Effectiveness of Group Hypnotherapy on Stress and Metacognitive Beliefs in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis
Keywords:
Hypnosis, Stress, Metacognitive Beliefs, Multiple SclerosisAbstract
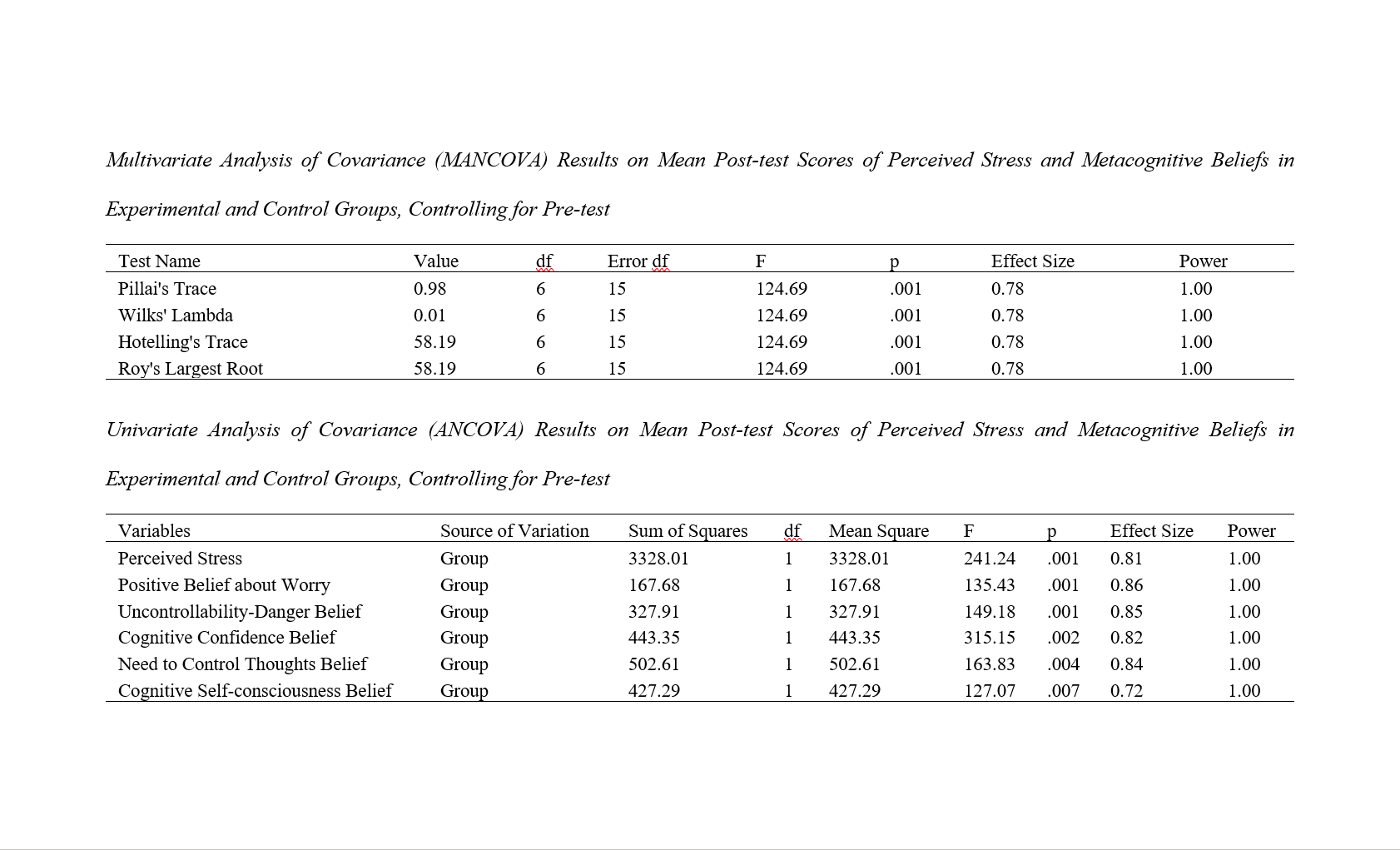
The objective of the present study was to investigate the effectiveness of group hypnotherapy on stress and metacognitive beliefs in individuals with multiple sclerosis. The research method was experimental (pre-test, post-test design with an equal control group). The research sample consisted of 30 individuals with multiple sclerosis, selected through purposive sampling. Subsequently, from the research sample, 15 individuals with multiple sclerosis were randomly assigned to the experimental group and 15 individuals with multiple sclerosis were assigned to the control group. The research instruments included the Cohen et al. (1983) Stress Questionnaire and the Wells (2004) Metacognitive Beliefs Questionnaire. Data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) methods. The results of data analysis indicated that group hypnotherapy resulted in a reduction of perceived stress and metacognitive beliefs in individuals with multiple sclerosis in the experimental group compared to the control group. Consequently, it can be concluded that group hypnotherapy with hypnotic techniques is an effective method for reducing perceived stress and metacognitive beliefs in individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Downloads
References
1. Donisi V, Poli S, Berti L, Gobbin F, Giusto G, Capurso M, et al. Combining acceptance and commitment therapy with adventure therapy to face vulnerability: Examples and insights from a sailing experience. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science. 2024:100759. [DOI]
2. Prakash RS. Mindfulness Meditation: Impact on Attentional Control and Emotion Dysregulation. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 2021;36(7):1283-90.
3. Rezaei Z, Abolghasemi S, Khalatbari J, Zarbakhsh R. The effectiveness of a training package based on motivational interviewing, therapy based on acceptance and commitment, and therapy focused on compassion on tolerance of failure and health anxiety in patients with multiple sclerosis. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS). 2023;4(2):86-96. [DOI]
4. Sadovnick AD, Dyment DA, Ebers GC, Risch NJ, the Canadian Collaborative Study G. Evidence for genetic basis of multiple sclerosis. The Lancet. 1996;347(9017):1728-30. [PMID: 8656905] [DOI]
5. Marsool MDM, Prajjwal P, John J, Keluskar HS, Sivarajan VV, Kundiri KA, et al. Association of multiple sclerosis with stroke: A comprehensive review. Health Science Reports. 2024;7(1):e1837. [PMID: 38264155] [PMCID: PMC10804671] [DOI]
6. Sandesjö F, Tremlett H, Fink K, Marrie RA, Zhu F, Wickström R, et al. Incidence rate and prevalence of pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis in Sweden: A population-based register study. European Journal of Neurology. 2024;31(5):e16253. [PMID: 38369806] [DOI]
7. Schlindwein MAM, Campos MHdM, Breis LC, Chara BS, Scherer CS, Caminski VAP, et al. Impacts of environmental tobacco smoke on the onset and progression of multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Arquivos de Neuro-psiquiatria. 2024;82(3):s00441779271. [DOI]
8. Goli ZS, Mirseify fard LS. The role of Metacognitive Beliefs and Resilience on Predicting Marital Adjustment in Both Groups of Patients with Chronic and Acute Pain. Journal of Assessment and Research in Applied Counseling (JARAC). 2021;3(3):55-63. [DOI]
9. Wells A. Metacognitive therapy for anxiety and depression. New York, NY, US: Guilford Press; 2009. xvii, 316-xvii, p
10. Kirsch I, Montgomery G, Sapirstein G. Hypnosis as an adjunct to cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy: A meta-analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1995;63(2):214-20. [PMID: 7751482] [DOI]
11. Patterson DR, Everett JJ, Burns GL, Marvin JA. Hypnosis for the treatment of burn pain. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1992;60(5):713-7. [PMID: 1383302] [DOI]
12. Moghtaderi S, Mirzamani S-M, Bahrami H. The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in the treatment of subjective tinnitus. Auditory and Vestibular Research. 2017;21(4).
13. Pasha G, Bozorgian R. The Relationship Between Metacognition, Perfectionism And Self-Efficacy, With Perceived Stress In The Students Of Azad Ahvaz University. Journal of Social Psychology (New Findings in Psychology). 2011.
14. Kianpour Barjoee L, Amini N, Keykhosrovani M, Shafiabadi A. Effectiveness of Positive Thinking Training on Perceived Stress, Metacognitive Beliefs, and Death Anxiety in Women with Breast Cancer: Perceived Stress in Women with Breast Cancer. Archives of Breast Cancer. 2022;9(2):195-203. [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ebrahim Habibi Khalifehloo (Author); Farah Naderi (Corresponding Author); Saeed Bakhtiarpour, Naser Seraj Khorami (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















