The Impact of a Bodyweight-Based Exercise Program (through Quadrupedal Movement Exercises) on Motor Competence and Functional Movement in Children Aged 8 to 10 Years
Keywords:
Bodyweight exercises, quadrupedal movement exercises, motor competence, functional movement, childrenAbstract
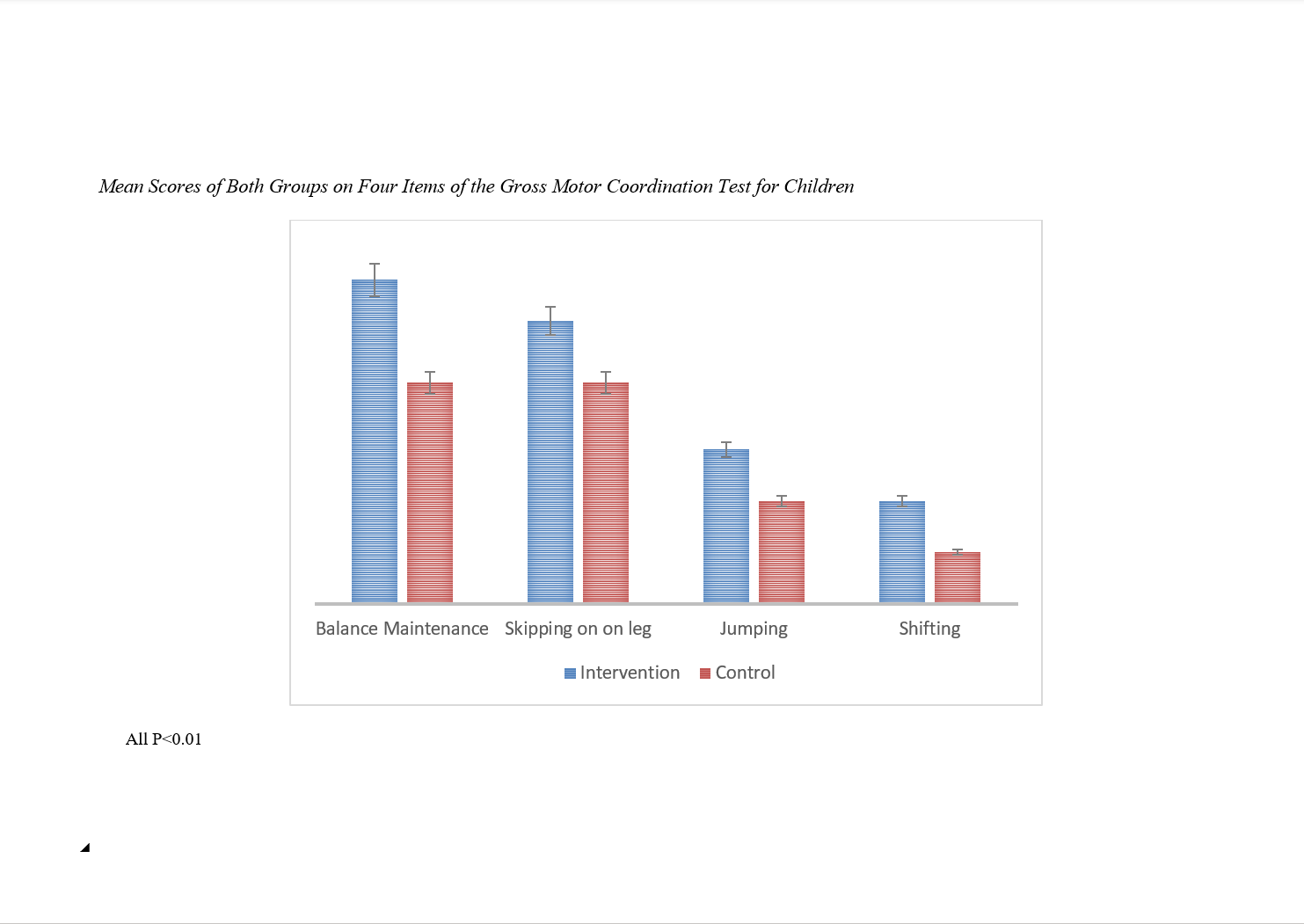
This study aimed to examine the effect of a bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises on motor competence and functional movement in children aged 8 to 10 years. In this quasi-experimental study, designed with a control group and pre-test–post-test format, 40 male participants aged 8 to 10 years from elementary schools in Bagh Malek County were selected. Participants were randomly assigned to either the intervention or control group. In the pre-test phase, functional movement and motor competence were measured using the Functional Movement Screening (FMS) test and the Pediatric Gross Motor Coordination Test, respectively. Subsequently, the intervention group participated in a bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movements for three 45-minute sessions per week over eight weeks. During this period, the control group attended only daily physical education classes. In each session, participants followed the bodyweight-based exercise protocol, which was presented through a pre-recorded video shown on a large display. All exercise sessions were conducted in groups and followed a specific system designed for these exercises, led by a certified instructor. Participants’ techniques were monitored, and adjustments were made when necessary. Finally, the dependent variables were re-measured in the post-test phase. Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-tests to compare pre- and post-test scores within each group, and independent t-tests to compare changes between the intervention and control groups. The bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises improved motor competence and functional movement in the intervention group, showing that the intervention program effectively impacted various aspects of motor competence and functional movement patterns, with all changes being significant compared to the control group (p ≤ 0.05). The bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises significantly improved motor competence and functional movement in children aged 8 to 10 years. Bodyweight-based exercises may serve as an effective intervention to enhance motor competence and functional movement in this age group.
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohamad Fatollahi (Author); Marzie Balali (Corresponding Author); Rasool Abedanzadeh , Behnam Maleki (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

























