The Impact of Aerobic Exercise Combined with Lactobacillus Supplementation on the Expression of Adiponectin and Appl1 Genes in the Liver Tissue of Wistar Rats with Fatty Liver Disease
Keywords:
Aerobic exercise, Lactobacillus, Adiponectin, APPL1, Fatty liverAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the effects of aerobic exercise combined with Lactobacillus supplementation on the expression of adiponectin and APPL1 genes in the liver tissue of rats induced with fatty liver.
Materials and Methods: A total of 32 rats with an average weight of 220±20 grams were divided into 4 groups: 1. FLCG (Fatty liver control group), 2. FLLSG(Fatty liver with Lactobacillus supplementation group), 3. FLAEG: (Fatty liver with aerobic exercise group), 4. FLAELS(Fatty liver with combined aerobic exercise and Lactobacillus supplementation group).The first group was fed a standard rodent diet, while the fatty liver groups were converted into a model group by receiving tetracycline via gavage. In the exercise and exercise ± supplementation groups, aerobic training was conducted on a treadmill for 6 weeks, 5 days a week. The supplementation groups received 109 CFU/ml of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG daily via gavage for 5 weeks. Surgery and liver biopsy were performed at the end of the study. The expression levels of adiponectin and APPL1 genes in liver tissue were measured using Real-Time PCR technique. All data from this study were analyzed using SPSS version 24. Two-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test were used for intergroup comparisons, with a significance level set at p<0.05.
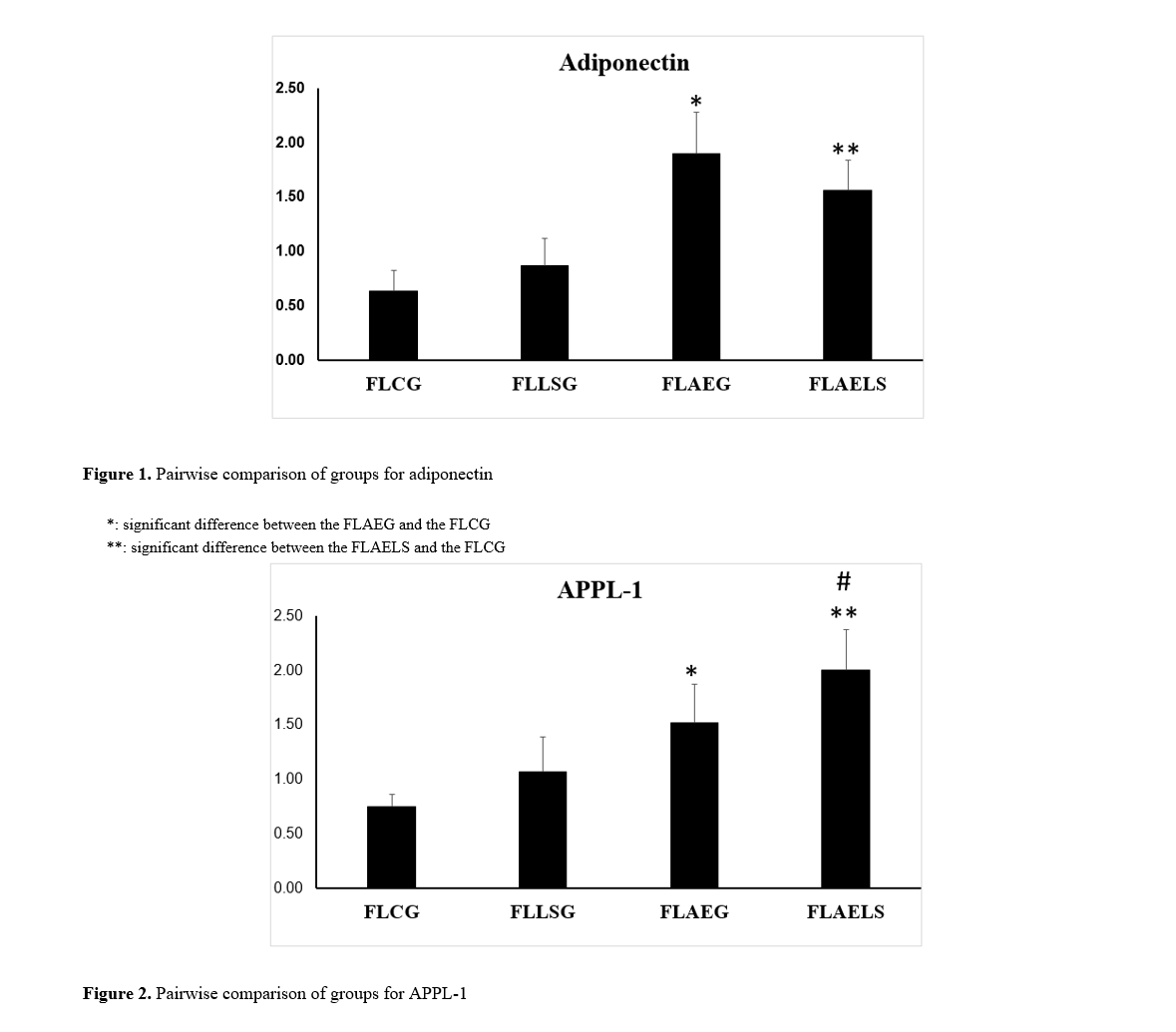
Findings: The findings regarding adiponectin gene expression indicated no significant difference between the control group and the supplementation group (p=0.401). However, both aerobic exercise and aerobic exercise with supplementation groups showed significant differences compared to the control group (p=0.001). Thus, aerobic exercise combined with Lactobacillus supplementation significantly affects adiponectin gene expression in the liver tissue of rats with induced fatty liver. Similarly, results for APPL1 gene expression showed no significant difference between the control and supplementation groups (p=0.200), but both aerobic exercise and aerobic exercise-supplementation groups exhibited significant differences compared to the control group (p=0.001). Therefore, aerobic exercise combined with Lactobacillus supplementation significantly impacts APPL1 gene expression in the liver tissue of rats with induced fatty liver.
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate the effective role of aerobic exercise and Lactobacillus consumption on the expression of adiponectin and APPL1 genes in liver tissue in laboratory samples of fatty liver disease. If the exercise regimen is sufficiently intense and prolonged, it can play a major role in treating fatty liver.
Downloads
References
1. Hassan K, Bhalla V, El Regal ME, A-Kader HH.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive review of a growing
epidemic. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG.
2014;20(34):12082. [PMID: 25232245] [PMCID: PMC4161796]
[DOI]
2. Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K,
Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the
Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328-57. [PMID:
28714183] [DOI]
3. Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ.
Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates
an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology.
2018;67(1):123-33. [PMID: 28802062] [PMCID: PMC5767767]
[DOI]
4. Arendt BM, Comelli EM, Ma DW, Lou W, Teterina A, Kim
T, et al. Altered hepatic gene expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease is associated with lower hepatic n‐3 and n‐6 polyunsaturated
fatty acids. Hepatology. 2015;61(5):1565-78. [PMID: 25581263]
[DOI]
5. Nd AM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, an overview.
Integrative Medicine: A Clinician's Journal. 2019;18(2):42.
6. Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Zavos C, Tsiaousi E. The role of
adiponectin in the pathogenesis and treatment of non‐alcoholic fatty
liver disease. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2010;12(5):365-83.
[PMID: 20415685] [DOI]
7. Gianopoulos I, Mantzoros CS, Daskalopoulou SS.
Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Endocrine
Reviews. 2024. [PMID: 39106421] [DOI]
8. Mojiminiyi OA, Abdella NA, Al Arouj M, Ben Nakhi A.
Adiponectin, insulin resistance and clinical expression of the metabolic
syndrome in patients with Type 2 diabetes. International Journal of
Obesity. 2007;31(2):213-20. [PMID: 16755284] [DOI]
9. Mohamed AA, Hassanin S, Mohamed AA, Zaafar D,
Mohamed R, Hassan MB, et al. Adipokine (adiponectin-rs1501299)
Gene Variant and Patient Characteristics in Relation to Metabolicassociated Fatty Liver Disease. Journal of Clinical and Experimental
Hepatology. 2024;14(5). [PMID: 38699515] [DOI]
10. Baldelli S, Aiello G, Mansilla Di Martino E, Campaci D,
Muthanna FM, Lombardo M. The role of adipose tissue and nutrition
in the regulation of adiponectin. Nutrients. 2024;16(15). [PMID:
39125318] [PMCID: PMC11313710] [DOI]
11. Deepa SS, Dong LQ. APPL1: role in adiponectin signaling
and beyond. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and
Metabolism. 2009;296(1):E22-E36. [PMID: 18854421] [PMCID:
PMC2636986] [DOI]
12. Artimani T, Najafi R. APPL1 as an important regulator of
insulin and adiponectin‐signaling pathways in the PCOS: A narrative
review. Cell Biology International. 2020;44(8):1577-87. [PMID:
32339379] [DOI]
13. Prudente S, Jungtrakoon P, Marucci A, Ludovico O,
Buranasupkajorn P, Mazza T, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in
APPL1 in familial diabetes mellitus. The American Journal of Human
Genetics. 2015;97(1):177-85. [PMID: 26073777] [PMCID:
PMC4571002] [DOI]
14. Uchida D, Takaki A, Oyama A, Adachi T, Wada N, Onishi
H, et al. Oxidative stress management in chronic liver diseases and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1576. [PMID:
32481552] [PMCID: PMC7352310] [DOI]
15. Engin A. Adiponectin Resistance in Obesity: Adiponectin
Leptin/Insulin Interaction. Obesity and Lipotoxicity. 2024:431-62.
[PMID: 39287861] [DOI]
16. Peng Y, Li A, Yu L, Qin G. The role of probiotics in
prevention and treatment for patients with allergic rhinitis: A
systematic review. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy.
2015;29(4):292-8. [PMID: 26163249] [DOI]
17. Whitsett M, VanWagner LB. Physical activity as a treatment
of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. World
Journal of Hepatology. 2015;7(16):2041. [PMID: 26261693][PMCID:
PMC4528277] [DOI]
18. Brouwers B, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Jelenik T,
Gemmink A, Sparks LM, Havekes B, et al. Exercise training reduces
intrahepatic lipid content in people with and people without
nonalcoholic fatty liver. American Journal of PhysiologyEndocrinology and Metabolism. 2018;314(2):E165-E73. [PMID:
29118014] [DOI]
19. Lee S, Deldin AR, White D, Kim Y, Libman I, Rivera-Vega
M, et al. Aerobic exercise but not resistance exercise reduces
intrahepatic lipid content and visceral fat and improves insulin
sensitivity in obese adolescent girls: a randomized controlled trial.
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.
2013;305(10):E1222-E9. [PMID: 24045865][PMCID: PMC3840217]
[DOI]
20. Nassis GP, Papantakou K, Skenderi K, Triandafillopoulou
M, Kavouras SA, Yannakoulia M, et al. Aerobic exercise training
improves insulin sensitivity without changes in body weight, body fat,
adiponectin, and inflammatory markers in overweight and obese girls.
Metabolism. 2005;54(11):1472-9. [PMID: 16253636] [DOI]
21. Petroni ML, Brodosi L, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G.
Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMJ. 2021;372.
[PMID: 33461969] [DOI]
22. Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM,
Delzenne NM, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic
endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity
and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008;57(6):1470-81. [PMID:
18305141] [DOI]
23. Ferolla SM, Ferrari TC, Lima ML, Reis TO, Tavares-Jr WC,
Couto OF, et al. Dietary patterns in Brazilian patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study. Clinics.
2013;68(1):11-7. [PMID: 23420151] [DOI]
24. Mhurchu CN, Poppitt SD, McGill AT, Leahy FE, Bennett
DA, Lin RB, et al. The effect of the dietary supplement, Chitosan, on
body weight: a randomised controlled trial in 250 overweight and obese
adults. International Journal of Obesity. 2004;28(9):1149-56. [PMID:
15311218] [DOI]
25. Gao X, Zhu Y, Wen Y, Liu G, Wan C. Efficacy of probiotics
in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in adult and children: A meta‐
analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hepatology Research.
2016;46(12):1226-33. [PMID: 26866817] [DOI]
26. Paolella G, Mandato C, Pierri L, Poeta M, Di Stasi M, Vajro
P. Gut-liver axis and probiotics: their role in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG. 2014;20(42):15518.
[PMID: 25400436] [PMCID: PMC4229517] [DOI]
27. Donati Zeppa S, Agostini D, Gervasi M, Annibalini G,
Amatori S, Ferrini F, et al. Mutual interactions among exercise, sport
supplements and microbiota. Nutrients. 2019;12(1):17. [PMID:
31861755] [PMCID: PMC7019274] [DOI]
28. Choi YJ, Lee CH, Lee KY, Jung SH, Lee BH. Increased
hepatic fatty acid uptake and esterification contribute to tetracyclineinduced steatosis in mice. Toxicological Sciences. 2015;145(2):273-
82. [PMID: 25745068] [DOI]
29. Hashemi-Khah MS, Arbab-Soleimani N, Forghanifard
MM, Gholami O, Taheri S, Amoueian S. An In vivo study of
Lactobacillus rhamnosus (PTCC 1637) as a new therapeutic candidate
in esophageal cancer. BioMed Research International.
2022;2022(1):7607470. [PMID: 35782061] [PMCID: PMC9249511]
[DOI]
30. Alhusseini NF, Belacy NA, Kasem EM, Allam MM. Effect
of exercise training on adiponectin receptor expression and insulin
resistance in mice fed a high fat diet. Am J Biochem Biotechnol.
2010;6(2):77-83. [DOI]
31. Guo Q, Cao S, Wang X. Adiponectin intervention to
regulate betatrophin expression, attenuate insulin resistance and
enhance glucose metabolism in mice and its response to exercise.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022;23(18):10630.
[PMID: 36142528] [PMCID: PMC9505482] [DOI]
32. Ishtiaq SM, Rashid H, Hussain Z, Arshad MI, Khan JA.
Adiponectin and PPAR: a setup for intricate crosstalk between obesity
and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Reviews in Endocrine and
Metabolic Disorders. 2019;20:253-61. [PMID: 31656991] [DOI]
33. Gamberi T, Magherini F, Modesti A, Fiaschi T. Adiponectin
signaling pathways in liver diseases. Biomedicines. 2018;6(2):52.
[PMID: 29735928] [PMCID: PMC6027295] [DOI]
34. Bayat Z, Damirchi A, Hasannejad-Bibalan M, Babaei P.
Metabotropic effect of probiotic supplementation and high-intensity
interval training in menopause-induced metabolic syndrome in rats.
Journal of Menopausal Medicine. 2023;29(1):29. [PMID: 37160300]
[PMCID: PMC10183765] [DOI]
35. Seo DI, So WY, Sung DJ. Changes in insulin resistance and
adipokines in obese women following a 12-week programme of
combined exercise training. South African Journal for Research in
Sport, Physical Education and Recreation. 2016;38(1):39-147.
36. Minuzzi LG, Kuga GK, Breda L, Gaspar RC, Muñoz VR,
Pereira RM, et al. Short-term resistance training increases APPL1
content in the liver and the insulin sensitivity of mice fed a long-term
high-fat diet. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.
2020;128(01):30-7. [PMID: 30991419] [DOI]
37. Fujita N, Aono S, Karasaki K, Sera F, Kurose T, Fujino H,
et al. Changes in lipid metabolism and capillary density of the skeletal
muscle following low-intensity exercise training in a rat model of
obesity with hyperinsulinemia. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196895.
[PMID: 29718998] [PMCID: PMC5931644] [DOI]
38. Rovina RL, Da Rocha AL, Marafon BB, Pauli JR, De
Moura LP, Cintra DE, et al. One bout of aerobic exercise can enhance
the expression of Nr1d1 in oxidative skeletal muscle samples. Frontiers
in Physiology. 2021;12:626096. [PMID: 33597895] [PMCID:
PMC7882602] [DOI]
39. Cao S, Ryan PM, Salehisahlabadi A, Abdulazeem HM,
Karam G, Černevičiūtė R, et al. Effect of probiotic and synbiotic
formulations on anthropometrics and adiponectin in overweight and
obese participants: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Journal of King Saud University-Science.
2020;32(2):1738-48. [DOI]
40. Baek KW, Gim JA, Park JJ. Regular moderate aerobic
exercise improves high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
via monoacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 pathway suppression.
Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2020;9(5):472-8. [PMID:
32928450] [PMCID: PMC7498633] [DOI]
41. Guo R, Liong EC, So KF, Fung ML, Tipoe GL. Beneficial
mechanisms of aerobic exercise on hepatic lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases
International. 2015;14(2):139-44. [PMID: 25865685] [DOI]
42. Chen YM, Liao CC, Huang YC, Chen MY, Huang CC,
Chen WC, et al. Proteome and microbiota analysis highlight
Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 supplementation improves energy
metabolism and exercise performance in mice. Food Science &
Nutrition. 2020;8(7):3525-34. [PMID: 32724615] [PMCID:
PMC7382123] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







