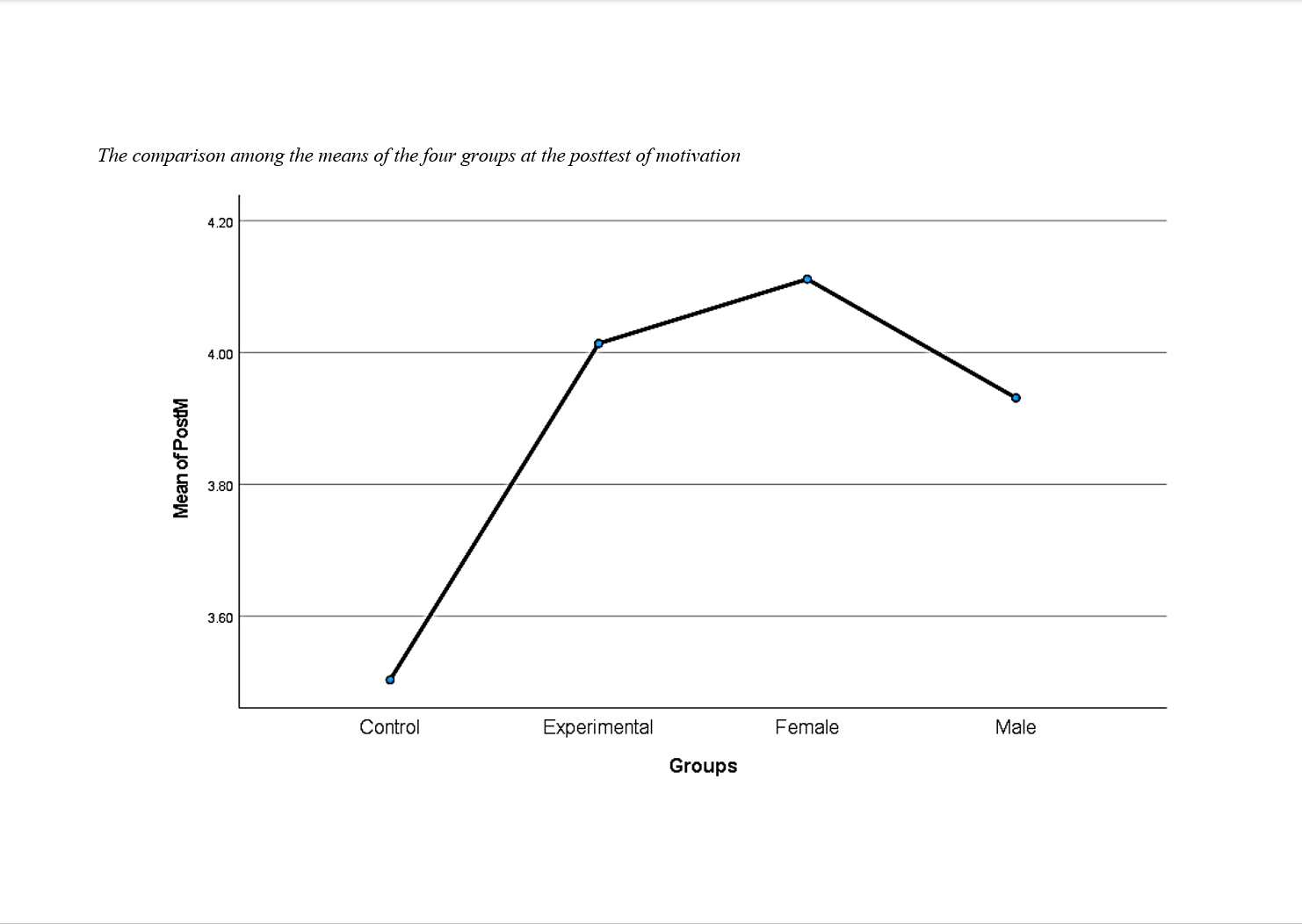
This study aimed to examine the effects of group work dynamics (GWDs) on the motivation of Iranian male and female EFL learners during communicative tasks. This mixed-methods research was conducted with 80 intermediate-level Iranian EFL learners randomly assigned to experimental and control groups. Each group comprised 20 male and 20 female participants. All participants completed a pretest and a posttest assessing speaking performance and motivation. The experimental group received structured group work interventions over 20 sessions featuring communicative tasks such as object assembly, information gap activities, and comic strip storytelling. In contrast, the control group completed the same tasks individually without collaborative strategies. Participants’ interactions were video-recorded for observation, and ten learners were randomly selected for semi-structured interviews. Quantitative data were analyzed using SPSS to conduct descriptive and inferential statistical analyses, including t-tests and ANOVA. Qualitative data from observations and interviews were thematically coded and analyzed to evaluate the complexity and effectiveness of group dynamics. Results revealed that learners in the experimental group showed a statistically significant increase in motivation (M = 4.0138 posttest) compared to the control group (M = 3.5038 posttest), with the difference confirmed by a paired samples t-test (p ≤ .05). Gender-based analysis showed that while male learners experienced a greater gain in motivation (1.036-point increase), female learners had higher absolute motivation scores at both pretest and posttest stages. ANOVA results confirmed significant posttest differences among the four subgroups (male/female, control/experimental), indicating the intervention’s overall impact. Observational data revealed differing gender-based interaction patterns, with males exhibiting competitiveness and females demonstrating collaborative support. Interview responses confirmed that positive group energy and peer support enhanced learner engagement and sustained motivation throughout the program. Group work dynamics significantly improve EFL learners’ motivation when implemented effectively. While both genders benefit, the nature of their interaction influences the quality and style of motivation enhancement.
Downloads
References
Abduramov, M. M. (2017). The effectiveness of using the cooperative language learning approach to enhance EFL writing skills among Saudi University students. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 5(3), 616-630. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276247788_The_Effectiveness_of_Using_the_Cooperative_Language_Learning_Approach_to_Enhance_EFL_Writing_Skills_among_Saudi_University_Students
Akobirove, F. (2017). The influence of technology on language learning and motivation with Uzbek EFL and United States ESL students. https://kuscholarworks.ku.edu/bitstream/handle/1808/25954/Akobirov_ku_0099D_15365_DATA_1.pdf
Alogiliy, M. A. (2024). The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Academic Achievement Mediated by Learning Motivation and Moderated by Socioeconomic Status Among Jordanian EFL Students. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 14(12), 3871-3879. https://doi.org/10.17507/tpls.1412.22
Asl, S. S., Rashtchi, M., & Rezaie, G. (2024). The effects of interactionist versus interventionist dynamic assessment models on Iranian EFL learners' speaking sub-skills: a mixed-method study. Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Language Education, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40862-023-00237-x
Assalihee, M., Boonsuk, Y., Bakoh, N., & Sano, I. L. (2019). Reconceptualizing the 21st century English pedagogies for Islamic school teachers in Asean. Journal of Nusantara Studies (JONUS), 4(1), 401-421. https://doi.org/10.24200/jonus.vol4iss1pp401-421
Collins, A., & Halverson, R. (2018). Rethinking education in the age of technology: The digital revolution and schooling in America. Teachers College Press. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264869053_Rethinking_education_in_the_age_of_technology_the_digital_revolution_and_the_schools
Costley, J., & Lange, C. (2018). The moderating effects of group work on the relationship between motivation and cognitive load. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 19(1), 177-201. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v19i1.3325
De Ruiter, N. M., Elahi Shirvan, M., & Talebzadeh, N. (2019). Emotional processes of foreign-language learning situated in real-time teacher support. Ecol. Psychol., 31, 127-145. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407413.2018.1554368
Derakhshan, A. (2022). The "5Cs" positive teacher interpersonal behaviors: Implications for learner empowerment and learning in an L2 context. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16528-3
Edouard, M., Venuste, N., & Andala, H. O. (2024). Influence of Parental Participation in School Academic Activities on Learners’ Motivation in Rwandan Public Primary Schools; A Case of Huye District. Journal of Education, 6(5), 61-76. https://doi.org/10.53819/81018102t5308
Egitim, S. (2024). Does language teachers' intercultural competence influence oral participation in EFL classrooms?: unveiling learner perspectives through a mixed methods inquiry. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1080/01434632.2024.2306169
Elahi Shirvan, M., & Talebzadeh, N. (2020). Tracing the signature dynamics of foreign language classroom anxiety and foreign language enjoyment: a retrodictive qualitative modeling. Eur. J. Appl. Linguist., 6, 23-44. https://doi.org/10.32601/ejal.710194
Faramarzi Babadi, S., Eskandari Asl, H. A., Dolatyari, F., & Alipoor, H. (2024). Limitations of English Language Learning in Universities of Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province and Strategies to Overcome Them [Research Article]. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology, 7(1), 124-132. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.ijes.7.1.12
Fatehirad, N., Sahragard, R., Razmjoo, S. A., & Ahmadi, A. (2017). Participatory approach from both teachers and EFL learners' perspective. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology, 1(2SP - 157), 175. https://iase-idje.ir/article-1-277-en.pdf
Fitria, T. N. (2024). Understanding the Educational Psychology and English Language Teaching: Insights for Both EFL and Non-Efl Learners. Jetlee Journal of English Language Teaching Linguistics and Literature, 4(1), 37-53. https://doi.org/10.47766/jetlee.v4i1.1932
Hamad, M. M., Metwally, A. A., & Alfaruque, S. Y. (2019). The Impact of Using YouTubes and Audio Tracks Imitation YATI on Improving Speaking Skills of EFL Learners. English Language Teaching, 12IS - 6, 191-198. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v12n6p191
Han, Z. H. (2019). Profiling learner language as a dynamic system. Multilingual Matters. https://doi.org/10.21832/9781788922807
Hu, X., Huang, Z., & Yang, M. (2023). Profiles of EFL Learners’ Online Self-regulation and Their Relationship with Dimensions of Self-determination Motivation in Mainland China. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 32(5), 685-694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-022-00686-x
Kreutz, J., & Rhodin, N. (2016). The influence of ICT on learners' motivation towards English. https://muep.mau.se/bitstream/handle/2043/20747/Degree%20Project%20Josefin%20&%20Natalie.pdf?s
Li, Y. (2023). The effect of online collaborative writing instruction on enhancing writing performance, writing motivation, and writing self-efficacy of Chinese EFL learners. Frontiers in psychology, 14, 1165221. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1165221
Mirzaei, A., Shakibaei, L., & Jafarpour, A. (2017). ZPD- based dynamic assessment and collaborative L2 vocabulary learning. The Journal of Asia TEFL., 14(1), 114-129. https://doi.org/10.18823/asiatefl.2017.14.1.8.114
Mugala, L., & Kabeta, R. M. (2023). Head Teacher’s Motivational Strategies for Teachers and Their Effect on Learners’ Academic Performance in Public Secondary Schools in Ndola District, Zambia. European Modern Studies Journal, 7(5), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.59573/emsj.7(5).2023.1
Namaziandost, E., Esfahani, F. R. A. U. N. M., & Mirshekaran, R. (2018). The effect of gallery walk technique on pre-intermediate EFL learners" speaking skill. Language Teaching Research Quarterly, 8, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.32038/ltrq.2018.08.01
Paquot, M., & Plonsky, L. (2017). Quantitative research methods and study quality in learner corpus research. International Journal of Learner Corpus Research, 3, 61-94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-008-9139-5
Rahimi, M. (2019). The role of teacher's corrective feedback in improving Iranian EFL learners' writing accuracy over time: Is learner's mother tongue relevant? Reading and Writing, 22(2), 219-243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-008-9139-5
Rajaee Harandi, S. (2015). Effects of e- learning on students' motivation. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 181, 423-430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.905
Sample, M. (2015). Authentic materials: A motivational tool for the EFL classroom? Educational and Linguistics Research, 1(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.5296/elr.v1i2.8488
Savasci, M., & Kaygisiz, S. (2019). One hand washes the other and both wash the face: Individuality versus collaboration in L2 writing. Eurasian Journal of Applied Linguistics, 5(1), 131-151. https://doi.org/10.32601/ejal.543789
Weyage, A., & Adade, R. (2024). Entry Behaviour, Learner Motivation, Self-Regulation and Academic Performance of First Year ICT Students: Evidence From Kibi Technical Institute. Ijcs, 2(4), 243-264. https://doi.org/10.55927/ijcs.v2i4.8934
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Arya Farshood (Author); Behzad Aghajanzadeh Kiasi (Corresponding Author); Hosein Siahpoosh, Davood Taghipour Bazargani (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







