The Effect of Continuous and Interval Aerobic Exercise Combined with Loquat Leaf Consumption on the Oxidative and Antioxidant Capacity in Overweight Women
Keywords:
Continuous aerobic exercise, interval aerobic exercise, loquat leaf, oxidative capacity, antioxidant capacityAbstract
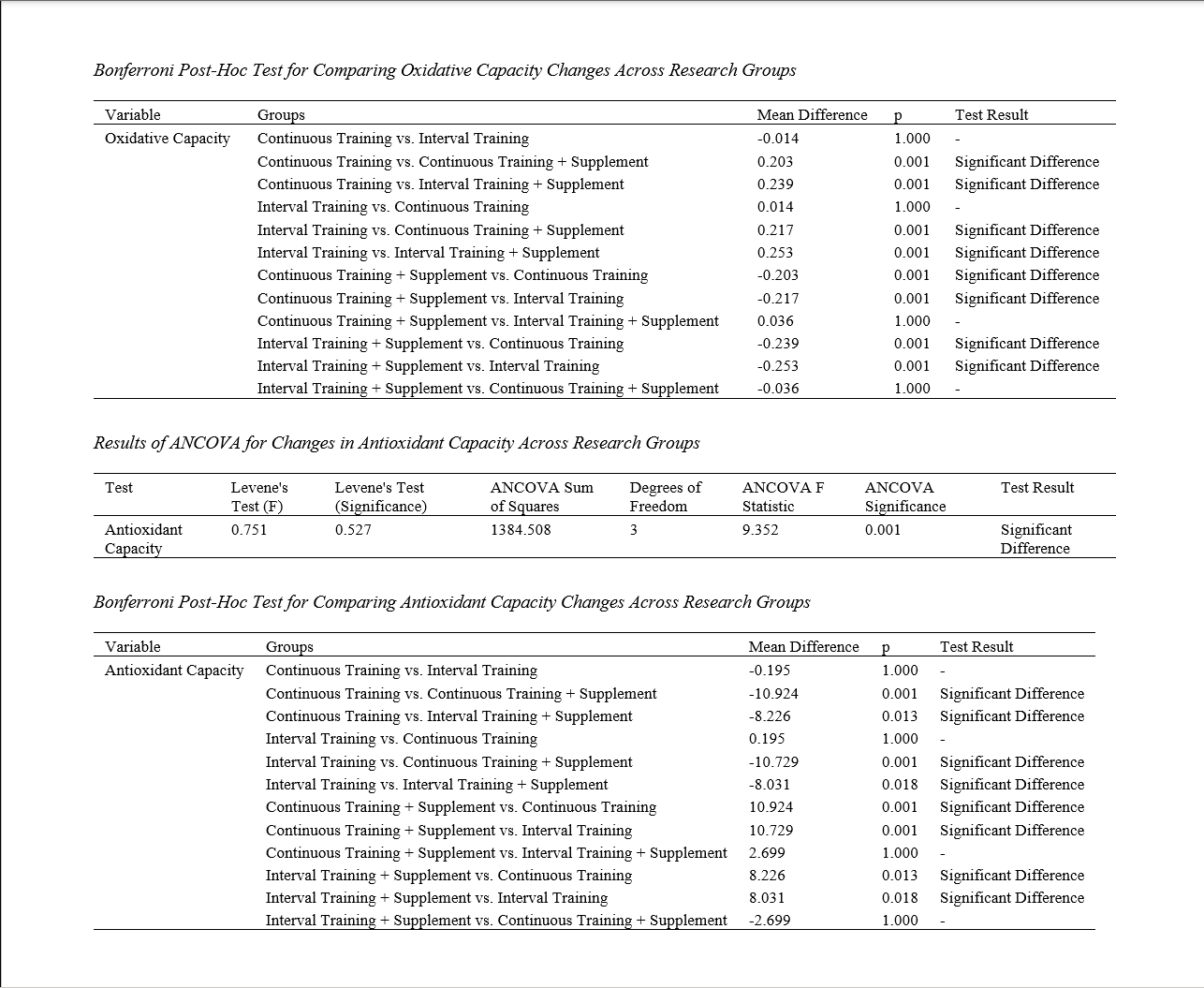
The present study aimed to determine the effect of continuous and interval aerobic exercise combined with loquat leaf consumption on the oxidative and antioxidant capacity in overweight women. The research method was quasi-experimental, with a pre-test and post-test design. Sixty overweight women from Qom city were purposefully divided into four equal groups of 15 participants: continuous aerobic exercise, interval aerobic exercise, continuous aerobic exercise combined with loquat leaf consumption, and interval aerobic exercise combined with loquat leaf consumption. The exercise protocol was conducted over eight weeks with three sessions per week. The continuous aerobic exercise program included continuous running without rest at an intensity of 55-60% of the heart rate reserve. The interval training program consisted of interval runs at distances of 100, 200, 300, 400, and 600 meters, with an intensity of 80-85% of the heart rate reserve. Data were analyzed using ANCOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test. The findings showed that continuous aerobic exercise combined with loquat leaf consumption significantly affected the oxidative capacity of overweight women. ANCOVA results indicated a significant difference in oxidative capacity between the four groups. Bonferroni post-hoc test results revealed a significant difference between the continuous and interval exercise groups and the two combined groups (continuous exercise with supplementation and interval exercise with supplementation). Additionally, the results demonstrated that aerobic exercise combined with loquat leaf consumption significantly affected the antioxidant capacity of overweight women. ANCOVA results indicated a significant difference in antioxidant capacity between the four groups, rejecting the null hypothesis and confirming the research hypothesis. The Bonferroni post-hoc test results further revealed a significant difference between the continuous and interval exercise groups and the two combined groups (continuous exercise with supplementation and interval exercise with supplementation). Based on the results, the combination of continuous and interval aerobic exercise with loquat leaf consumption is an effective method for improving the oxidative and antioxidant capacity in overweight women.
Downloads
References
1. Muskan F, Jain S, Bains K. Efficacy of short-term cognitive group treatment to reduce obesity among overweight Indian women: a randomized control trial. Current Science (00113891). 2024;126(3):1-8.
2. Tiwari A, Balasundaram P. Public Health Considerations Regarding Obesity. In StatPearls [Internet]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572122/: StatPearls Publishing Treasure Island (FL); 2023.
3. Chen HH, Lee CF, Huang JP, Hsiung Y, Chi LK. Effectiveness of a nurse‐led mHealth app to prevent excessive gestational weight gain among overweight and obese women: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Nursing Scholarship. 2023;55(1):304-18. [DOI]
4. Tabatabaei Melazi A, Larijani B. A review of the prevalence and management of obesity in Iran. Iranian Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism. 2013;12(5):374-57.
5. Lindberg L, Hagman E, Danielsson P, Marcus C, Persson M. Anxiety and depression in children and adolescents with obesity: a nationwide study in Sweden. BMC medicine. 2020;18(1):1-9. [DOI]
6. Sohrabi F, Pasha R, Naderi F, Asgari P, Ehtesham Zadeh P. The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy on body mass index and self-concept in overweight individuals. Journal of Iranian Nutrition and Food Sciences. 2017;12(4):43-51.
7. Rayner G, Lang T. Obesity: Using the Ecologic Public Health Approach to Overcome Policy Cacophony. Clinical obesity in adults and children2010. p. 452[DOI]
8. Khoury M, Manlhiot C, McCrindle BW. Role of the waist/height ratio in the cardiometabolic risk assessment of children classified by body mass index. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2013;62(8):742-51. [DOI]
9. Brellenthin AG, Lee DC, Bennie JA, Sui X, Blair SN. Resistance exercise, alone and in combination with aerobic exercise, and obesity in Dallas, Texas, US: A prospective cohort study. PLoS medicine. 2021;18(6):e1003687. [DOI]
10. Atashak S, Niloufari A, Azizbighi K. The effect of short-term supplemental Blackberry extract on total antioxidant capacity of the plasma and lipid oxidation index of obese men following one session of resistance activity. Food Science and Nutrition. 2014;11(Spring 1393):55-62.
11. Radak Z, Chung HY, Koltai E, Taylor AW, Goto S. Exercise, oxidative stress and hormesis. Ageing research reviews. 2008;7(1):34-42. [DOI]
12. Bae D, You Y, Yoon HG, Kim K, Lee YH, Kim Y, et al. Protective effects of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) leaves against ethanol-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells transfected with CYP2E1. Food Science and Biotechnology. 2010;19(4):1093-6. [DOI]
13. Xiao S, Wang W, Liu Y. Research Progress on Extraction and Separation of Active Components from Loquat Leaves. Separations. 2023;10(2):126. [DOI]
14. Mun J, Park J, Yoon HG, You Y, Choi KC, Lee YH, et al. Effects of eriobotrya japonica water extract on alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver impairment. Journal of medicinal food. 2019;22(12):1262-70. [DOI]
15. Akbarpour M, Fathollahi Shoorabeh F, Mardani M, Amini Majd F. Effects of Eight Weeks of Resistance Training and Consumption of Pomegranate on GLP-1, DPP-4 and Glycemic Statuses in Women with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrition and Food Sciences Research. 2021;8(1):5-10.
16. Siahkouhian M. Practical Tests of Cardiovascular Fitness. Tehran: Yazdani Publications; 2016.
17. Behout Moghadam T, Mosaferi Ziyaldini M, Fathi M, Attarzadeh Hosseini SR. A review of the effects of high-intensity interval training on obesity-related hormones. Research in Sports Sciences and Medicinal Plants. 2020;1(1):1-18.
18. Hazell TJ, Hamilton CD, Olver TD, Lemon PW. Running sprint interval training induces fat loss in women. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2014;39(8):944-50. [DOI]
19. Martins C, Morgan LM, Bloom SR, Robertson MD. Effects of exercise on gut peptides, energy intake and appetite. Journal of Endocrinology. 2007;193(2):251-8. [DOI]
20. Jakicic JM, Powell KE, Campbell WW, Dipietro L, Pate RR, Pescatello LS, et al. Physical activity and the prevention of weight gain in adults: a systematic review. Medicine and science in sports and exercise. 2019;51(6):1262. [DOI]
21. Tondpa Khanaqahi B, Dehkhoda MR, Amani Shalamzari S. Improvement of aerobic capacity and health status in overweight patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through high-intensity aerobic interval training. Payavard Health. 2019;13(1):71-80.
22. Bahram M, Afzondeh R, Ghayami Taklami SH, Sadeghi A, Gholamhosseini M. The effect of high-intensity interval training and loquat leaf extract on liver enzymes in obese men with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Quarterly Journal of Complementary Medicine. 2021;11(2):102-15. [DOI]
23. Baratzadeh Shokri M, Fathi R, Talebi Garkani E, Safarzadeh A. The effect of 8 weeks of aerobic exercise on plasma levels of Apolipoprotein M in women with normal weight and overweight. Journal of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. 2014;57(7):852-8.
24. Nikro H. Comparison of the effects of intermittent and continuous aerobic training programs on maximum oxygen consumption, body mass index, and body fat percentage in military students. Military Medicine. 2022;15(4):245-51.
25. Nelson ME, Rejeski WJ, Blair SN, Duncan PW, Judge JO, King AC. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(8):1435-45. [DOI]
26. Cho YH, Lee SY, Kim CM, Kim ND, Choe S, Lee CH, et al. Effect of loquat leaf extract on muscle strength, muscle mass, and muscle function in healthy adults: A randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled trial. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016. [DOI]
27. Roozbehan B, Abed Natanzai H, Ebrahim K, Ghazalian F. The effect of aerobic exercise and pomegranate juice consumption on serum levels of oxidative and antioxidant enzymes in breast cancer survivors. Journal of Iranian Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Infertility. 2021;24(6):25-35.
28. Naghi Zadeh H, Heidari F. The effect of twelve weeks of high-intensity interval training and curcumin supplementation on oxidative markers in obese men with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Exercise Physiology and Physical Activity. 2022;15(4):67-81. [DOI]
29. Moradpourian MR, Shakermi N. The effect of eight weeks of resistance training on oxidative/antioxidant indices in middle-aged women with type 2 diabetes. Research in Life Sciences and Physical Activity. 2017;4(7):1-8.
30. Sani S, editor The effect of aerobic exercise and peanut supplementation on total antioxidant capacity and serum malondialdehyde in overweight women. Second National Conference on Applied Sports Sciences and Wellness; 2016; Tabriz.
31. Ribeiro AS, Avelar A, dos Santos L, Silva AM, Gobbo LA, Schoenfeld BJ, et al. Hypertrophy-type resistance training improves phase angle in young adult men and women. International journal of sports medicine. 2017;38(1):35-40. [DOI]
32. Soares JP, Silva AM, Oliveira MM, Peixoto F, Gaivão I, Mota MP. Effects of combined physical exercise training on DNA damage and repair capacity: role of oxidative stress changes. Age. 2015;37(3):61. [DOI]
33. Bouzid MA, Filaire E, McCall A, Fabre C. Radical oxygen species, exercise and aging: an update. Sports Medicine. 2015;45(9):1245-61. [DOI]
34. Johnson ML, Irving BA, Lanza IR, Vendelbo MH, Konopka AR, Robinson MM, et al. Differential effect of endurance training on mitochondrial protein damage, degradation, and acetylation in the context of aging. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2014;70(11):1386-93. [DOI]
35. Mitranun W, Deerochanawong C, Tanaka H, Suksom D. Continuous vs interval training on glycemic control and macro‐and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports. 2014;24(2):e69-e76. [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nahid Afshari Fard (Author); Jamshid Banai (Corresponding Author); Elham Eftekhari , Saeed Keshavarz (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















