The Impact of Socio-Economic Status and Physical Activity on Psychological Well-being and Sleep Quality Among College Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Keywords:
COVID-19, college students, socio-economic status, physical activity, psychological well-being, sleep quality, gender differencesAbstract
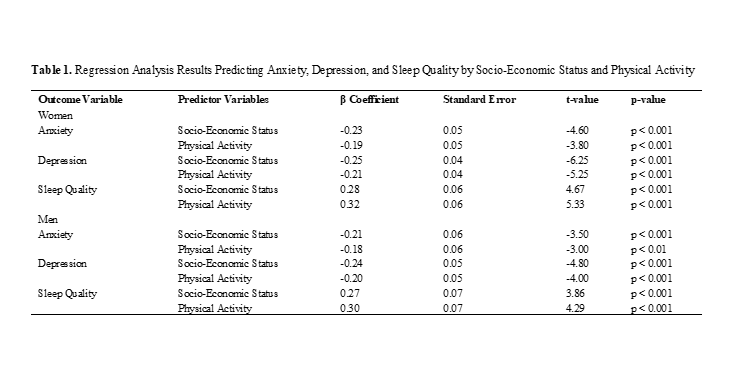
This study aims to examine the effects of socio-economic status and physical activity on anxiety, depression, and sleep quality among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic, with an emphasis on gender differences in these relationships. In this cross-sectional study, a total of 525 participants, including 93 men and 432 women from a university setting were recruited. Data were collected through online surveys, using standard tools, that assessed socio-economic status, physical activity levels, anxiety, depression, and sleep quality. For data analysis, regression analyses were conducted to determine the predictive power of socio-economic status and physical activity on the psychological outcomes. Regression analysis indicated that socio-economic status significantly predicted anxiety (Women: β = -0.23, p < 0.001; Men: β = -0.21, p < 0.001), depression (Women: β = -0.25, p < 0.001; Men: β = -0.24, p < 0.001), and sleep quality (Women: β = 0.28, p < 0.001; Men: β = 0.27, p < 0.001) in both genders. Physical activity also emerged as a significant predictor, with negative associations with anxiety (Women: β = -0.19, p < 0.001; Men: β = -0.18, p < 0.01) and depression (Women: β = -0.21, p < 0.001; Men: β = -0.20, p < 0.001), and a positive relationship with sleep quality (Women: β = 0.32, p < 0.001; Men: β = 0.30, p < 0.001). Thus, it can be concluded that socio-economic status and physical activity are crucial factors influencing psychological well-being and sleep quality among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic which address the importance of considering socio-economic disparities and promoting physical activity as potential strategies to mitigate psychological distress and improve sleep quality in this population. According to the findings, gender-specific considerations should also be incorporated into intervention designs to effectively address the unique needs of male and female students.
Downloads
References
1. Taheri M, Esmaeili A, Irandoust K, Mirmoezzi M,
Souissi A, Laher I, et al. Mental health, eating habits and physical
activity levels of elite Iranian athletes during the COVID-19
pandemic. Science & Sports. 2023;38(5):527-33. [PMID:
37362084] [PMCID: PMC10243596] [DOI]
2. Courtney D, Watson P, Battaglia M, Mulsant BH,
Szatmari PJTCJoP. COVID-19 impacts on child and youth anxiety
and depression: challenges and opportunities. 2020;65(10):688-91.
[PMID: 32567353] [PMCID: PMC7502880] [DOI]
3. Chen P, Mao L, Nassis GP, Harmer P, Ainsworth BE, Li
F. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): The need to maintain regular
physical activity while taking precautions. Journal of Sport and
Health Science. 2020;9(2):103-4. [PMID: 32099716] [PMCID:
PMC7031771] [DOI]
4. Joyce R, Xu XJIfFSBNB. Sector shutdowns during the
coronavirus crisis: which workers are most exposed. 2020;6.
5. Duan L, Zhu GJTLP. Psychological interventions for
people affected by the COVID-19 epidemic. 2020;7(4):300-2.
[PMID: 32085840] [DOI]
6. Shigemura J, Ursano RJ, Morganstein JC, Kurosawa M,
Benedek DM. Public responses to the novel 2019 coronavirus
(2019‐nCoV) in Japan: Mental health consequences and target
populations. Psychiatry and clinical neurosciences.
2020;74(4):281. [PMID: 32034840] [PMCID: PMC7168047]
[DOI]
7. Brooks L, Manias E, Bloomer M. How Do Intensive Care
Clinicians Ensure Culturally Sensitive Care for Family Members at
the End of Life? A Retrospective Descriptive Study. Intensive and
Critical Care Nursing. 2022. [PMID: 35931595] [DOI]
8. Li S, Wang Y, Xue J, Zhao N, Zhu T. The impact of
COVID-19 epidemic declaration on psychological consequences: a
study on active Weibo users. International journal of environmental
research and public health. 2020;17(6):2032. [PMID: 32204411]
[PMCID: PMC7143846] [DOI]
9. Cahuas A, He Z, Zhang Z, Chen WJJoAch. Relationship
of physical activity and sleep with depression in college students.
2020;68(5):557-64. [PMID: 30908132] [DOI]
10. Darbani SA, Parsakia K. The effectiveness of strengthbased counseling on the reduction of divorced women's depression.
Journal of Assessment and Research in Applied Counseling.
2022;4(2):28-32. [DOI]
11. Plante TG, Rodin JJCp. Physical fitness and enhanced
psychological health. 1990;9(1):3-24. [DOI]
12. Knapen J, Vancampfort D, Moriën Y, Marchal YJD,
rehabilitation. Exercise therapy improves both mental and physical
health in patients with major depression. 2015;37(16):1490-5.
[PMID: 25342564] [DOI]
13. Yeh YH, Tai IC, Hsieh PT, Chou SW, Chieh LM, Lee
LTJ. The Study of Correlation between the Levels of Exercise and
Depression among College Students. 2013;2013(2):189-.
14. Harbour VJ, Behrens TK, Kim HS, Kitchens CLJJoPa,
Health. Vigorous physical activity and depressive symptoms in
college students. 2008;5(4):516-26. [PMID: 18648117] [DOI]
15. Ortega FB, Ruiz JR, Castillo MJ, Sjöström MJIjoo.
Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: a powerful marker
of health. 2008;32(1):1-11. [PMID: 18043605] [DOI]
16. Taheri M, Saad HB, Washif JA, Reynoso-Sánchez LF,
Mirmoezzi M, Youzbashi L, et al. Comparative Study of the LongTerm Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Mental Health and
Nutritional Practices Among International Elite and Sub-Elite
Athletes: A Sample of 1420 Participants from 14 Countries. Sports
Medicine - Open. 2023;9(1):104. [PMID: 37938473] [PMCID:
PMC10632320] [DOI]
17. Özdin S, Bayrak Özdin Ş. Levels and predictors of
anxiety, depression and health anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic
in Turkish society: The importance of gender. International Journal
of Social Psychiatry. 2020;66(5):504-11. [PMID: 32380879]
[PMCID: PMC7405629] [DOI]
18. Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, et al.
Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with
SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International
Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2020;94:91-5. [PMID: 32173574]
[PMCID: PMC7194638] [DOI]
19. Fakari FR, Simbar M. Coronavirus pandemic and worries
during pregnancy; a letter to editor. Archives of academic
emergency medicine. 2020;8(1):e21-e.
20. Cao W, Fang Z, Hou G, Han M, Xu X, Dong J, Zheng
JJPr. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on
college students in China. 2020:112934. [PMID: 32229390]
[PMCID: PMC7102633] [DOI]
21. Lewis K. COVID-19: preliminary data on the impact of
social distancing on loneliness and mental health. Journal of
Psychiatric Practice. 2020;26(5):400-4. [PMID: 32936586] [DOI]
22. Zhang Y, Wang D, Zhao J, Xiao-Yan C, Chen H, Ma Z,
et al. Insomnia and other sleep-related problems during the
remission period of the COVID-19 pandemic: a large-scale survey
among college students in China. Psychiatry Research.
2021;304:114153. [PMID: 34403874] [PMCID: PMC8424256]
[DOI]
23. Lee JE, Jang S-I, Ju YJ, Kim W, Lee HJ, Park E-C.
Relationship between Mobile phone addiction and the incidence of
poor and short sleep among Korean adolescents: a longitudinal
study of the Korean Children & Youth Panel Survey. Journal of
Korean medical science. 2017;32(7):1166-72. [PMID: 28581275]
[PMCID: PMC5461322] [DOI]
24. Gogtay N, Giedd JN, Lusk L, Hayashi KM, Greenstein
D, Vaituzis AC, et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical
development during childhood through early adulthood.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
2004;101(21):8174-9. [PMID: 15148381] [PMCID: PMC419576]
[DOI]
25. Wang X, Hegde S, Son C, Keller B, Smith A, Sasangohar
F. Investigating mental health of US college students during the
COVID-19 pandemic: cross-sectional survey study. Journal of
medical Internet research. 2020;22(9):e22817. [PMID: 32897868]
[PMCID: PMC7505693] [DOI]
26. Schuch FB, Bulzing RA, Meyer J, Vancampfort D, Firth
J, Stubbs B, et al. Associations of moderate to vigorous physical
activity and sedentary behavior with depressive and anxiety
symptoms in self-isolating people during the COVID-19 pandemic:
A cross-sectional survey in Brazil. 2020;292:113339. [PMID:
32745795] [PMCID: PMC7384423] [DOI]
27. Lesser IA, Nienhuis CPJIJoER, Health P. The Impact of
COVID-19 on Physical Activity Behavior and Well-Being of
Canadians. 2020;17(11):3899. [PMID: 32486380] [PMCID:
PMC7312579] [DOI]
28. Stanton R, To QG, Khalesi S, Williams SL, Alley SJ,
Thwaite TL, et al. Depression, Anxiety and Stress during COVID19: Associations with Changes in Physical Activity, Sleep,
Tobacco and Alcohol Use in Australian Adults. 2020;17(11):4065.
[PMID: 32517294] [PMCID: PMC7312903] [DOI]
29. Ammar A, Brach M, Trabelsi K, Chtourou H, Boukhris
O, Masmoudi L, et al. Effects of COVID-19 Home Confinement
on Eating Behaviour and Physical Activity: Results of the ECLBCOVID19 International Online Survey. 2020;12(6):1583. [DOI]
30. Smith L, Jacob L, Butler L, Schuch F, Barnett Y,
Grabovac I, et al. Prevalence and correlates of physical activity in
a sample of UK adults observing social distancing during the
COVID-19 pandemic. 2020;6(1):e000850. [PMID: 34192006]
[PMCID: PMC7358093] [DOI]
31. Meyer J, McDowell C, Lansing J, Brower C, Smith L,
Tully M, Herring M. Changes in physical activity and sedentary
behaviour due to the COVID-19 outbreak and associations with
mental health in 3,052 US adults. 2020. [DOI]
32. Akbari A, Mirakhori F, Ashouri M, Nehzat Norozi
Tehrani S. The Effect of Micronutrient Intake on Cognitive
Function and Physical Activity of the Elderly. Int J Sport Stud
Health. 2021;4(1):e121360. [DOI]
33. Abootorabi Kashani P, Safarzadeh S, Hafezi F, Eftekhar
Saadi Z. The effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy on
Reducing of Symptoms of Attention Deficit / Hyperactivity and
Suicidal Ideation in Symptoms of Attention Deficit / Hyperactivity
Disorder Adolescents. Journal of Nursing Education. 2020;8(5):25-
33.
34. Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory
for measuring clinical anxiety: Psychometric properties. Journal of
Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1988;56(6):893-7. [PMID:
3204199] [DOI]
35. Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown G. Beck depression
inventory–II. Psychological assessment. 1996. [DOI]
36. Steer RA, Clark DA, Beck AT, Ranieri WF. Common
and specific dimensions of self-reported anxiety and depression:
the BDI-II versus the BDI-IA. Behaviour Research and Therapy.
1999;37(2):183-90. [PMID: 9990749] [DOI]
37. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer
DJ. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for
psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research.
1989;28(2):193-213. [PMID: 2748771] [DOI]
38. Dabirinejad S, Minasian E, Kashani AT, Rundmo T,
Afshar A. Predicting Pedestrian Behavior by Sleep Quality and
Emotional Self-Regulation. Transportation Research Record.
2023;2677(5):1077-84. [DOI]
39. Sharif Ara B, Khosropour F, Molayi Zarandi H.
Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) on
Emotional Processing, Irrational Beliefs and Rumination in
Patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Journal of Adolescent
and Youth Psychological Studies. 2023;4(4):34-44. [DOI]
40. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief
measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7.
Archives of internal medicine. 2006;166(10):1092-7. [PMID:
16717171] [DOI]
41. Brand R, Timme S, Nosrat S. When pandemic hits:
exercise frequency and subjective well-being during COVID-19
pandemic. Frontiers in psychology. 2020;11:2391. [PMID:
33071902] [PMCID: PMC7541696] [DOI]
42. Linehan MM, Korslund KE, Harned MS, Gallop RJ,
Lungu A, Neacsiu AD, et al. Dialectical Behavior Therapy for High
Suicide Risk in Individuals With Borderline Personality Disorder:
A Randomized Clinical Trial and Component Analysis. JAMA
Psychiatry. 2015;72(5):475-82. [PMID: 25806661] [DOI]
43. LoParo D, Mack SA, Patterson B, Negi LT, Kaslow NJ.
The Efficacy of Cognitively-Based Compassion Training for
African American Suicide Attempters. Mindfulness.
2018;9(6):1941-54. [DOI]
44. Patten SB, Williams JVA, Lavorato DH, Bulloch AGM,
Wiens K, Wang J. Why is major depression prevalence not
changing? Journal of Affective Disorders. 2016;190:93-7. [PMID:
26485311] [DOI]
45. Smith NB, Monteith LL, Rozek DC, Meuret AE.
Childhood Abuse, the Interpersonal–Psychological Theory of
Suicide, and the Mediating Role of Depression. Suicide and LifeThreatening Behavior. 2018;48(5):559-69. [PMID: 29068069]
[DOI]
46. Rosso G, Aragno E, Cuomo A, Fagiolini A, Di Salvo G,
Maina G. Five-year follow-up of first-episode depression treated
with psychodynamic psychotherapy or antidepressants. Psychiatry
Research. 2019;275:27-30. [PMID: 30878853] [DOI]
47. Norouzi E, Hosseini F, Vaezmosavi M, Gerber M, Pühse
U, Brand S. Zumba dancing and aerobic exercise can improve
working memory, motor function, and depressive symptoms in
female patients with fibromyalgia. European journal of sport
science. 2020;20(7):981-91. [PMID: 31630663] [DOI]
48. Stubbs B, Vancampfort D, Hallgren M, Firth J, Veronese
N, Solmi M, et al. EPA guidance on physical activity as a treatment
for severe mental illness: a meta-review of the evidence and
Position Statement from the European Psychiatric Association
(EPA), supported by the International Organization of Physical
Therapists in Mental Health (IOPTMH). European Psychiatry.
2018;54:124-44. [PMID: 30257806] [DOI]
49. Atkinson SR. Elevated psychological distress in
undergraduate and graduate entry students entering first year
medical school. PloS one. 2020;15(8):e0237008. [PMID:
32776950] [PMCID: PMC7416945] [DOI]
50. Feter N, Caputo E, Doring I, Leite J, Cassuriaga J,
Reichert F, et al. Sharp increase in depression and anxiety among
Brazilian adults during the COVID-19 pandemic: findings from the
PAMPA cohort. Public health. 2021;190:101-7. [PMID:
33387848] [PMCID: PMC7773543] [DOI]
51. Pieh C, Budimir S, Probst T. The effect of age, gender,
income, work, and physical activity on mental health during
coronavirus disease (COVID-19) lockdown in Austria. Journal of
psychosomatic research. 2020;136:110186. [PMID: 32682159]
[PMCID: PMC7832650] [DOI]
52. Talapko J, Perić I, Vulić P, Pustijanac E, Jukić M, Bekić
S, et al., editors. Mental health and physical activity in healthrelated university students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Healthcare; 2021: Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
[PMID: 34202384] [PMCID: PMC8304952] [DOI]
53. Rodríguez-Larrad A, Mañas A, Labayen I, GonzálezGross M, Espin A, Aznar S, et al. Impact of COVID-19
confinement on physical activity and sedentary behaviour in
Spanish University Students: role of gender. International Journal
of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(2):369.
[PMID: 33418907] [PMCID: PMC7825050] [DOI]
54. Wathelet M, Duhem S, Vaiva G, Baubet T, Habran E,
Veerapa E, et al. Factors associated with mental health disorders
among university students in France confined during the COVID19 pandemic. JAMA network open. 2020;3(10):e2025591-e.
[PMID: 33095252] [PMCID: PMC7584927] [DOI]
55. Schilling S, French B, Berkowitz SJ, Dougherty SL,
Scribano PV, Wood JN. Child–Adult Relationship
Enhancement in Primary Care (PriCARE): A Randomized Trial of
a Parent Training for Child Behavior Problems. Academic
Pediatrics. 2017;17(1):53-60. [PMID: 27353449] [DOI]
56. Rodriguez-Besteiro S, Tornero-Aguilera JF, FernándezLucas J, Clemente-Suárez VJ. Gender differences in the covid-19
pandemic risk perception, psychology and behaviors of spanish
university students. International Journal of Environmental
Research and Public Health. 2021;18(8):3908. [PMID: 33917827]
[PMCID: PMC8068216] [DOI]
57. Romero-Blanco C, Rodríguez-Almagro J, Onieva-Zafra
MD, Parra-Fernández ML, Prado-Laguna MDC, HernándezMartínez A. Physical activity and sedentary lifestyle in university
students: changes during confinement due to the COVID-19
pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and
Public Health. 2020;17(18):6567. [PMID: 32916972] [PMCID:
PMC7558021] [DOI]
58. Ripon RK, Mim SS, Puente AE, Hossain S, Babor MMH,
Sohan SA, Islam N. COVID-19: psychological effects on a
COVID-19 quarantined population in Bangladesh. Heliyon.
2020;6(11):e05481. [PMID: 33200105] [PMCID: PMC7654365]
[DOI]
59. Ahmadabadi S. Comparison of General-Social Health
and Corona-Induced Anxiety Between Active and Inactive
Students in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in psychiatry. 2021
Dec 21;12:798947. [DOI]
60. Mekonen EG, Workneh BS, Ali MS, Muluneh NY. The
psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic on graduating class
students at the University of Gondar, northwest Ethiopia.
Psychology research and behavior management. 2021;14:109.
[PMID: 33603512] [PMCID: PMC7881778] [DOI]
61. Islam MA, Barna SD, Raihan H, Khan MNA, Hossain
MT. Depression and anxiety among university students during the
COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh: A web-based cross-sectional
survey. PloS one. 2020;15(8):e0238162. [PMID: 32845928]
[PMCID: PMC7449469] [DOI]
62. Salman M, Asif N, Mustafa ZU, Khan TM, Shehzadi N,
Hussain K, et al. Psychological impact of COVID-19 on Pakistani
university students and how they are coping. Medrxiv. 2020. [DOI]
63. Moriarty T, Bourbeau K, Fontana F, McNamara S,
Pereira da Silva M. The Relationship between Psychological Stress
and Healthy Lifestyle Behaviors during COVID-19 among
Students in a US Midwest University. International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021;18(9):4752.
[PMID: 33946873] [PMCID: PMC8125243] [DOI]
64. Stanton R, To QG, Khalesi S, Williams SL, Alley SJ,
Thwaite TL, et al. Depression, anxiety and stress during COVID19: associations with changes in physical activity, sleep, tobacco
and alcohol use in Australian adults. International journal of
environmental research and public health. 2020;17(11):4065.
[PMID: 32517294] [PMCID: PMC7312903] [DOI]
65. Maugeri G, Castrogiovanni P, Battaglia G, Pippi R,
D'Agata V, Palma A, et al. The impact of physical activity on
psychological health during Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Heliyon.
2020;6(6):e04315. [PMID: 32613133] [PMCID: PMC7311901]
[DOI]
66. Rogowska AM, Pavlova I, Kuśnierz C, Ochnik D,
Bodnar I, Petrytsa P. Does physical activity matter for the mental
health of university students during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020;9(11):3494. [PMID: 33138047]
[PMCID: PMC7693909] [DOI]
67. Zhou S-J, Wang L-L, Yang R, Yang X-J, Zhang L-G,
Guo Z-C, et al. Sleep problems among Chinese adolescents and
young adults during the coronavirus-2019 pandemic. Sleep
medicine. 2020;74:39-47. [PMID: 32836185] [PMCID:
PMC7274988] [DOI]
68. Akulwar-Tajane I, Naik PH, Parmar KK, Shah AV.
Impact of Excessive Screen Time and the Mediating Effect of
Physical Exercise on Sleep in Physiotherapy Students During
Covid-19. Sumerianz Journal of Medical and Healthcare,
2021;4(3):149-59. [DOI]
69. Anderson EH, Shivakumar G. Effects of exercise and
physical activity on anxiety. Frontiers in psychiatry. 2013;4:27.
[PMID: 23630504] [PMCID: PMC3632802] [DOI]
70. Aylett E, Small N, Bower P. Exercise in the treatment of
clinical anxiety in general practice–a systematic review and metaanalysis. BMC health services research. 2018;18(1):1-18. [PMID:
30012142] [PMCID: PMC6048763] [DOI]
71. El-Rafie MM, Khafagy GM, Gamal MG. Effect of
aerobic exercise during pregnancy on antenatal depression.
International journal of women's health. 2016;8:53. [PMID:
26955293] [PMCID: PMC4772941] [DOI]
72. Hatami K, Shokrollahi B, Haidari N. The Effect of
Aerobic Activities on Depression and Anxiety Symptoms and
Sleep Disturbance of Female Students. Middle-East Journal Of
Scientific Research. 2013;14(2).
73. Gilani SRM, Feizabad AK. The effects of aerobic
exercise training on mental health and self-esteem of type 2
diabetes mellitus patients. Health psychology research. 2019;7(1).
[PMID: 30997432] [PMCID: PMC6441819] [DOI]
74. Nabkasorn C, Miyai N, Sootmongkol A, Junprasert S,
Yamamoto H, Arita M, Miyashita K. Effects of physical exercise
on depression, neuroendocrine stress hormones and physiological
fitness in adolescent females with depressive symptoms. European
journal of public health. 2006;16(2):179-84. [PMID: 16126743]
[DOI]
75. Peluso MAM, Andrade LHSGd. Physical activity and
mental health: the association between exercise and mood. Clinics.
2005;60:61-70. [PMID: 15838583] [DOI]
76. De Moor MH, Boomsma DI, Stubbe JH, Willemsen G,
de Geus EJ. Testing causality in the association between regular
exercise and symptoms of anxiety and depression. Archives of
general psychiatry. 2008;65(8):897-905. [PMID: 18678794] [DOI]
77. Tehrani H, Vahedian Shahroodi M, Fadayevatan R,
Abusalehi A, Esmaeili H. Mental health status and its related
factors in elderly people residing in nursing homes of Mashhad,
Iran. Health and Development Journal. 2020;6(3):171-81.
78. Ivy A, Rodriguez F, Garcia C, Chen M, Russo-Neustadt
A. Noradrenergic and serotonergic blockade inhibits BDNF mRNA
activation following exercise and antidepressant. Pharmacology
Biochemistry and Behavior. 2003;75(1):81-8. [PMID: 12759116]
[DOI
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hadi Nobari, Atie Rassolnia (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







