Comparison of Visual and Auditory Reaction Times in Athletes and Sedentary Individuals with Different Somatotypes: A Neuroperformance Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.intjssh.3.1.5Keywords:
Somatotype, Reaction Time, Anthropometry, Neuroperformance, AthleteAbstract
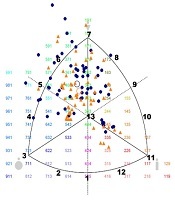
Background: Body composition, which is affected by body fat ratio is an important factor affecting parameters such as strength, endurance, flexibility and agility required for superiority in sportive performance. Objectives: The aim of this study is to compare visual (VRT) and auditory (ART) reaction times of athletes and sedentary individuals with different somatotypes. Methods: The study included 148 individuals (73 athletes and 75 sedentary) with no symptoms. Somatotype character analysis was performed with Somatotype (1.2.6 trial) program using Heath-Carter formula after the determined anthropometric measurements were taken. Reaction time measurements were performed with Hubbard reaction meter. Results: Six different somatotypes were determined in both sedentary and athlete groups that participated in the study. In the comparison of VRT and ART scores of athletes and sedentary individuals in terms of each somatotype, statistically significant difference was found in VRT score in balanced ectomorph somatotype and in both VRT and ART scores of endomorphic mesomorph somatotype (P < 0.05). Conclusions: We think that regular training and sports shorten VRT and ART. We presume that these characteristics of athletes shorten their reaction times since sports events require more concentration. The results of our study are interesting in terms of being a new subject for scientists working in this field.Downloads
Downloads
Published
2020-02-08
Issue
Section
Articles
How to Cite
Şenol, D., Altınoğlu, M., Kısaoğlu, A., Toy, Şeyma, Duz, S., & Ozbağ, D. (2020). Comparison of Visual and Auditory Reaction Times in Athletes and Sedentary Individuals with Different Somatotypes: A Neuroperformance Study. International Journal of Sport Studies for Health, 3(1), 27-32. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.intjssh.3.1.5




