Effects of 6-Week Interval Aerobic Training (IAT) and Nano-Selenium Supplementation on Laminin α5 and Collagen IV Expression in the Extracellular Matrix of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Lungs of Healthy and Cigarette Smoke-Exposed Rats
Keywords:
Interval aerobic training, Nano-selenium supplementation, laminin α5, collagen IV, COPDAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effects of six weeks of interval aerobic training (IAT) and nano-selenium supplementation on laminin α5 and collagen IV expression in the extracellular matrix of alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs of cigarette smoke-exposed rats.
Methods and Materials: This experimental laboratory study used thirty-five male Wistar rats weighing 180-220 grams. The rats were randomly divided into seven groups: Healthy control, COPD control, COPD IAT, Healthy IAT, Healthy Selenium, Healthy Selenium-IAT, and COPD Selenium-IAT. Cigarette smoke extract was used to induce lung injury. Nano-selenium particles were administered via gavage. Interval aerobic training was performed for six weeks, five days per week. The expression of laminin α5 and collagen IV in the extracellular matrix of alveolar epithelial cells was evaluated. Data were analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test, two-way ANOVA, and Tukey's post hoc test.
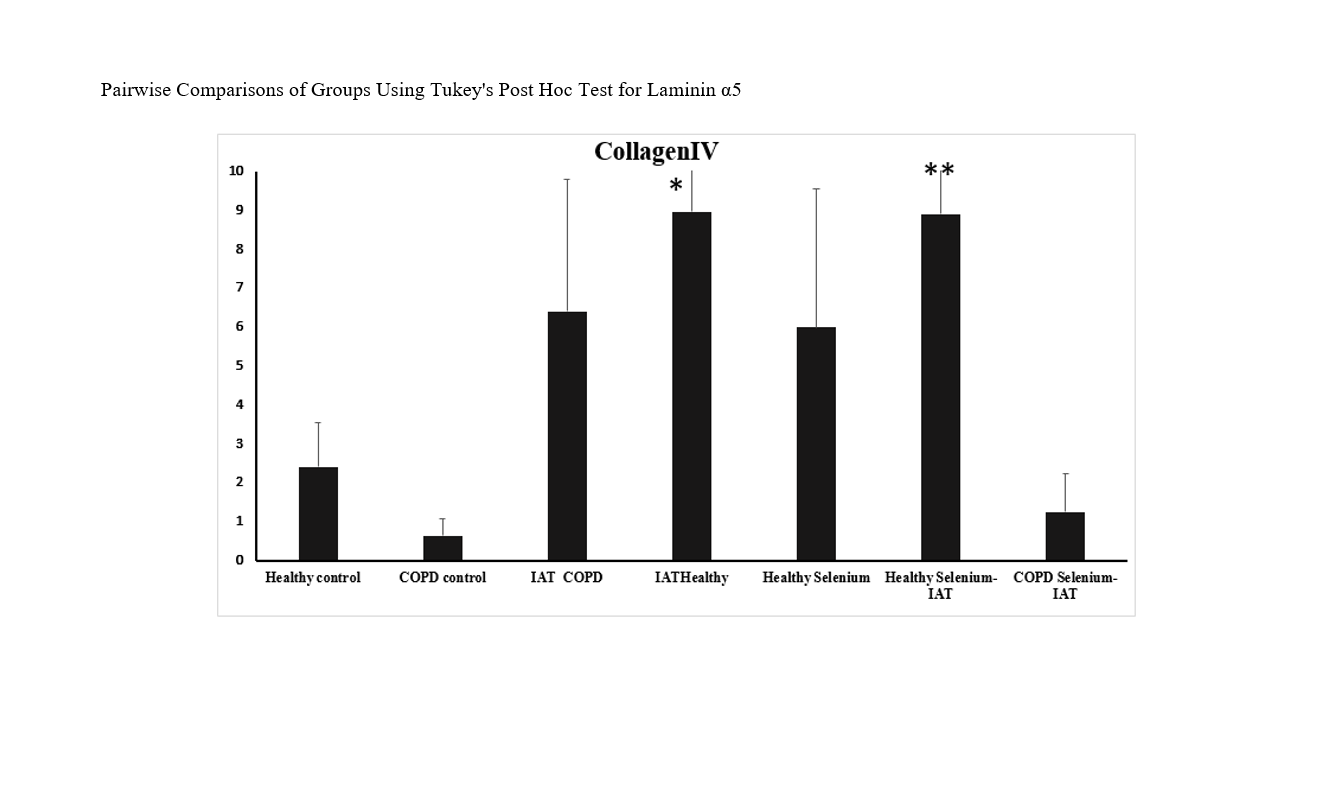
Findings: Two-way ANOVA showed a significant difference in laminin α5 expression between the healthy control and COPD control groups (P=0.011), but no significant difference for collagen IV (P=0.971). There was also a significant difference in laminin α5 expression between the COPD control and COPD + IAT groups (P=0.011), but no significant difference for collagen IV (P=0.999). No significant differences in laminin α5 and collagen IV expression were found between the control and training or supplementation groups (P=0.999).
Conclusion: The results suggest that six weeks of interval aerobic training may be beneficial for mitigating the negative effects of cigarette smoke on laminin α5 expression in the lungs of rats with induced COPD.
Downloads
References
1. Amini M, Gholami M, Aabed Natanzi H, Shakeri N,
Haddad H. Effect of diaphragmatic respiratory training on some
pulmonary indexes in older people with chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. Iranian Journal of Ageing. 2019;14(3):332-41.
2. Wang L, Chen X, Li X, Liu D, Wang X, Chang X, et al.
Developing a novel strategy for COPD therapy by targeting Nrf2
and metabolism reprogramming simultaneously. Free Radical
Biology and Medicine. 2021;169:436-45. [PMID: 33812998]
[DOI]
3. Yadegari M, Riahy S, Mirdar S, Hamidian G, Afkhami
SM, Saeidi A, et al. The TNF-α, P53 protein response and lung
respiratory changes related to exercise, chronic hypoxia and
adiantum capillus-veneris supplementation. Advances in
Respiratory Medicine. 2019;87(4):226-34. [PMID: 31476010]
[DOI]
4. Domej W, Oettl K, Renner W. Oxidative stress and free
radicals in COPD-implications and relevance for treatment.
International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
2014:1207-24. [PMID: 25378921] [PMCID: PMC4207545] [DOI]
5. Zhu B, Wang Y, Ming J, Chen W, Zhang L. Disease
burden of COPD in China: a systematic review. International
Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2018:1353-64.
[PMID: 29731623] [PMCID: PMC5927339] [DOI]
6. Dekkers BG, Maarsingh H, Meurs H, Gosens R. Airway
structural components drive airway smooth muscle remodeling in
asthma. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society.
2009;6(8):683-92. [PMID: 20008876] [DOI]
7. Wright DB, Meurs H, Dekkers BG. Integrins: therapeutic
targets in airway hyperresponsiveness and remodelling? Trends in
Pharmacological Sciences. 2014;35(11):567-74. [PMID:
25441775] [DOI]
8. Burgess JK, Boustany S, Moir LM, Weckmann M, Lau
JY, Grafton K, et al. Reduction of tumstatin in asthmatic airways
contributes to angiogenesis, inflammation, and
hyperresponsiveness. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical
Care Medicine. 2010;181(2):106-15. [PMID: 19875687] [DOI]
9. Ito JT, Lourenço JD, Righetti RF, Tibério IF, Prado CM,
Lopes FD. Extracellular matrix component remodeling in
respiratory diseases: what has been found in clinical and
experimental studies? Cells. 2019;8(4):342. [PMID: 30979017]
[PMCID: PMC6523091] [DOI]
10. Shariati M, Mehdi J, Alireza F, Mojtaba S, Bideskan A.
Effects of maternal nicotine exposure on expression of laminin
alpha 5 in lung tissue of newborn. Pakistan Journal of Biological
Sciences: PJBS. 2012;15(24):1168-75. [PMID: 23755407] [DOI]
11. Karimfar MH, Nikravesh MR, Jalali M, Moeen AA,
Mohammadi S. Maternal nicotine exposure-induced collagen
pulmonary changes in Balb/C mice offspring's. 2011.
12. Yurchenco PD. Basement membranes: cell scaffoldings
and signaling platforms. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in
Biology. 2011;3(2):a004911. [PMID: 21421915] [PMCID:
PMC3039528] [DOI]
13. Annoni R, Lanças T, Tanigawa RY, de Medeiros
Matsushita M, de Morais Fernezlian S, Bruno A, et al. Extracellular
matrix composition in COPD. European Respiratory Journal.
2012;40(6):1362. [PMID: 22496324] [DOI]
14. Soltani A, Reid DW, Sohal SS, Wood-Baker R, Weston
S, Muller HK, et al. Basement membrane and vascular remodelling
in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a crosssectional study. Respiratory Research. 2010;11:105. [PMID:
20670454] [PMCID: PMC2918561] [DOI]
15. Yadegari M, Sellami M, Riahy S, Mirdar S, Hamidian G,
Saeidi A, et al. Supplementation of Adiantum capillus-veneris
modulates alveolar apoptosis under hypoxia condition in Wistar
rats exposed to exercise. Medicina. 2019;55(7):401. [PMID:
31340610] [PMCID: PMC6681305] [DOI]
16. Nesi RT, de Souza PS, Dos Santos GP, Thirupathi A,
Menegali BT, Silveira PCL, et al. Physical exercise is effective in
preventing cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary oxidative response
in mice. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
Disease. 2016:603-10. [PMCID: 27042047] [DOI]
17. Mirdar S, Arab A, Hedayati M, Hajizadeh A. Evaluation
of the effect of a swimming training program on levels of lung
hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in pups of mother rats
exposed to cadmium. 2024.
18. Elassal G, Samy H, Said M, Elbatrawy S. Significance of
selenium levels in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A
comparative study. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and
Tuberculosis. 2014;63(4):1019-23. [DOI]
19. Gloeckl R, Schneeberger T, Jarosch I, Kenn K.
Pulmonary rehabilitation and exercise training in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International.
2018;115(8):117. [DOI]
20. Hirayama F, Lee AH, Oura A, Mori M, Hiramatsu N,
Taniguchi H. Dietary intake of six minerals in relation to the risk
of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Asia Pacific Journal of
Clinical Nutrition. 2010;19(4):572-7.
21. Hou W, Hu S, Li C, Ma H, Wang Q, Meng G, et al.
Cigarette smoke induced lung barrier dysfunction, EMT, and tissue
remodeling: a possible link between COPD and lung cancer.
BioMed Research International. 2019;2019(1):2025636. [PMID:
31341890] [PMCID: PMC6613007] [DOI]
22. Qin F, Xu MX, Wang ZW, Han ZN, Dong YN, Zhao JX.
Effect of aerobic exercise and different levels of fine particulate
matter (PM2.5) on pulmonary response in Wistar rats. Life
Sciences. 2020;254:117355. [PMID: 31987872] [DOI]
23. Høydal MA, Wisløff U, Kemi OJ, Ellingsen Ø. Running
speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: practical
implications for exercise training. European Journal of Preventive
Cardiology. 2007;14(6):753-60. [PMID: 18043295] [DOI]
24. Kojouri GA, Sadeghian S, Mohebbi A, Mokhber
Dezfouli MR. The effects of oral consumption of selenium
nanoparticles on chemotactic and respiratory burst activities of
neutrophils in comparison with sodium selenite in sheep.
Biological Trace Element Research. 2012;146:160-6. [PMID:
22105658] [PMCID: PMC3310134] [DOI]
25. Yazdi MH, Mahdavi M, Faghfuri E, Faramarzi MA,
Sepehrizadeh Z, Hassan ZM, et al. Th1 immune response induction
by biogenic selenium nanoparticles in mice with breast cancer:
preliminary vaccine model. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology.
2015;13(2):1. [PMID: 28959284] [PMCID: PMC5434999] [DOI]
26. Li A, Liu Y, Zhu X, Sun X, Feng X, Li D, et al. Protective
effect of methylallyl sulfone in the development of cigarette smoke
extract-induced apoptosis in rats and HFL-1 cells. Biochemical and
Biophysical Research Communications. 2018;498(3):627-32.
[PMID: 29524412] [DOI]
27. Confalonieri P, Volpe MC, Jacob J, Maiocchi S, Salton
F, Ruaro B, et al. Regeneration or repair? The role of alveolar
epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
(IPF). Cells. 2022;11(13):2095. [PMID: 35805179] [PMCID:
PMC9266271] [DOI]
28. Miyamoto-Mikami E, Tsuji K, Horii N, Hasegawa N,
Fujie S, Homma T, et al. Gene expression profile of muscle
adaptation to high-intensity interval exercise training in young
men. Scientific Reports. 2018;8(1):16811. [PMID: 30429512]
[PMCID: PMC6235852] [DOI]
29. Yadegari MM, S., Hamidian G. The effect of highintensity interval training on lung parenchymal and nonparenchymal structural changes. Daneshvar Medicine.
2016;24(3):51-60.
30. Checa M, Hagood JS, Velazquez-Cruz R, Ruiz V,
Garcia-De-Alba C, Rangel-Escareno C, et al. Cigarette smoke
enhances the expression of profibrotic molecules in alveolar
epithelial cells. PloS One. 2016;11(3):e0150383. [PMID:
26934369] [PMCID: PMC4775036] [DOI]
31. Crosby LM, Waters CM. Epithelial repair mechanisms in
the lung. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and
Molecular Physiology. 2010;298(6):L715-L31. [PMID: 20363851]
[PMCID: PMC2886606] [DOI]
32. Tsutsumi A, Ozaki M, Chubachi S, Irie H, Sato M,
Kameyama N, et al. Exposure to cigarette smoke enhances the
stemness of alveolar type 2 cells. American Journal of Respiratory
Cell and Molecular Biology. 2020;63(3):293-305. [PMID:
32338993] [DOI]
33. Song Y, Jia H, Hua Y, Wu C, Li S, Li K, et al. The
molecular mechanism of aerobic exercise improving vascular
remodeling in hypertension. Frontiers in Physiology.
2022;13:792292. [PMID: 35295586] [PMCID: PMC8919036]
[DOI]
34. Zhuo H, Smith AH, Steinmaus C. Selenium and lung
cancer: a quantitative analysis of heterogeneity in the current
epidemiological literature. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers &
Prevention. 2004;13(5):771-8. [DOI]
35. Witschi H, Espiritu I, Suffia M, Pinkerton KE.
Expression of cyclin D1/2 in the lungs of strain A/J mice fed
chemopreventive agents. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23(2):289-94.
[PMID: 11872634] [DOI]
36. Mavropalias G, Boppart M, Usher KM, Grounds MD,
Nosaka K, Blazevich AJ. Exercise builds the scaffold of life:
muscle extracellular matrix biomarker responses to physical
activity, inactivity, and aging. Biological Reviews.
2023;98(2):481-519. [PMID: 36412213] [DOI]
37. Bidan CM, Veldsink AC, Meurs H, Gosens R. Airway
and extracellular matrix mechanics in COPD. Frontiers in
Physiology. 2015;6:346. [PMID: 26696894] [PMCID:
PMC4667091] [DOI]
38. Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of
macrophage activation. Nature Reviews Immunology.
2008;8(12):958-69. [PMID: 19029990] [PMCID: PMC2724991]
[DOI]
39. Kanazawa Y, Nagano M, Koinuma S, Sugiyo S,
Shigeyoshi Y. Effects of endurance exercise on basement
membrane in the soleus muscle of aged rats. Acta Histochemica et
Cytochemica. 2021;54(5):167-75. [PMID: 34764525] [PMCID:
PMC8569134] [DOI]
40. Zhu ML, Gao ZT, Lu JX, Wang Y, Wang G, Zhu TT, et
al. Amorphous nano-selenium quantum dots prevent pulmonary
arterial hypertension through recoupling endothelial nitric oxide
synthase. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(3):3368. [PMID:
33323558] [PMCID: PMC7906187] [DOI]
41. Arabzadeh E, Shirvani H, Masjedi MR, Ghanei M,
Hofmeister M, Rostamkhani F. Treadmill exercise with
nanoselenium supplementation affects the expression of
Irisin/FNDC5 and semaphorin 3A in rats exposed to cigarette
smoke extract. 3 Biotech. 2024;14(1):4. [PMID: 38058362] [DOI]
42. Parmar K, Siddiqui A, Nugent K. Bacillus CalmetteGuerin vaccine and nonspecific immunity. The American Journal
of the Medical Sciences. 2021;361(6):683-9. [PMID: 33705721]
[PMCID: PMC7938189] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







