Structural Model of Children’s Behavioral Problems Based on Mothers’ Adverse Childhood Experiences with the Mediating Role of Maternal Mentalization
Keywords:
Adverse childhood experiences, Mentalization, Internalizing behavioral problems, Externalizing behavioral problemsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the structural model of children’s behavioral problems based on mothers’ adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), with maternal mentalization as a mediating factor.
Methods and Materials: A correlational design using structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed. The sample consisted of 323 mothers with children aged 6 to 12 years in Isfahan, selected through convenience sampling during 2023–2024. Data were collected using the World Health Organization’s Adverse Childhood Experiences International Questionnaire (ACE-IQ), the Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) parent version, and the Persian version of the Reflective Functioning Questionnaire (Mentalization Questionnaire). Data analysis was conducted using SPSS-24 and AMOS-24, applying confirmatory factor analysis, maximum likelihood estimation, and bootstrapping with 2,000 resamples to test direct and indirect pathways.
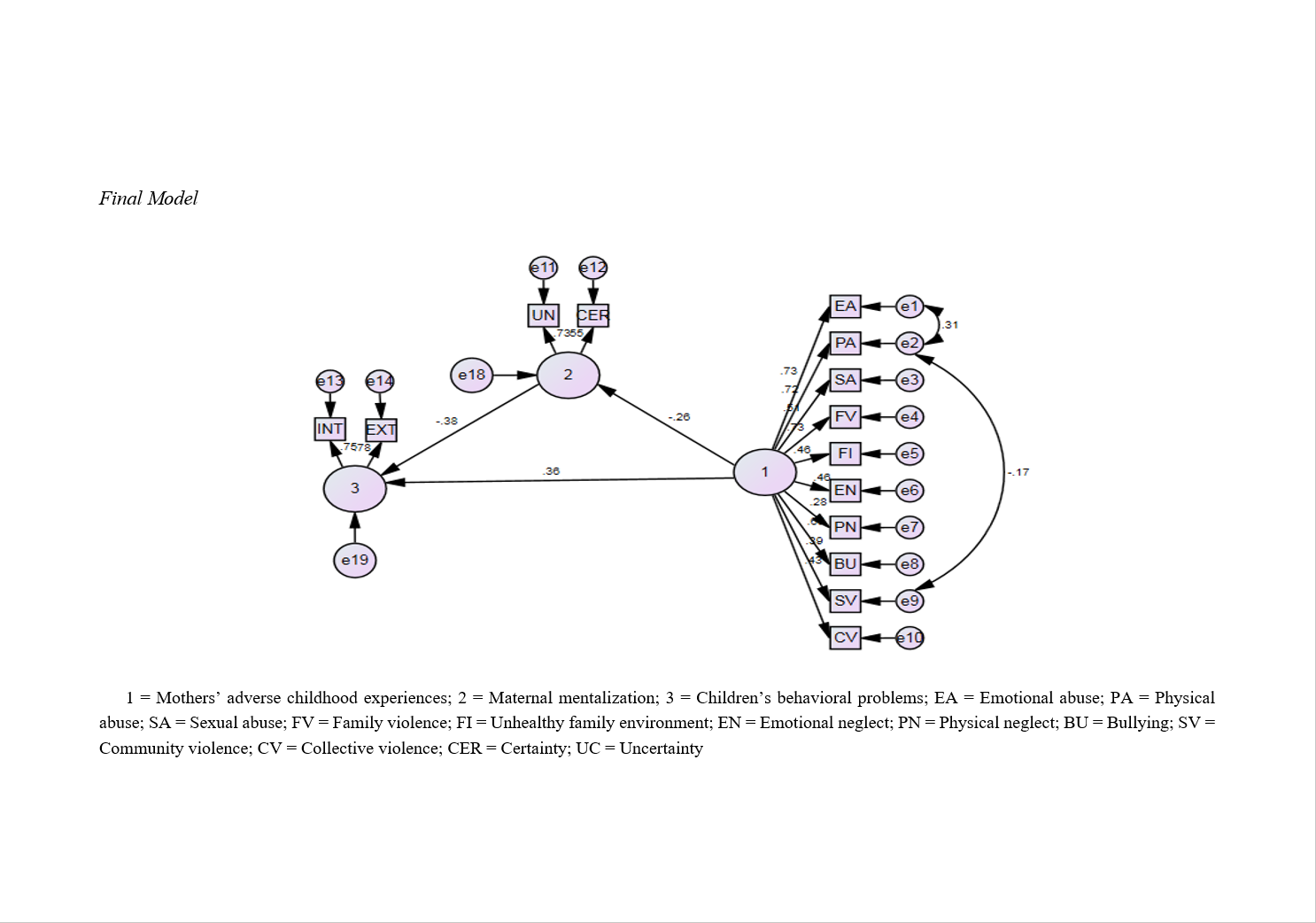
Findings: The results revealed that maternal ACEs were positively and significantly associated with children’s internalizing and externalizing behavioral problems. Maternal ACEs were also negatively and significantly related to maternal mentalization. In turn, maternal mentalization showed a significant negative relationship with children’s behavioral problems. Structural modeling confirmed that maternal mentalization partially mediated the relationship between maternal ACEs and children’s behavioral outcomes. Bootstrapping results demonstrated that the indirect effects of maternal ACEs on both internalizing and externalizing problems through maternal mentalization were statistically significant. Model fit indices indicated acceptable to excellent fit across all parameters, supporting the robustness of the structural model.
Conclusion: The findings highlight the intergenerational transmission of adversity, demonstrating that mothers’ adverse childhood experiences contribute to children’s behavioral problems both directly and indirectly through diminished maternal mentalization. Strengthening maternal reflective functioning may serve as a critical intervention target to reduce the negative impact of maternal trauma histories on child behavioral outcomes. These results emphasize the importance of trauma-informed, family-centered interventions to disrupt cycles of adversity and promote healthier socioemotional development in children.
Downloads
References
Abd Rahim, M. H., Ibrahim, M. I., Ab Rahman, A., Yaacob, N. M., & Hashim, N. S. F. (2023). Emotional and Behavioural Problems among Preschool Children in Northeast Peninsular Malaysia: Parent Report Version. Healthcare, 11(13), 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131828
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2007). Multicultural Understanding of Child and Adolescent Psychopathology: Implications for Mental Health Assessment. The Guilford Press. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225988748_Thomas_M_Achenbach_and_Leslie_A_Rescorla_Multicultural_Understanding_of_Child_and_Adolescent_Psychopathology_Implications_for_Mental_Health_Assessment
Adkins, T., Reisz, S., Doerge, K., & Nulu, S. (2020). Adverse Childhood Experience Histories in Foster Parents: Connections to Foster Children's Emotional and Behavioral Difficulties. Child abuse & neglect, 104, 104475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104475
Alvarez, N., Lazaro, M. H., Gordo, L., Elejalde, L. I., & Pampliega, A. M. (2022). Maternal Mentalization and Child Emotion Regulation: A Comparison of Different Phases of Early Childhood. Infant Behavior and Development, 66, 101681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2021.101681
Arikan, G., & Kumru, A. (2020). Patterns of Associations Between Maternal Symptoms and Child Problem Behaviors. Child Psychiatry & Human Development. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2020-64893-001
Brown, S. M., Doom, J. R., Lechuga-Peña, S., Watamura, S. E., & Koppels, T. (2020). Stress and Parenting during the Global COVID-19 Pandemic. Child abuse & neglect, 110, 104699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104699
Cooke, J. E., Racine, N., Plamondon, A., Tough, S., & Madigan, S. (2019). Maternal Adverse Childhood Experiences, Attachment Style, and Mental Health: Pathways of Transmission to Child Behavior Problems. Child abuse & neglect, 93, 27-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2019.04.011
Dorouger, E., Fathi Ashtiani, A., & Ashrafi, E. (2020). Validation and Reliability Testing of the Persian Version of the Mentalization Questionnaire. Clinical Psychology, 12(1), 1-12. https://jcp.semnan.ac.ir/article_4434.html
Driscoll, K. J. (2023). Human services case managers' perceptions of their adverse childhood experiences and professional practice, A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Capella University].
Fonagy, P. (2018). Affect Regulation, Mentalization and the Development of the Self. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429471643
Gil, M. (2023). Collecting trauma history in latinx clients: A therapy review investigation of the adverse childhood experiences questionnaire Capella University].
Hughes, C., & Aldercotte, A. A. U. F. S. (2017). Maternal Mind-Mindedness Provides a Buffer for Pre-Adolescents at Risk for Disruptive Behavior. Journal of abnormal child psychology, 45(2), 225-235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-016-0165-5
Hughes, K., Bellis, M. A., Hardcastle, K. A. A. U. S. D., Butchart, A., Mikton, C., Jones, C., & Dunne, M. P. (2017). The Effect of Multiple Adverse Childhood Experiences on Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Lancet Public Health, 2(8), e356-e366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(17)30118-4
Jimenez, M. E., Wade, R., Jr., Yong, L., Morrow, L. M., & Reichman, N. E. (2016). Adverse Experiences in Early Childhood and Kindergarten Outcomes. Pediatrics, 137(2), e20151839. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-1839
Kajani, M., & Raeisi, Z. (2018). Investigating the Effectiveness of Drama Therapy on Working Memory and Behavioral Problems of Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Primary School Islamic Azad University, Najafabad Branch].
Letourneau, N., Dewey, D., Kaplan, B. J., Ntanda, H., Novick, J., Thomas, J. C., the, A. S. T., & Lawson, C. M. C. (2023). Intergenerational Transmission of Adverse Childhood Experiences via Maternal Depression and Anxiety and Moderation by Child Sex The impact of pre-military therapy on post-military posttraumatic stress disorder severity in veterans with adverse childhood experiencesPB - Azusa, California. Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, 10(1), 88-99. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2040174418000648
Lucenko, B. A., Sharkova, I. V., Huber, A. A. U. J. R., & Mancuso, D. (2015). Childhood Adversity and Behavioral Health Outcomes for Youth: An Investigation Using State Administrative Data. Child abuse & neglect, 47, 748-758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2015.07.006
Lupien, S. J., Juster, R. P., Raymond, C., & Marin, M. F. (2018). The Effects of Chronic Stress on the Human Brain: From Neurotoxicity to Vulnerability to Opportunity. Frontiers in neuroendocrinology, 49, 91-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.02.001
Madigan, S., Wade, M., Plamondon, A., McDonald, S., Racine, N., & Jenkins, J. (2017). Maternal Adverse Childhood Experience and Infant Health: Biomedical and Psychosocial Risks as Intermediary Mechanisms. Journal of Pediatrics, 187, 282-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.052
Marsicek, S. M., Morrison, J. M., Manikonda, N., O'Halleran, M., Spoehr-Labutta, Z., & Brinn, M. (2019). Implementing standardized screening for adverse childhood experiences in a pediatric resident continuity clinic. Pediatric Quality & Safety, 4(2), e154. https://doi.org/10.1097/pq9.0000000000000154
McDonald, S. W., Madigan, S., Racine, N., Benzies, K., Tomfohr, L., & Tough, S. (2019). Maternal Adverse Childhood Experiences, Mental Health, and Child Behavior at Age 3: The All Our Families Community Cohort Study. Preventive Medicine, 118, 286-294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.11.013
Merrick, M. T., Ford, D. C., Ports, K. A., Guinn, A. S., Chen, J., Klevens, J., Metzler, M., Jones, C. M., Simon, T. R., Daniel, V. M., Ottley, P., & Mercy, J. A. (2019). Vital Signs: Estimated proportion of adult health problems attributable to Adverse Childhood Experiences and implications for prevention - 25 states, 2015-2017. MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 68, 99-1005. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6844e1
Racine, N., Plamondon, A., Madigan, S., McDonald, S., & Tough, S. (2018). Maternal Adverse Childhood Experiences and Infant Development. Pediatrics, 141(4), e20172495. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-2495
Schickedanz, A., Halfon, N., Sastry, N., & Chung, P. J. (2018). Parents' Adverse Childhood Experiences and Their Children's Behavioral Health Problems. Pediatrics, 142(2), e20180023. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2018-0023
Schiff, M., Pat-Horenczyk, R., Ziv, Y., & Brom, D. (2017). Multiple Traumas, Maternal Depression, Mother–Child Relationship, Social Support, and Young Children’s Behavioral Problems. Journal of interpersonal violence, 36(1-2), 892-914. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260517725738
Seçer, İ., Ulaş, S., Tatlı, E., Çi̇men, F., Bülbül, B., & Tosunoğlu, B. (2025). Investigation of the Effectiveness of Parent-Child Interaction Therapy on Adjustment and Behavioral Problems in Children With Subthreshold Autism. Frontiers in psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1408847
Senehi, N., Brophy-Herb, H. E., & Vallotton, C. D. (2018). Effects of maternal mentalization-related parenting on toddlers' self-regulation. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 44, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2018.02.001
Sklyarov, O. (2019). The Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences on Attachment and Mentalization in Sex Offenders Capella University]. https://digitalcommons.georgefox.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1263&context=psyd
Smaling, H. J., Huijbregts, S. C., van der Heijden, K. B., van Goozen, S. H., & Swaab, H. (2016). Maternal Reflective Functioning as a Multidimensional Construct: Differential Associations with Children's Temperament and Externalizing Behavior. Infant Behavior & Development, 44, 263-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2016.06.007
Sullivan, M. J., Pruett, M. K., & Johnston, J. R. (2024). Parent‐child contact problems: Family violence and parental alienating behaviors either/or, neither/nor, both/and, one in the same? Family Court Review, 62(1), 68-85. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcre.12764
Tavakoli, S., Abbasi, F., Heydari, B., & Akhondzadeh, M. (2024). Comparing the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Play Therapy and Gestalt Play Therapy on Vandalistic Behaviors, Impulsivity, and Cognitive Flexibility in Aggressive Male Elementary Students. Journal of Assessment and Research in Applied Counseling (JARAC), 6(3), 28-36. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jarac.6.3.4
Wagner-Skacel, J., Riedl, D., Kampling, H., & Lampe, A. (2022). Mentalization and Dissociation After Adverse Childhood Experiences. Scientific reports, 12(1), 6809. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10787-8
World Health Organization. (2018). Adverse Childhood Experiences International Questionnaire (ACE-IQ). WHO. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/adverse-childhood-experiences-international-questionnaire-(ace-iq)
Yousefi Khaneh Bargh, H., & Zeynali, A. (2024). The role of child temperament and maternal attachment and parenting styles in predicting behavioral problems in 3-5 year-old children with working mothers. Quarterly Journal of Child Mental Health, 11(1), 61-47. https://doi.org/10.61186/jcmh.11.1.5
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mina Kejani (Author); Mojtaba Ansari Shahidi (Corresponding Author); Salar Faramarzi , Mostafa Khanzadeh (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.